Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following is the defining characteristic of hominins?
Which of the following is the defining characteristic of hominins?
- Bipedalism (correct)
- Tool use
- Enlarged canines
- Increased body size
Sahelanthropus tchadensis, dating to approximately 7 million years ago, is considered the definitive hominin ancestor and the point at which the hominin lineage diverged.
Sahelanthropus tchadensis, dating to approximately 7 million years ago, is considered the definitive hominin ancestor and the point at which the hominin lineage diverged.
False (B)
What is the term for the method of classifying organisms based on shared derived traits from a common ancestor?
What is the term for the method of classifying organisms based on shared derived traits from a common ancestor?
Cladistics
The East African Rift Valley is an important location for hominin fossil discoveries because of its volcanic activity and sediment ________.
The East African Rift Valley is an important location for hominin fossil discoveries because of its volcanic activity and sediment ________.
Match the hominin genus with a key characteristic:
Match the hominin genus with a key characteristic:
What insight does the 'Turkana Boy' fossil provide about Homo erectus?
What insight does the 'Turkana Boy' fossil provide about Homo erectus?
The Lomekwi tool industry, dating back approximately 3.3 million years, represents the earliest known stone tool culture and is associated with Homo habilis.
The Lomekwi tool industry, dating back approximately 3.3 million years, represents the earliest known stone tool culture and is associated with Homo habilis.
Name one anatomical change that supports bipedalism in hominins.
Name one anatomical change that supports bipedalism in hominins.
The forward placement of the foramen magnum in hominins is an indicator of an upright posture and ________ locomotion.
The forward placement of the foramen magnum in hominins is an indicator of an upright posture and ________ locomotion.
Match the following adaptations with the hominin genus in which they are most prominent:
Match the following adaptations with the hominin genus in which they are most prominent:
What aspect of hominin evolution does sexual dimorphism provide insights into?
What aspect of hominin evolution does sexual dimorphism provide insights into?
The Oldowan tool industry is the earliest known stone tool culture, dating back approximately 2.6 million years, and is associated with Neanderthals.
The Oldowan tool industry is the earliest known stone tool culture, dating back approximately 2.6 million years, and is associated with Neanderthals.
Aside from tool use, what is one example of symbolic behavior exhibited by Homo sapiens?
Aside from tool use, what is one example of symbolic behavior exhibited by Homo sapiens?
Controlling ________ provided warmth, protection, cooking benefits, and facilitated social bonding for hominins.
Controlling ________ provided warmth, protection, cooking benefits, and facilitated social bonding for hominins.
Match the climatic event with its impact on hominin evolution:
Match the climatic event with its impact on hominin evolution:
Which adaptation is directly related to efficient bipedal walking?
Which adaptation is directly related to efficient bipedal walking?
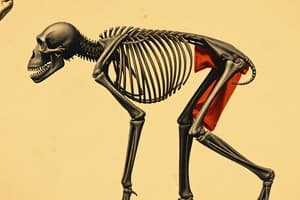
Apes typically have a shorter, broader pelvis to better support the upright posture required for bipedalism, while hominins have a longer, narrower pelvis.
Apes typically have a shorter, broader pelvis to better support the upright posture required for bipedalism, while hominins have a longer, narrower pelvis.
Name one way the hominin foot changed to adapt to bipedalism.
Name one way the hominin foot changed to adapt to bipedalism.
In comparison to apes, hominins have a barrel-shaped ribcage, which allows for improved ________ in bipedal posture.
In comparison to apes, hominins have a barrel-shaped ribcage, which allows for improved ________ in bipedal posture.
Which cultural advancement is associated with the given evidence?
Which cultural advancement is associated with the given evidence?
What is a potential benefit of evolving a post-reproductive lifespan, according to the Grandmother Hypothesis?
What is a potential benefit of evolving a post-reproductive lifespan, according to the Grandmother Hypothesis?
Impact of language development primarily influenced physical strength rather than communication or social organization.
