Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of these chambers of the heart receives the non-oxygenated blood from the body's largest veins?
Which of these chambers of the heart receives the non-oxygenated blood from the body's largest veins?
- Right Ventricle
- Left Ventricle
- Right Atrium (correct)
- Left Atrium
Which of these valves is located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery?
Which of these valves is located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery?
- Mitral
- Pulmonary (correct)
- Tricuspid
- Aortic
What is the function of the right ventricle?
What is the function of the right ventricle?
- Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs
- Pumps blood to the lungs for oxygenation (correct)
- Receives non-oxygenated blood from the body
- Pumps blood to the body
What is the name of the blood vessel that carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart?
What is the name of the blood vessel that carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart?
Which two veins carry non-oxygenated blood to the right atrium?
Which two veins carry non-oxygenated blood to the right atrium?
What is the typical location of the apex in the human chest?
What is the typical location of the apex in the human chest?
What does RVH stand for?
What does RVH stand for?
In what condition does the apex shift outwards and downwards?
In what condition does the apex shift outwards and downwards?
What is the nature of the apex?
What is the nature of the apex?
How is the apex shift in RVH described?
How is the apex shift in RVH described?
What is the primary diagnostic tool for investigating congenital heart disease?
What is the primary diagnostic tool for investigating congenital heart disease?
Which of the following additional tests is suggested if congenital heart disease is suspected?
Which of the following additional tests is suggested if congenital heart disease is suspected?
Which blood vessel is NOT mentioned in the diagram of fetal circulation?
Which blood vessel is NOT mentioned in the diagram of fetal circulation?
What do the figures related to the cardiovascular system primarily illustrate?
What do the figures related to the cardiovascular system primarily illustrate?
What does the legend in the fetal circulation diagram represent?
What does the legend in the fetal circulation diagram represent?
What is the most common type of congenital heart disease?
What is the most common type of congenital heart disease?
Which of the following is NOT classified as a cyanotic heart disease?
Which of the following is NOT classified as a cyanotic heart disease?
What causes the first heart sound (S1)?
What causes the first heart sound (S1)?
Which condition is associated with an increased first heart sound (S1)?
Which condition is associated with an increased first heart sound (S1)?
What is a common cause of congenital heart disease related to maternal factors?
What is a common cause of congenital heart disease related to maternal factors?
Where is the second heart sound (S2) best heard?
Where is the second heart sound (S2) best heard?
Which of the following conditions is associated with Down syndrome?
Which of the following conditions is associated with Down syndrome?
Which statement is true regarding the third heart sound (S3)?
Which statement is true regarding the third heart sound (S3)?
What is a potential effect of fetal alcohol syndrome on congenital heart diseases?
What is a potential effect of fetal alcohol syndrome on congenital heart diseases?
How does aortic murmur change with positional changes?
How does aortic murmur change with positional changes?
What is the primary function of the left atrium?
What is the primary function of the left atrium?
Which valve prevents backflow from the left ventricle to the left atrium?
Which valve prevents backflow from the left ventricle to the left atrium?
What is the role of the aortic semilunar valve?
What is the role of the aortic semilunar valve?
Which valve is located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary trunk?
Which valve is located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary trunk?
How many cusps does the mitral valve have?
How many cusps does the mitral valve have?
What characterizes hyper dynamic heart sounds?
What characterizes hyper dynamic heart sounds?
What is a common sign of left ventricular enlargement?
What is a common sign of left ventricular enlargement?
Which condition is associated with a palpable diastolic thrill?
Which condition is associated with a palpable diastolic thrill?
What initial action should be taken if a patient is not feeling well during examination?
What initial action should be taken if a patient is not feeling well during examination?
Which of the following is NOT a sign of pulmonary hypertension?
Which of the following is NOT a sign of pulmonary hypertension?
What type of blood flows from the placenta to the fetus through the umbilical cord?
What type of blood flows from the placenta to the fetus through the umbilical cord?
Which of the following conditions results in the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood?
Which of the following conditions results in the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood?
Which symptom is associated with Tetralogy of Fallot?
Which symptom is associated with Tetralogy of Fallot?
What is a common symptom of Acyanotic Defects?
What is a common symptom of Acyanotic Defects?
What is the effect of a Patent Ductus Arteriosus on the body's blood flow?
What is the effect of a Patent Ductus Arteriosus on the body's blood flow?
What is one of the main characteristics of Fallot Tetralogy?
What is one of the main characteristics of Fallot Tetralogy?
How does the presence of a large ventricular septal defect (VSD) affect blood flow in Fallot Tetralogy?
How does the presence of a large ventricular septal defect (VSD) affect blood flow in Fallot Tetralogy?
What is a likely outcome if an infant has severe pulmonary stenosis from birth?
What is a likely outcome if an infant has severe pulmonary stenosis from birth?
Which symptom indicates central cyanosis in Fallot Tetralogy?
Which symptom indicates central cyanosis in Fallot Tetralogy?
What does an overriding aorta in Fallot Tetralogy describe?
What does an overriding aorta in Fallot Tetralogy describe?
Which phase of the cardiac cycle corresponds to the QRS complex on the ECG?
Which phase of the cardiac cycle corresponds to the QRS complex on the ECG?
During which phase of the cardiac cycle do the semilunar valves open?
During which phase of the cardiac cycle do the semilunar valves open?
Which of the following valves closes during the first phase of ventricular systole?
Which of the following valves closes during the first phase of ventricular systole?
