Podcast
Questions and Answers
Indirect staining utilizes fluorescent probes or antibodies tagged with fluorescent moieties to identify molecular targets in ________ environments or fixed tissues
Indirect staining utilizes fluorescent probes or antibodies tagged with fluorescent moieties to identify molecular targets in ________ environments or fixed tissues
native
Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) employs DNA probes labeled with fluorescent tags to visualize the location of particular genetic elements within a ________ sample
Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) employs DNA probes labeled with fluorescent tags to visualize the location of particular genetic elements within a ________ sample
tissue
Immunostaining involves employing antibodies conjugated to fluorescent dyes to observe the distribution of specific antigens within ________ or tissues
Immunostaining involves employing antibodies conjugated to fluorescent dyes to observe the distribution of specific antigens within ________ or tissues
cells
Staining techniques play instrumental roles in endeavors such as identification of microbes responsible for ________
Staining techniques play instrumental roles in endeavors such as identification of microbes responsible for ________
Researchers continue to explore innovative dual-color staining schemes and multiplex imaging modalities, leveraging cutting-edge technologies such as super-resolution microscopy and computational algorithms to extract meaningful data from intricate ________ scenes
Researchers continue to explore innovative dual-color staining schemes and multiplex imaging modalities, leveraging cutting-edge technologies such as super-resolution microscopy and computational algorithms to extract meaningful data from intricate ________ scenes
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Hitotechnology: Exploring Staining Techniques
Hitotechnology, often referred to as biotechnology, represents the intersection of biology and technology aimed at improving human health, agriculture, and environmental sustainability. Within this expansive field, techniques like staining have played significant roles in visualizing biological specimens and understanding their essential characteristics.
Historically, staining methods originated with the invention of petri dishes by Friedrich Traugott Schmidt and Robert Koch's discovery of penicillin, the antibacterial substance from the fungal strain Penicillium notatum, in 1898. These developments led to improvements in the observation and identification of microorganisms, eventually resulting in the importance of staining techniques within modern biotechnology.
Common Staining Methods
Two fundamental staining approaches include:
-
Direct staining: Employs dyes that bind directly to specific molecules, coloring them distinctively to facilitate recognition under a microscope (Figure 1). Examples include Gram staining, which discriminates between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria based on differences in cell wall architecture, and methylene blue dye, which labels nucleic acids in various samples.
 Fig. 1: Example image showing Gram stained bacteria
Fig. 1: Example image showing Gram stained bacteria -
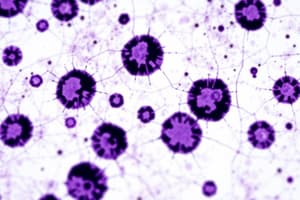
Indirect staining: Utilizes fluorescent probes or antibodies tagged with fluorescent moieties to identify molecular targets in native environments or fixed tissues (Figure 2). For instance, fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) employs DNA probes labeled with fluorescent tags to visualize the location of particular genetic elements within a tissue sample. Similarly, immunostaining involves employing antibodies conjugated to fluorescent dyes to observe the distribution of specific antigens within cells or tissues.
 Fig. 2: Image depicting a fluorescently stained section of human lung tissue
Fig. 2: Image depicting a fluorescently stained section of human lung tissue
These methods have become indispensable in biomedical research and diagnostic laboratories, offering valuable insights into the structure, function, and interactions among biological entities.
Applications of Staining Techniques
Applied across fields ranging from molecular biology to epidemiology, staining techniques play instrumental roles in various endeavors, such as:
- Identification of microbes responsible for infection
- Visualization of cellular structures, organelles, and membranes
- Localization of specific proteins, RNA, and other macromolecular constituents
- Measurement of physical properties, such as size, shape, and orientation
Yet despite their widespread utility, challenges remain concerning optimizing staining protocols, minimizing toxic effects, and gaining accurate quantitative information from fluorescent signals. To overcome these hurdles, researchers continue to explore innovative dual-color staining schemes and multiplex imaging modalities, leveraging cutting-edge technologies such as super-resolution microscopy and computational algorithms to extract meaningful data from intricate biological scenes.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.