Impact of language development primarily influenced physical strength rather than communication or social organization.
What gene, also found in Neanderthals, is linked to language and speech development in humans?
What gene, also found in Neanderthals, is linked to language and speech development in humans?
During glacial cycles, lower sea levels created __________, facilitating hominin migrations to new continents.
During glacial cycles, lower sea levels created __________, facilitating hominin migrations to new continents.
Match the factor with the adaptation associated with Pleistocene glaciations:
Match the factor with the adaptation associated with Pleistocene glaciations:
What are populations thought to have done during harsh climatic periods, according to the refugia model?
What are populations thought to have done during harsh climatic periods, according to the refugia model?
Homo sapiens relied solely on terrestrial resources and did not exploit coastal environments for marine resources.
Homo sapiens relied solely on terrestrial resources and did not exploit coastal environments for marine resources.
What hypothesis proposes early Homo sapiens migrated along coastlines?
What hypothesis proposes early Homo sapiens migrated along coastlines?
Climate change and competition with Homo sapiens are thought to have contributed to ___________ extinction.
Climate change and competition with Homo sapiens are thought to have contributed to ___________ extinction.
What is each factor credited to facilitating Homo Sapiens Outcompete
What is each factor credited to facilitating Homo Sapiens Outcompete
The process of modifying the environment to suit human needs, such as building shelters and domesticating animals, is known as what?
The process of modifying the environment to suit human needs, such as building shelters and domesticating animals, is known as what?
Genetic studies show modern human populations have greater genetic diversity in Europe, indicating the origin of Homo sapiens is on that continent.
Genetic studies show modern human populations have greater genetic diversity in Europe, indicating the origin of Homo sapiens is on that continent.
Name one unresolved question in hominin evolution related to the relationship between different hominin groups.
Name one unresolved question in hominin evolution related to the relationship between different hominin groups.
Defining a hominin is ________, as it relies on both physical traits and genetic evidence, leading to differing views on which species qualify as hominins.
Defining a hominin is ________, as it relies on both physical traits and genetic evidence, leading to differing views on which species qualify as hominins.
Match the evolutionary relationship:
Match the evolutionary relationship:
What DNA is used to gain evolutionary human insights?
What DNA is used to gain evolutionary human insights?
The evidence of Neanderthals lacks any proof of Homo sapiens coexistence, as fossil sites show distinct and separate time periods for both species.
The evidence of Neanderthals lacks any proof of Homo sapiens coexistence, as fossil sites show distinct and separate time periods for both species.
Which hypothesis argues with the multiregional in terms of human ancestors?
Which hypothesis argues with the multiregional in terms of human ancestors?
___________ are some common challenges when dating hominin fossils.
___________ are some common challenges when dating hominin fossils.
Adaptive radiation, or postcranial anatomical differences in Hominins
Adaptive radiation, or postcranial anatomical differences in Hominins
Which of the following is the defining trait of hominins, differentiating them from other primates?
Which of the following is the defining trait of hominins, differentiating them from other primates?
Sahelanthropus tchadensis, dating back approximately 7 million years ago, is considered the definitive first hominin with no debate in the scientific community.
Sahelanthropus tchadensis, dating back approximately 7 million years ago, is considered the definitive first hominin with no debate in the scientific community.
What major geographical feature in East Africa is well-known for its abundance of hominin fossil discoveries?
What major geographical feature in East Africa is well-known for its abundance of hominin fossil discoveries?
The 'Turkana Boy' fossil is a significant specimen of ________ providing insights into growth patterns and body proportions.
The 'Turkana Boy' fossil is a significant specimen of ________ providing insights into growth patterns and body proportions.
Match the dating technique with what it measures:
Match the dating technique with what it measures:
Which anatomical change is NOT associated with the skeletal adaptations to bipedalism in hominins?
Which anatomical change is NOT associated with the skeletal adaptations to bipedalism in hominins?
The position of the foramen magnum (the opening in the skull for the spinal cord) being located further back is an indicator of bipedalism.
