Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the first major system to function in the embryo?
What is the first major system to function in the embryo?
- Cardiovascular system (correct)
- Respiratory system
- Musculoskeletal system
- Nervous system
Which structure is described as a quadrangular space that precedes the atria?
Which structure is described as a quadrangular space that precedes the atria?
- Aortic arch
- Pulmonary trunk
- Cardiac loop
- Sinus venosus (correct)
During which week does the primordial heart and vascular system appear?
During which week does the primordial heart and vascular system appear?
- Week 1
- Week 5
- Week 3 (correct)
- Week 6
What embryonic layer primarily contributes to the development of the cardiovascular system?
What embryonic layer primarily contributes to the development of the cardiovascular system?
Where is the cardiogenic area located initially?
Where is the cardiogenic area located initially?
What process brings paired cardiac tubes together to form a single tube?
What process brings paired cardiac tubes together to form a single tube?
What happens as the forebrain grows in relation to the heart?
What happens as the forebrain grows in relation to the heart?
What structure receives blood from the left and right sinus horns?
What structure receives blood from the left and right sinus horns?
What happens to the left horn of the sinus venosus?
What happens to the left horn of the sinus venosus?
Which structure maintains blood flow between the atria during septum formation?
Which structure maintains blood flow between the atria during septum formation?
What is the primary function of the endocardial cushions in the heart development?
What is the primary function of the endocardial cushions in the heart development?
What is the name of the opening left by the septum secundum after birth?
What is the name of the opening left by the septum secundum after birth?
Which of the following structures develops from the right horn of the sinus venosus?
Which of the following structures develops from the right horn of the sinus venosus?
Which component is directly involved in the fusion of the septum primum and the endocardial cushions?
Which component is directly involved in the fusion of the septum primum and the endocardial cushions?
What shape does the septum primum resemble during its development?
What shape does the septum primum resemble during its development?
Which of the following is formed by merging perforations in the septum primum?
Which of the following is formed by merging perforations in the septum primum?
What must students acknowledge regarding the faculty members during the use of class recordings?
What must students acknowledge regarding the faculty members during the use of class recordings?
Which statement is true regarding the distribution of recorded lectures?
Which statement is true regarding the distribution of recorded lectures?
Which of the following accurately describes the emotional aspects of viewing past lecture recordings?
Which of the following accurately describes the emotional aspects of viewing past lecture recordings?
What do students agree to regarding the usage of recordings?
What do students agree to regarding the usage of recordings?
What is NOT listed as a consequence of not agreeing to the terms for class recordings?
What is NOT listed as a consequence of not agreeing to the terms for class recordings?
Which embryonic tissues are essential for developing cardiovascular structures?
Which embryonic tissues are essential for developing cardiovascular structures?
What is the focus of the content regarding heart anomalies?
What is the focus of the content regarding heart anomalies?
What change occurs in circulation after birth, according to developmental studies?
What change occurs in circulation after birth, according to developmental studies?
What forms the atrioventricular (AV) valves during development?
What forms the atrioventricular (AV) valves during development?
Which structures attach the atrioventricular valves to the papillary muscles?
Which structures attach the atrioventricular valves to the papillary muscles?
What characterizes Ebstein anomaly?
What characterizes Ebstein anomaly?
What is the result of the migration of cardiac neural crest cells?
What is the result of the migration of cardiac neural crest cells?
What condition can result from disruption in outflow tract development?
What condition can result from disruption in outflow tract development?
What happens to the muscular cords that attach the valves during development?
What happens to the muscular cords that attach the valves during development?
Which condition is characterized by a tricuspid valve that is displaced towards the apex of the right ventricle?
Which condition is characterized by a tricuspid valve that is displaced towards the apex of the right ventricle?
What do conotruncal ridges grow to divide?
What do conotruncal ridges grow to divide?
What is the primary defect in transposition of the great vessels?
What is the primary defect in transposition of the great vessels?
Which of the following conditions is NOT associated with tetralogy of Fallot?
Which of the following conditions is NOT associated with tetralogy of Fallot?
Which part of the interventricular septum is responsible for closing the IV foramen?
Which part of the interventricular septum is responsible for closing the IV foramen?
What is a common factor associated with ventricular septal defects?
What is a common factor associated with ventricular septal defects?
What type of birth defect is associated with a conotruncal septum failing to take a spiral course?
