Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary role of legislatures within a political system?
What is the primary role of legislatures within a political system?
- To interpret laws
- To enact legislation (correct)
- To oversee executive actions
- To implement laws
Which feature is essential to understanding the relationship between legislative and executive authority?
Which feature is essential to understanding the relationship between legislative and executive authority?
- The separation of judicial powers
- The oversight capabilities of parliaments
- The concept of checks and balances
- The role of assemblies in governance (correct)
What is NOT a principal function of assemblies?
What is NOT a principal function of assemblies?
- Scrutiny and oversight
- Legislation
- Public administration (correct)
- Political recruitment
In a parliamentary system, which aspect is often misleading about the authority of assemblies?
In a parliamentary system, which aspect is often misleading about the authority of assemblies?
Why is the power of an assembly considered an index of democratic government?
Why is the power of an assembly considered an index of democratic government?
Which of the following correctly describes the nature of the term 'assembly'?
Which of the following correctly describes the nature of the term 'assembly'?
What is one of the key reasons liberal democracies adopt a parliamentary system?
What is one of the key reasons liberal democracies adopt a parliamentary system?
Which principle characterizes the role of legislatures in respect to legislation?
Which principle characterizes the role of legislatures in respect to legislation?
What is a primary function of assemblies in relation to the executive?
What is a primary function of assemblies in relation to the executive?
Which type of representation involves representatives 'acting for' their constituents?
Which type of representation involves representatives 'acting for' their constituents?
What aspect of representation did Saward (2006) emphasize?
What aspect of representation did Saward (2006) emphasize?
How do assemblies promote the legitimacy of a regime?
How do assemblies promote the legitimacy of a regime?
What challenge do assemblies face in effectively overseeing the executive?
What challenge do assemblies face in effectively overseeing the executive?
What is a criticism regarding the recruitment role of assemblies?
What is a criticism regarding the recruitment role of assemblies?
Which term refers to an assembly composed of a single legislative chamber?
Which term refers to an assembly composed of a single legislative chamber?
In what context are assemblies less effective as channels for recruitment?
In what context are assemblies less effective as channels for recruitment?
Flashcards
Representative Function
Representative Function
How representatives act on behalf of their constituents.
Scrutiny and Oversight
Scrutiny and Oversight
Assemblies checking and holding the executive accountable.
Recruitment and Training
Recruitment and Training
Assemblies selecting and shaping future leaders.
Legitimacy Functions
Legitimacy Functions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Unicameralism
Unicameralism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Descriptive Representation
Descriptive Representation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Symbolic Representation
Symbolic Representation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Formalistic Representation
Formalistic Representation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Three Branches of Power
Three Branches of Power
Signup and view all the flashcards
Legislature's Role
Legislature's Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Assembly/Parliament
Assembly/Parliament
Signup and view all the flashcards
Legislative-Executive Relationship
Legislative-Executive Relationship
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parliamentary System
Parliamentary System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Functions of Assemblies
Functions of Assemblies
Signup and view all the flashcards
Legislative Power
Legislative Power
Signup and view all the flashcards
Representation in Assemblies
Representation in Assemblies
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
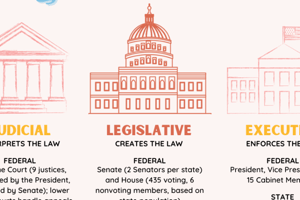
The Three Branches of Power
- Three distinct branches exist in government
- Executives implement law
- Legislatures create laws
- Judiciaries interpret laws
Role of Assemblies
- "Assembly" refers to legislative bodies (houses/chambers)
- The relationship between the legislative and executive branches is crucial
- Assemblies are vital for a functioning political system.
Parliamentary System of Government
- Most liberal democracies use this system
- The executive is accountable to the assembly
- The assembly is elected by the people
Functions of Assemblies
- Legislatures: Create laws
- Representation: Link to citizens
- Scrutiny & Oversight: Control the executive
- Political Recruitment: Choose and train leaders
- Legitimacy: Provide authority to the system
Legislation
- Assemblies are given the power to make laws
- However, assemblies don't always have complete control over legislation.
Representation
- Assemblies ideally connect the government to the people
- The power of assemblies is often seen as a measure of democracy
- The practical effectiveness of representation is complex.
Representation (Pitkin)
- Formalistic Representation
- Descriptive Representation (“standing for”)
- Symbolic Representation
- Substantive Representation (“acting for”)
Scrutiny and Oversight
- Assemblies oversee the executive branch
- Oversight needs effective resources and expert advice.
Recruitment and Training
- Assemblies are important in the political recruitment process
- This role is less prominent in authoritarian/presidential systems
Legitimacy
- Assemblies promote the legitimacy of the government
- This is true even in authoritarian regimes.
Structure of Assemblies
- Unicameralism: One legislative chamber (e.g., Israel, New Zealand, Denmark)
- Bicameralism: Two legislative chambers (e.g., UK, USA, Fiji)
Assemblies in Decline
- In the 20th century, assemblies lost some power
- This was largely due to:
- Stronger political parties
- Larger governments
- Weak organizational structures
- Rise of interest groups and media
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.