The position of the foramen magnum (the opening in the skull for the spinal cord) being located further back is an indicator of bipedalism.
What anatomical feature of Paranthropus reflects its dietary adaptation to chewing tough plant materials?
What anatomical feature of Paranthropus reflects its dietary adaptation to chewing tough plant materials?
The average hominin brain size increased significantly over evolutionary time, from about 400cc in early hominins to over ________ in modern Homo sapiens.
The average hominin brain size increased significantly over evolutionary time, from about 400cc in early hominins to over ________ in modern Homo sapiens.
Match each tool industry with its description:
Match each tool industry with its description:
Which of the following is an example of symbolic behavior in early Homo sapiens?
Which of the following is an example of symbolic behavior in early Homo sapiens?
Controlling fire provided hominins with warmth and protection from predators, but it had little impact on social dynamics.
Controlling fire provided hominins with warmth and protection from predators, but it had little impact on social dynamics.
What term describes the hypothesis that open grassland environments prompted the evolution of bipedalism in hominins?
What term describes the hypothesis that open grassland environments prompted the evolution of bipedalism in hominins?
The discovery of ________ DNA indicates interbreeding between this hominin group and modern human populations, particularly in Asia and Oceania.
The discovery of ________ DNA indicates interbreeding between this hominin group and modern human populations, particularly in Asia and Oceania.
Match the term to its definition.
Match the term to its definition.
Compared to apes, hominins have a different ribcage. Hominins have a:
Compared to apes, hominins have a different ribcage. Hominins have a:
Evidence of cooperative hunting can be identified using stable isotope studies on fossilized remains found at organized kill sites.
Evidence of cooperative hunting can be identified using stable isotope studies on fossilized remains found at organized kill sites.
What significant cognitive advancement is reflected in the diverse range of symbolic behavior seen in early Homo sapiens, such as cave paintings and burial rituals?
What significant cognitive advancement is reflected in the diverse range of symbolic behavior seen in early Homo sapiens, such as cave paintings and burial rituals?
The ________ Cave in South Africa is known for containing evidence of early symbolic behavior, like engraved ochre and shell beads, dating back approximately 75,000 years.
The ________ Cave in South Africa is known for containing evidence of early symbolic behavior, like engraved ochre and shell beads, dating back approximately 75,000 years.
Match each tool 'Mode' with its description
Match each tool 'Mode' with its description
Which of the following statements best describes Neanderthal burial practices?
Which of the following statements best describes Neanderthal burial practices?
The 'Grandmother Hypothesis' suggests that post-reproductive lifespans in males evolved to allow grandfathers to help raise offspring, improving survival rates.
The 'Grandmother Hypothesis' suggests that post-reproductive lifespans in males evolved to allow grandfathers to help raise offspring, improving survival rates.
What critical development in hominin evolution facilitated complex communication, cultural transmission, and advanced social organization?
What critical development in hominin evolution facilitated complex communication, cultural transmission, and advanced social organization?
The ________ gene, which is linked to language and speech development in humans, has also been found in Neanderthal DNA, suggesting potential communication capabilities.
The ________ gene, which is linked to language and speech development in humans, has also been found in Neanderthal DNA, suggesting potential communication capabilities.
Match the cause to the effect.
Match the cause to the effect.
What does analysis of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) primarily reveal about human evolution?
What does analysis of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) primarily reveal about human evolution?
The long-held traditional view of hominin evolution is that it consisted of separate, distinct species with no interbreeding between groups.
The long-held traditional view of hominin evolution is that it consisted of separate, distinct species with no interbreeding between groups.
What hypothesis regarding human origins contrasts with the 'Out of Africa' model by proposing that regional populations evolved into modern humans through continuous gene flow?
What hypothesis regarding human origins contrasts with the 'Out of Africa' model by proposing that regional populations evolved into modern humans through continuous gene flow?
Analysis of the ________ chromosome traces paternal lineages and supports the theory of multiple migration waves out of Africa.