What type of birth defect is associated with a conotruncal septum failing to take a spiral course?
Which of the following describes the incidence of ventricular septal defects?
Which of the following describes the incidence of ventricular septal defects?
What cell type influences the formation of semilunar valves?
What cell type influences the formation of semilunar valves?
Which type of congenital heart defect is characterized as acyanotic?
Which type of congenital heart defect is characterized as acyanotic?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
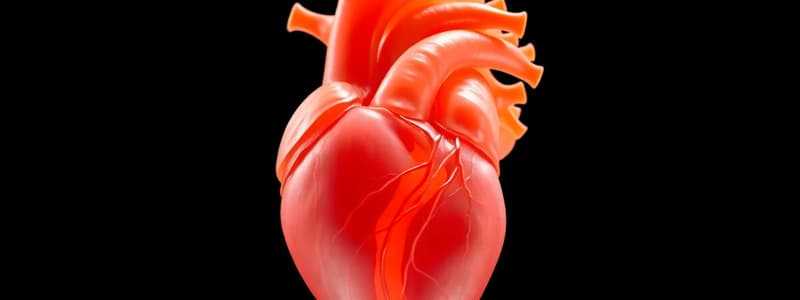
Heart Development
- The cardiovascular system is the first major system to function in the embryo
- The primordial heart and the vascular system appear in the middle of the third week
- The rapidly growing embryo can no longer satisfy its nutritional and oxygen requirements from diffusion
- The heart is derived from mesoderm with contributions from the neural crest
Formation and Position of the Heart Tube
- The cardiogenic area is originally anterior to the future mouth and forebrain
- The forebrain grows over the heart to lie in the thorax position
- The lateral folding of the embryo brings paired cardiac tubes together as a single tube
Development of the Sinus Venosus
- The sinus venosus is a quadrangular space that precedes the atria
- The sinus venosus receives all blood for the embryo from the left and right sinus horns
- The left sinus horns contributes veins that degenerate and form the coronary sinus
- The right sinus horn enlarges from the shunting of blood
- The right sinus horn develops into the valves of the IVC and the valves of the coronary sinus
Formation of Cardiac Septa
- Endocardial cushions are growing masses of endocardium that project into the lumen to divide a canal
- These endocardial cushions form atrioventricular septa to divide the common atria
- The septum primum is a sickle-shaped crest that grows from the roof of the common atrium towards the endocardial cushions in the atrioventricular canal
- The ostium primum is an opening between the lower rim of the septum primum and the atrioventricular opening
- The ostium secundum are merging perforations in the septum primum that maintain blood flow between the atria
- The septum secundum is a crescent-shaped fold from the incorporation of the sinus horn in the right atrium
- The oval foramen is an opening left by the septum secundum, and this closes off after birth
- The oval foramen becomes the fossa ovalis after birth
Atrioventricular Valves
- Local proliferations of mesenchyme become fibrous and form the AV valves
- Muscular cords attaching the valves degenerate and are replaced by dense connective tissues
- The valves are attached to the papillary muscles by chordae tendineae
Septum Formation in the Outflow Tract
- Cardiac neural crest cells migrate to contribute to the outflow tract, disruption of migration can cause birth defects like tetralogy of Fallot, pulmonary stenosis, persistent truncus arteriosus, and transposition of great vessels
- The conotruncal ridges grow and divide the outflow tract into the aortic and pulmonary channels
Ventricular Septal Defects
- Occur in membranous or muscular portions
- Are associated with abnormal partitioning in the conotruncal region
Tetralogy of Fallot
- The unequal division of the conus due to the anterior displacement of the conotruncal septum
- This defect is associated with a patent ductus arteriosus and pulmonary stenosis
Transposition of the Great Vessels
- The conotruncal septum fails to take a spiral course and goes straight down
- The aorta originates from the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery from the left ventricle
- This defect is associated with a defect in the membranous IV septum and a patent ductus arteriosus
Septum Formation in the Ventricles
- The medial walls expand to form the muscular IV septum
- The membranous part of the IV septum closes the IV foramen
- Tubercles on the main truncus swellings form the semilunar valves, swelling is influenced by neural crest cells
Ebstein Anomaly
- The tricuspid valve is displaced toward the apex of the right ventricle
- This causes an expanded right atrium and a small right ventricle
- There are also abnormal valve leaflets
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.