Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the specialized name given to the zonula adherens found in cardiac muscle?
What is the specialized name given to the zonula adherens found in cardiac muscle?
- Terminal bar
- Fascia adherens (correct)
- Macula adherens
- Intercalated disc
Which type of cell junction is characterized by the presence of intermediate filaments, specifically keratin?
Which type of cell junction is characterized by the presence of intermediate filaments, specifically keratin?
- Gap junctions
- Zonula adherens
- Zonula occludens
- Macula adherens (correct)
Which of the following describes the mode of secretion where the cell's product is released via vesicles without loss of cytoplasm?
Which of the following describes the mode of secretion where the cell's product is released via vesicles without loss of cytoplasm?
- Endocrine
- Holocrine
- Apocrine
- Merocrine (correct)
Which type of secretion involves the entire cell undergoing lysis to release its secretory products?
Which type of secretion involves the entire cell undergoing lysis to release its secretory products?
What is a key characteristic of 'apocrine' secretion?
What is a key characteristic of 'apocrine' secretion?
Based on the provided images about gland types, which of the following is classified as simple tubular?
Based on the provided images about gland types, which of the following is classified as simple tubular?
In a histological slide observed under the microscope, which of the following structural details facilitates the rapid movement or passage of molecules (e.g., ATP) between adjacent cells?
In a histological slide observed under the microscope, which of the following structural details facilitates the rapid movement or passage of molecules (e.g., ATP) between adjacent cells?
If a cell uses intermediate filaments made of keratin to provide a strong anchor between cells, what type of junction is most likely being described?
If a cell uses intermediate filaments made of keratin to provide a strong anchor between cells, what type of junction is most likely being described?
Which of the following is NOT explicitly described as a type of epithelial gland secretion in the given content?
Which of the following is NOT explicitly described as a type of epithelial gland secretion in the given content?
Considering all options available, the most accurate and descriptive way to characterize the secretion method involving the discharge of both cellular product and a portion of apical cytoplasm is...?
Considering all options available, the most accurate and descriptive way to characterize the secretion method involving the discharge of both cellular product and a portion of apical cytoplasm is...?
Flashcards
Epithelial Cell Surface Modifications
Epithelial Cell Surface Modifications
Specialized junctions that attach epithelial cells to each other and to the basement membrane, providing structural support and regulating cell-cell interactions.
Hemidesmosomes
Hemidesmosomes
A type of cell junction that anchors epithelial cells to the underlying basement membrane, providing structural support.
Desmosomes
Desmosomes
A type of cell junction that provides a strong adhesion between epithelial cells, contributing to tissue integrity.
Zonula Adherens
Zonula Adherens
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tight Junctions
Tight Junctions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gap Junctions
Gap Junctions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epithelial Glands
Epithelial Glands
Signup and view all the flashcards
Merocrine Glands
Merocrine Glands
Signup and view all the flashcards
Holocrine Glands
Holocrine Glands
Signup and view all the flashcards
Apocrine Glands
Apocrine Glands
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Epithelial Tissue Part 3
- Epithelial cells have modifications on their basolateral, lateral, and basal surfaces, and also in glands.
- Basolateral surface specialization includes lateral folds and basal folds.
- Lateral folds are prominent in cells rapidly transporting fluids. Infoldings increase lateral surface. This is found in intestines and kidney tubules. Water enters apically (at the top) and leaves laterally.
- Basal folds are characteristic of cells actively transporting molecules. The folds and mitochondria are oriented together, providing energy for active transport. This is seen in proximal and distal tubules of kidneys and salivary gland ducts.
- The folds form a "striated" appearance in the basal aspect of cells, such as in striated ducts of salivary glands.
- Microscopic images of examples like proximal tubules show basolateral folds with mitochondria.
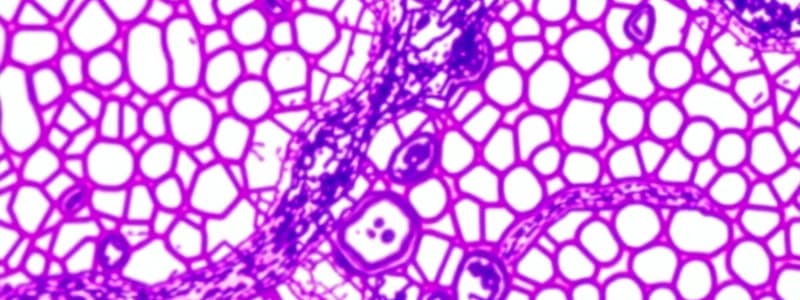
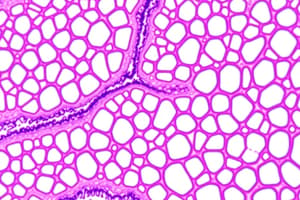
Cell-to-Cell Adhesions
- Cell-to-cell adhesions involve terminal bars, and a junctional complex with three components: occluding (zonula occludens/tight junctions), anchoring junctions, and communicating junctions.
- Occluding junctions (zonula occludens/tight junctions) form a ring around cells to prevent diffusion. They are composed of proteins like occludin and claudins. ZO proteins interact with cytoskeletal actin filaments.
- Anchoring junctions include zonula adherens and macula adherens/desmosomes.
- Zonula adherens are formed by cadherin proteins, which bind to catenin proteins. They are calcium-dependent and involved in cell-cell adhesion.
- Macula adherens/desmosomes are spot adhesions used for strong attachment between cells. They contain cadherin family proteins like desmogleins and desmocollins that bind with plakoglobins and desmoplakins, which then attach to intermediate filaments like keratins (tonofilaments).
- The zonula adherens of cardiac muscle is called fascia adherens.
Gap Junctions
- Gap junctions are channels on the lateral surfaces of adjoining cells allowing the movement of signaling molecules.
- Specialized transmembrane proteins called connexins form the channels (connexons). Six of these form each connexon.
- They allow communication between cells, such as the exchange of ions.
Basal Surface Anchoring Junctions
- Hemidesmosomes are half-desmosomes located on the basal surface of cells.
- These have intracellular attachment plaques and are attached to basal lamina via transmembrane proteins such as integrins and BP180/type XVII collagen.
- Focal adhesions include proteins for connecting cells to the extracellular matrix, connecting cytoskeleton and sensing and transmitting extracellular signals.
Epithelial Glands
- Glands are an organized collection of secretory epithelial cells that project into underlying connective tissue.
- Exocrine glands maintain direct continuity with the surface through ducts, while endocrine glands do not. Glands form by proliferation of epithelial cells.
- Unicellular glands are rare, such as goblet cells in intestines and respiratory epithelium.
- Multicellular glands with their ducts are classified based on shapes, structures and secretion mechanisms. Several forms of secretion mechanisms include merocrine, holocrine, and apocrine.
- Based on secretion: Serous (protein), mucous (mucin), or mixed (both).
Useful Definitions
- Parenchyma: Functional tissue of an organ
- Stroma: Supporting tissue composed of connective tissue, blood vessels and nerve fibers
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
Test your knowledge on the structure and function of different cell junctions and gland types in epithelial and cardiac tissues. This quiz covers topics such as zonula adherens, secretion modes, and key characteristics of gland types. Perfect for students studying histology or related fields.