Analysis of the ________ chromosome traces paternal lineages and supports the theory of multiple migration waves out of Africa.
Match the dating method with what is being analyzed.
Match the dating method with what is being analyzed.
How did fluctuating temperatures during the Pleistocene epoch specifically impact hominin adaptation?
How did fluctuating temperatures during the Pleistocene epoch specifically impact hominin adaptation?
Homo floresiensis is significant because its discovery indicates that small, isolated hominin species may have persisted longer than previously thought.
Homo floresiensis is significant because its discovery indicates that small, isolated hominin species may have persisted longer than previously thought.
What anatomical characteristic of Orrorin tugenensis suggests it was bipedal?
What anatomical characteristic of Orrorin tugenensis suggests it was bipedal?
______ in dating analyzes the rock layer characteristics to establish relative fossil ages and site correlations.
______ in dating analyzes the rock layer characteristics to establish relative fossil ages and site correlations.
Match the description with the correct species of hominin.
Match the description with the correct species of hominin.
Which of the following morphological changes is indicative of encephalization?
Which of the following morphological changes is indicative of encephalization?
Early hominins, such as Australopithecus, have a parabolic dental arcade shape whereas modern humans have a U-shaped dental arcade.
Early hominins, such as Australopithecus, have a parabolic dental arcade shape whereas modern humans have a U-shaped dental arcade.
Describe what the introgression of Neanderthal and Denisovan genes contributed to the human population.
Describe what the introgression of Neanderthal and Denisovan genes contributed to the human population.
Mutations in the ______ gene found in Neanderthals suggest they had variations in skin and hair color, possibly including lighter skin tones and red hair
Mutations in the ______ gene found in Neanderthals suggest they had variations in skin and hair color, possibly including lighter skin tones and red hair
Match each Y-chromosome with its proper origin.
Match each Y-chromosome with its proper origin.
Which of the following is considered the defining trait of hominins?
Which of the following is considered the defining trait of hominins?
The Lomekwi tools are younger than the Oldowan tools.
The Lomekwi tools are younger than the Oldowan tools.
What anatomical feature's forward placement indicates an upright posture and bipedal locomotion in hominins?
What anatomical feature's forward placement indicates an upright posture and bipedal locomotion in hominins?
The East African _______ Valley is a major site for fossil discoveries, preserving hominin remains due to volcanic activity and sediment deposition.
The East African _______ Valley is a major site for fossil discoveries, preserving hominin remains due to volcanic activity and sediment deposition.
Match the following hominin genera with their dietary adaptations:
Match the following hominin genera with their dietary adaptations:
What technique measures the decay of radioactive isotopes to determine the age of fossils?
What technique measures the decay of radioactive isotopes to determine the age of fossils?
Neanderthals did not bury their dead; this practice was unique to Homo sapiens.
Neanderthals did not bury their dead; this practice was unique to Homo sapiens.
Name one cave site providing evidence of early symbolic behavior in Homo sapiens.
Name one cave site providing evidence of early symbolic behavior in Homo sapiens.
The idea that post-reproductive lifespans in humans evolved to allow grandmothers to help raise offspring, improving survival rates, is known as the _______ Hypothesis.
The idea that post-reproductive lifespans in humans evolved to allow grandmothers to help raise offspring, improving survival rates, is known as the _______ Hypothesis.
Match the following tool industries with their corresponding characteristics:
Match the following tool industries with their corresponding characteristics:
What is the significance of the FOXP2 gene in hominin evolution?
What is the significance of the FOXP2 gene in hominin evolution?
The 'Out of Africa' hypothesis is solely supported by fossil evidence and has no genetic basis.
The 'Out of Africa' hypothesis is solely supported by fossil evidence and has no genetic basis.
Name one adaptive trait that hominins developed as a result of fluctuating temperatures during the Pleistocene epoch.
Name one adaptive trait that hominins developed as a result of fluctuating temperatures during the Pleistocene epoch.
________ DNA indicates interbreeding between Denisovans and modern human populations, particularly among populations in Asia and Oceania.