What is the primary function of the P-wave on the ECG?
What is the primary function of the P-wave on the ECG?
During which phase of the cardiac cycle does blood flow passively into the ventricles?
During which phase of the cardiac cycle does blood flow passively into the ventricles?
Flashcards
Right Atrium
Right Atrium
The upper chamber of the heart that receives deoxygenated blood from the body via the superior and inferior vena cava.
Right Ventricle
Right Ventricle
The lower chamber of the heart that pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs through the pulmonary valve.
Tricuspid Valve
Tricuspid Valve
The valve that separates the right atrium and the right ventricle.
Pulmonary Valve
Pulmonary Valve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Superior and Inferior Vena Cava
Superior and Inferior Vena Cava
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the Left Atrium?
What is the function of the Left Atrium?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the Left Ventricle?
What is the function of the Left Ventricle?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the Atrio-Ventricular (AV) valves?
What is the function of the Atrio-Ventricular (AV) valves?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Describe the Tricuspid valve.
Describe the Tricuspid valve.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Describe the Aortic semilunar valve.
Describe the Aortic semilunar valve.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thrill
Thrill
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tachycardia
Tachycardia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Heaving apex beat
Heaving apex beat
Signup and view all the flashcards
Palpitation
Palpitation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Right ventricular lift
Right ventricular lift
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cardiac Apex
Cardiac Apex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Apex Shift in RVH
Apex Shift in RVH
Signup and view all the flashcards
Apex Shift in LVH
Apex Shift in LVH
Signup and view all the flashcards
Localized Apex
Localized Apex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diffuse Apex
Diffuse Apex
Signup and view all the flashcards
What creates the first heart sound (S1)?
What creates the first heart sound (S1)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What creates the second heart sound (S2)?
What creates the second heart sound (S2)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a thrill?
What is a thrill?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does body position affect a mitral murmur?
How does body position affect a mitral murmur?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does the character of a murmur differ between stenosis and regurgitation?
How does the character of a murmur differ between stenosis and regurgitation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are Congenital Heart Diseases (CHD)?
What are Congenital Heart Diseases (CHD)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How are CHDs classified?
How are CHDs classified?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are cyanotic CHDs?
What are cyanotic CHDs?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are obstructive CHDs?
What are obstructive CHDs?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are some causes of CHDs?
What are some causes of CHDs?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Describe fetal blood flow.
Describe fetal blood flow.
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)?
What is Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are Cyanogenic Heart Defects?
What are Cyanogenic Heart Defects?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are Acyanotic Heart Defects?
What are Acyanotic Heart Defects?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Tachycardia?
What is Tachycardia?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Atrial Systole
Atrial Systole
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the four components of Fallot Tetralogy?
What are the four components of Fallot Tetralogy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Explain what causes Lung Oligemia in Fallot Tetralogy.
Explain what causes Lung Oligemia in Fallot Tetralogy.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ventricular Systole (First Phase)
Ventricular Systole (First Phase)
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does a large VSD contribute to cyanosis in Fallot Tetralogy ?
How does a large VSD contribute to cyanosis in Fallot Tetralogy ?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ventricular Systole (Second Phase)
Ventricular Systole (Second Phase)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ventricular Diastole (Early)
Ventricular Diastole (Early)
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is central cyanosis and when is it typically observed in Fallot Tetralogy?
What is central cyanosis and when is it typically observed in Fallot Tetralogy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ventricular Diastole (Late)
Ventricular Diastole (Late)
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a heaving apex beat and how is it linked to Fallot Tetralogy?
What is a heaving apex beat and how is it linked to Fallot Tetralogy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Echocardiography with Doppler?
What is Echocardiography with Doppler?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the uses of Doppler Echocardiography?
What are the uses of Doppler Echocardiography?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does Doppler Echocardiography work?
How does Doppler Echocardiography work?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of Doppler in Echocardiography?
What is the role of Doppler in Echocardiography?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why is Doppler Echocardiography important in diagnosing congenital heart disease?
Why is Doppler Echocardiography important in diagnosing congenital heart disease?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
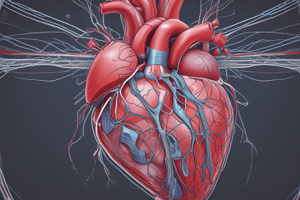
Heart Structure and Function
- The heart is a four-chambered organ
- Two upper chambers are the atria (left atrium and right atrium)
- Two lower chambers are the ventricles (left ventricle and right ventricle)
- The heart also has four valves: tricuspid, pulmonary, mitral, and aortic valves
Atrio-Ventricular Valves
- Function: prevent backflow from ventricles to atria
- Tricuspid valve: located between right atrium and right ventricle, has three cusps (anterior/anterosuperior, septal, and posterior/inferior)
- Mitral valve: located between left atrium and left ventricle, has two cusps (anterior/aortic and posterior/mural)
Semilunar Valves
- Function: prevent backflow from great vessels to ventricles
- Pulmonary semilunar valve: located between right ventricle and pulmonary trunk, has three cusps (anterior/non-adjacent, left/left adjacent, and right/right adjacent)
- Aortic semilunar valve: located between left ventricle and aorta, has three cusps (left/left coronary valve, right/right coronary valve, and posterior/non-adjacent)
Left Atrium
- Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs
- Pumps it through the mitral valve to the left ventricle
Left Ventricle
- Pumps oxygen-rich blood to the aorta and the rest of the body
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.