________ DNA indicates interbreeding between Denisovans and modern human populations, particularly among populations in Asia and Oceania.
Match the following concepts with their descriptions:
Match the following concepts with their descriptions:
The S-shaped curvature of the vertebral column in hominins is primarily associated with which adaptation?
The S-shaped curvature of the vertebral column in hominins is primarily associated with which adaptation?
Stable isotope studies can only determine the age of a fossil, not dietary habits.
Stable isotope studies can only determine the age of a fossil, not dietary habits.
Name one significant advantage provided by fire control in human evolution.
Name one significant advantage provided by fire control in human evolution.
The inward angle of the femur, known as the _______ angle, helps position the knee under the body for efficient bipedal walking.
The inward angle of the femur, known as the _______ angle, helps position the knee under the body for efficient bipedal walking.
Match each hominin species with the discovery that led to more insights:
Match each hominin species with the discovery that led to more insights:
Flashcards
Hominin
Hominin
Any species belonging to the human lineage after diverging from chimpanzees.
Bipedalism
Bipedalism
Walking on two legs, the primary defining trait of hominins.
Key genera in hominin evolution
Key genera in hominin evolution
Australopithecus, Paranthropus, and Homo are important.
Earliest potential hominin
Earliest potential hominin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Morphology in hominin classification
Morphology in hominin classification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cladistics
Cladistics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hybridization in hominin taxonomy
Hybridization in hominin taxonomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Significance of Homo naledi
Significance of Homo naledi
Signup and view all the flashcards
Genetic evidence of hominin relationships
Genetic evidence of hominin relationships
Signup and view all the flashcards
East African Rift Valley
East African Rift Valley
Signup and view all the flashcards
Radiometric dating
Radiometric dating
Signup and view all the flashcards
Laetoli footprints
Laetoli footprints
Signup and view all the flashcards
Homo erectus differences
Homo erectus differences
Signup and view all the flashcards
Significance of the 'Turkana Boy' fossil
Significance of the 'Turkana Boy' fossil
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oldest known hominin tool industry
Oldest known hominin tool industry
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anatomical changes supporting bipedalism
Anatomical changes supporting bipedalism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Importance of foramen magnum position
Importance of foramen magnum position
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dietary adaptations in Paranthropus
Dietary adaptations in Paranthropus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hominin brain size change
Hominin brain size change
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sexual dimorphism in hominin evolution
Sexual dimorphism in hominin evolution
Signup and view all the flashcards
Significance of tool use in hominin evolution
Significance of tool use in hominin evolution
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oldowan tool industry
Oldowan tool industry
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cultural differences between Neanderthals and Homo sapiens
Cultural differences between Neanderthals and Homo sapiens
Signup and view all the flashcards
Evidence of symbolic behavior in Homo sapiens
Evidence of symbolic behavior in Homo sapiens
Signup and view all the flashcards
Importance of fire control in human evolution
Importance of fire control in human evolution
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ice Age
Ice Age
Signup and view all the flashcards
Savanna Hypothesis
Savanna Hypothesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Replacement of Hominins
Replacement of Hominins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Denisovan DNA
Denisovan DNA
Signup and view all the flashcards
Carrying Angle
Carrying Angle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pelvis Shape
Pelvis Shape
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hominin Foot Changes
Hominin Foot Changes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ribcage Comparison
Ribcage Comparison
Signup and view all the flashcards
S-shaped Vertebral Column
S-shaped Vertebral Column
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cooperative Hunting Evidence
Cooperative Hunting Evidence
Signup and view all the flashcards
Symbolic Behavior Examples
Symbolic Behavior Examples
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blombos Cave Significance
Blombos Cave Significance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mode 1 vs Mode 2 Tools
Mode 1 vs Mode 2 Tools
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neanderthal Burial Practices
Neanderthal Burial Practices
Signup and view all the flashcards
Grandmother Hypothesis
Grandmother Hypothesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Impact of Language Development
Impact of Language Development
Signup and view all the flashcards
FOXP2 Gene Significance
FOXP2 Gene Significance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glacial Cycles and Migration
Glacial Cycles and Migration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pleistocene Climate Effects
Pleistocene Climate Effects
Signup and view all the flashcards
Changing Vegetation and Diet
Changing Vegetation and Diet
Signup and view all the flashcards
Refugia Model
Refugia Model
Signup and view all the flashcards
High-altitude Adaptations
High-altitude Adaptations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Denisova Cave
Denisova Cave
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Hominins are species on the human lineage after the split from the last common ancestor with chimpanzees.
- Bipedalism, or the ability to walk on two legs, is the key defining trait of hominins.
- Key genera in hominin evolution include Australopithecus, Paranthropus, and Homo.
Potential Earliest Hominin
- The earliest potential hominin is Sahelanthropus tchadensis, dating to approximately 7 million years ago.
Using Morphology
- Skull shape, tooth structure, and limb proportions are morphological features that help define evolutionary relationships among hominins.
- Cladistics is a classification method that groups organisms based on shared derived traits from a common ancestor.
- Interbreeding among species, like Neanderthals and Denisovans with Homo sapiens, provides evidence of Hybridization, which can blur distinct species boundaries.
- Homo naledi exhibits a mix of archaic and modern traits, challenging traditional views on hominin evolution.
- DNA analysis demonstrates that Neanderthals, Denisovans, and modern humans shared genetic material through interbreeding.
- The East African Rift Valley is a major site for fossil discoveries due to volcanic activity and sediment deposition, preserving hominin remains.
- Radiometric dating is a technique that measures the decay of radioactive isotopes to determine the age of fossils.
Laetoli Footprints
- These fossilized hominin footprints from 3.6 million years ago provide direct evidence of bipedal locomotion.
Homo erectus Differences
- Homo erectus had a larger brain (~900cc), modern limb proportions, and showed evidence of fire use and long-distance migration.
- The 'Turkana Boy' fossil is a nearly complete Homo erectus skeleton providing insight into growth patterns and body proportions.
- The Lomekwi tools (~3.3 million years ago) represent the oldest known hominin tool industry, predating Oldowan tools.
Anatomical Changes Supporting Bipedalism
- Shortened pelvis, inward-angled femur, arched foot, and forward-placed foramen magnum.
- A forward foramen magnum indicates upright posture and bipedal locomotion.
Dietary Adaptations in Paranthropus
- Large molars, thick enamel, and a sagittal crest allowed for powerful chewing muscles.
- Hominin brain size increased significantly, from around 400cc in early hominins to over 1300cc in modern Homo sapiens.
- Sexual dimorphism (differences in size between males and females) in hominin evolution can indicate social structures and mating behaviors.
- Tool use reflects cognitive advancements, problem-solving abilities, and changes in diet.
- The Oldowan tool industry (~2.6 million years ago) is the earliest known stone tool culture, associated with Homo habilis.
- Neanderthals buried their dead, used symbolic ornaments, and had advanced tools, but overall their culture was less complex compared with early Homo sapiens.
- Cave paintings, personal ornaments, and burial practices indicate abstract thinking in Homo sapiens.
- Fire control provided warmth, protection, cooking benefits, and social bonding opportunities.
- Climate change affected hominin evolution.
- Ice Age glacial cycles created land bridges, facilitating migration out of Africa.
- The Savanna Hypothesis suggests that open grassland environments favored bipedal locomotion.
- Advanced cognitive abilities, tool use, adaptability, and social cooperation contributed to the replacement of other hominins by Homo sapiens.
Traces of Denisovans
- Denisovan DNA indicates interbreeding, particularly among populations in Asia and Oceania.
- The carrying angle is the inward angle of the femur, which helps position the knee under the body for efficient bipedal walking.
- Bipeds have a shorter, broader pelvis, for supporting upright posture, whereas quadrupeds have a longer, narrower pelvis.
Hominin Foot Changes
- Development of arches for shock absorption, forward-facing big toe for balance, and shortened toes for efficient walking.
- Hominins have a barrel-shaped ribcage for better balance in bipedal posture while apes have a conical ribcage for climbing.
- The S-shaped vertebral column provides shock absorption and helps balance the head and torso over the pelvis during upright walking.
- Fossilized remains with tool cut marks and organized kill sites indicate cooperative hunting behavior.
- Fire use benefits included warmth, protection, cooking advantages, and facilitated social bonding.
- Examples of symbolic behavior include cave paintings, burial rituals, body ornamentation, and tool decoration.
Significance of Blombos Cave
- It contains evidence of early symbolic behavior, such as engraved ochre and shell beads, dating to ~75,000 years ago.
- Mode 1 (Oldowan) tools are simple flakes and choppers, while Mode 2 (Acheulean) tools include bifacial handaxes.
- Neanderthals buried their dead with some evidence of grave goods, but their rituals were less elaborate than those of early Homo sapiens.
- The Grandmother Hypothesis suggests that post-reproductive lifespans in humans evolved to allow grandmothers to help raise offspring, improving survival rates.
- Language development allowed for complex communication, cultural transmission, and social organization.
- The FOXP2 gene is linked to language and speech development in humans and has been found in Neanderthal DNA.
- Lower sea levels during glacial cycles created land bridges, allowing hominins to migrate to new continents.
- Fluctuating temperatures during the Pleistocene led to adaptations like larger brain size, controlled fire use, and clothing production.
- Expansion of grasslands led to dietary shifts, favoring more omnivorous and meat-based diets.
- The Refugia Model suggests that populations survived in isolated areas (refugia) during harsh climatic periods, later expanding when conditions improved.
- High-altitude adaptations include larger lung capacity, increased red blood cell production, and genetic adaptations like those seen in Tibetan populations.
Denisova Cave
- It provided DNA evidence of Denisovans, a distinct hominin group that interbred with both Neanderthals and modern humans.
- To determine the types of plant against meat consumption, scientists perform stable isotope studies by analyzing chemical signatures in bones and teeth.
- Homo sapiens exploited marine resources, which led to increased brain nutrition and technological advancements.
- The coastal migration route hypothesis proposes that early Homo sapiens migrated along coastlines using boats or rafts, which facilitated rapid dispersal.
- Climate change, competition with Homo sapiens, and genetic assimilation contributed to Neanderthal extinction.
- Homo sapiens outcompeted other hominins because of their superior cognitive abilities, broader diets, advanced technology, and larger social networks.
Niche Construction
- Niche Construction is the process of modifying the environment to suit human needs, such as building shelters and domesticating animals.
- Clothing and textiles provided protection from harsh climates and allowed for migration into colder regions for early Homo sapiens.
- Genetic studies reveal that modern human populations show greater genetic diversity in Africa, indicating an African origin for Homo sapiens, supporting the Out of Africa theory.
- Unresolved questions in hominin evolution include the exact relationship between Denisovans, Neanderthals, and Homo sapiens, as well as the full extent of interbreeding.
- The classification of hominins is subjective, relying on physical traits and genetic evidence.
- Morphological traits such as skull shape, dentition, and bipedal adaptations are traditionally used for classification but can lead to ambiguity.
- DNA studies reveal interbreeding and gene flow between species, which makes it difficult to establish clear species boundaries when discussing genetic evidence and hominin taxonomy.
Biological Species Concept
- The concept defines species based on reproductive isolation, however, fossil evidence does not directly show whether extinct species could interbreed.
- Australopithecus afarensis is considered a key transitional species with both arboreal and bipedal adaptations, exemplified by the famous 'Lucy' fossil.
- Some researchers argue that robust australopithecines belong in a separate genus of Paranthropus, while others group them with Australopithecus.
- Cladistics groups species based on shared ancestry and derived traits, offering an objective method for mapping evolutionary relationships.
- Homo naledi possesses a mix of archaic and modern traits, challenging traditional views on the timeline and classification of hominin evolution.
Discovery Impact
- New discoveries frequently lead to re-evaluation of species definitions, such as the placement of Neanderthals and Denisovans in relation to Homo sapiens.
- Interbreeding contributed genetic adaptations, such as immunity-related genes and high-altitude adaptations in Tibetan populations.
- Mitochondrial DNA reveals insights about human evolution.
Out of Africa Hypothesis
- The hypothesis traces maternal lineages and supports the origins of modern Homo sapiens.
- Hybridization led to genetic mixing, complicating the traditional view of hominins as separate, distinct species in hominin evolution.
- Denisovans contributed genetic material to modern populations in Asia and Oceania, indicating interbreeding with Homo sapiens.
- Neanderthals had burial practices, tool use, and symbolic behavior, but their culture was less complex than that of Homo sapiens.
- Fossil sites with overlapping time frames and DNA evidence of interbreeding suggest prolonged interaction between Neanderthals and Homo sapiens.
Competing Theories
- The 'Out of Africa' model and the 'Multiregional Hypothesis' differ in explanations of human dispersal and regional evolution for modern human origins.
- Y-chromosome analysis traces paternal lineages and supports multiple migration waves out of Africa.
- The East African Rift Valley has preserved numerous early hominin fossils, providing critical insights into our evolutionary history.
- Stable isotope studies analyze chemical signatures in bones and teeth to determine plant versus meat consumption in ancient hominins.
- Radiometric dating measures the decay of radioactive isotopes in rocks and fossils to provide precise numerical ages.
Laetoli Footprints Significance
- These 3.6-million-year-old fossilized footprints provide direct evidence of early bipedal locomotion in Australopithecus afarensis.
Challenges in Dating Fossils
- Contamination, geological disturbances, and uncertainties in decay rate assumptions when dating hominin fossils.
- Optically stimulated luminescence dating determines when sediment grains were last exposed to sunlight, helping date archaeological layers.
Dmanisi Fossils Significance
- These fossils, dating to ~1.8 million years ago, provide the earliest evidence of hominins outside Africa.
- The discovery of Homo floresiensis indicates that small, isolated hominin species may have persisted longer than previously thought.
- The Ardipithecus ramidus discovery provided key insights into early bipedal adaptations while retaining significant arboreal traits.
- Orrorin tugenensis's femur structure indicates bipedalism, which makes it a strong candidate for an early hominin.
- Lithostratigraphy analyzes rock layer characteristics to establish relative fossil ages and site correlations.
- Australopithecus sediba's discovery suggested a potential transitional species between Australopithecus and early Homo.
- Adaptive radiation occurs where a single ancestral species rapidly diversifies into multiple species, adapting to different ecological niches during hominin evolution.
Postcranial Anatomical Differences
- Homo habilis exhibits a more modern hand structure adapted for tool use, longer legs for efficient bipedalism, and a less arboreal shoulder than Australopithecus afarensis.
Morphological Indicators of Encephalization
- Include a larger cranial vault, reorganization of the prefrontal cortex, and reduction in postorbital constriction indicate increasing brain size and complexity.
- Early hominins, such as Australopithecus, have a U-shaped dental arcade, whereas modern humans have a parabolic dental arcade.
- Australopithecus sediba shares traits with both genera, including a small brain size like Australopithecus but more advanced hand morphology and dentition similar to early Homo species.
- Neanderthal and Denisovan DNA contributed genetic variants that enhanced immune responses, resistance to pathogens, and high-altitude adaptation in certain populations through introgression.
- The FOXP2 gene is associated with language and speech capabilities, and its presence in Neanderthals suggests they may have had some capacity for complex communication.
- Mutations in the MC1R gene found in Neanderthals suggest they had variations in skin and hair color, possibly including lighter skin tones and red hair.
- Y-chromosome haplogroup diversity is highest in Africa, consistent with a recent African origin and subsequent dispersal of modern Homo sapiens.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.