Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary role of glycolysis in cellular metabolism?
What is the primary role of glycolysis in cellular metabolism?
- To synthesize glucose from pyruvate
- To break down glucose into pyruvate (correct)
- To transport glucose across the cell membrane
- To produce oxygen for aerobic respiration
Which molecule is produced at the end of glycolysis?
Which molecule is produced at the end of glycolysis?
- NADH
- Lactate
- Pyruvate (correct)
- Glucose
Glycolysis does not require oxygen. What type of process is this characterized as?
Glycolysis does not require oxygen. What type of process is this characterized as?
- Substrate-level phosphorylation
- Aerobic
- Anaerobic (correct)
- Oxidative
What is the starting substrate for glycolysis?
What is the starting substrate for glycolysis?
Which enzyme catalyzes the final step of glycolysis, producing pyruvate?
Which enzyme catalyzes the final step of glycolysis, producing pyruvate?
During glycolysis, how many molecules of ATP are produced as outputs?
During glycolysis, how many molecules of ATP are produced as outputs?
What role does NADPH play in the phosphorylation step of glycolysis?
What role does NADPH play in the phosphorylation step of glycolysis?
What happens to pyruvate under anaerobic conditions after glycolysis?
What happens to pyruvate under anaerobic conditions after glycolysis?
Glycolysis is the breakdown of ______, which is a 6-carbon molecule.
Glycolysis is the breakdown of ______, which is a 6-carbon molecule.
The end product of glycolysis is two molecules of ______.
The end product of glycolysis is two molecules of ______.
Glycolysis occurs in the ______ of the cell.
Glycolysis occurs in the ______ of the cell.
Oxidative phosphorylation involves the transfer of a phosphate group to ______.
Oxidative phosphorylation involves the transfer of a phosphate group to ______.
The enzyme used in the first step of glycolysis is called ______.
The enzyme used in the first step of glycolysis is called ______.
In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted into ______.
In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted into ______.
The metabolic pathway that converts glucose into energy is known as ______.
The metabolic pathway that converts glucose into energy is known as ______.
Two molecules of ______ are produced as outputs of glycolysis.
Two molecules of ______ are produced as outputs of glycolysis.
Flashcards
What is Glycolysis?
What is Glycolysis?
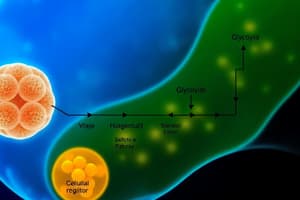
Glycolysis is the breakdown of glucose (a 6-carbon sugar) into two molecules of pyruvate (a 3-carbon molecule).
Is Glycolysis aerobic or anaerobic?
Is Glycolysis aerobic or anaerobic?
Glycolysis can occur with or without oxygen, making it an anaerobic process. However, the presence of oxygen influences the fate of pyruvate.
What happens to pyruvate after glycolysis?
What happens to pyruvate after glycolysis?
With oxygen present, pyruvate from glycolysis enters the Krebs Cycle. Without oxygen, pyruvate is converted to lactate.
What are the inputs of glycolysis?
What are the inputs of glycolysis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the outputs of glycolysis?
What are the outputs of glycolysis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is phosphorylation in glycolysis?
What is phosphorylation in glycolysis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is oxidative phosphorylation in glycolysis?
What is oxidative phosphorylation in glycolysis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where does glycolysis take place?
Where does glycolysis take place?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is phosphorylation?
What is phosphorylation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is oxidative phosphorylation?
What is oxidative phosphorylation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Glycolysis Overview
- Glycolysis is the breakdown of glucose (a 6-carbon molecule) into two molecules of pyruvate (a 3-carbon molecule).
- It's a metabolic pathway converting glucose to energy and intermediates for other metabolic pathways.
- It's an anaerobic process, meaning it doesn't require oxygen, but the presence or absence of oxygen affects the fate of pyruvate.
- It's the first step in cellular respiration, preceding the Krebs Cycle and the Electron Transport Chain (ETC).
- Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell.
- With oxygen, pyruvate enters the Krebs Cycle; without oxygen, it's converted to lactate.
Inputs and Outputs
- Inputs: One glucose molecule, 2 ATP molecules, and 2 NAD+ molecules.
- Outputs: Two pyruvate molecules, 2 ADP molecules, and 2 NADH molecules.
Glycolysis Steps
- Phosphorylation (Hexokinase): A dehydrogenase enzyme is used to oxidize and phosphorylate Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate, forming 1,3-Bisphosphoglyceric acid. The phosphate comes from NAD+.
- Oxidative Phosphorylation: A phosphate group from 1,3-Bisphosphoglyceric acid is transferred to ADP, forming ATP and 3-Phosphoglyceric acid. This reaction is catalyzed by phosphoglycerate kinase. The source of the inorganic phosphate in this step is not NADPH, but is a result of a high-energy phosphate bond being transferred.
- Transfer of Phosphate Group (Phosphoglycerate Mutase): The phosphate group is moved to the second carbon atom, producing 2-Phosphoglyceric acid, catalyzed by phosphoglycerate mutase.
- Dehydration (Enolase): 2-Phosphoglyceric acid loses a water molecule to produce Phosphoenolpyruvate. The enzyme responsible is enolase.
- Transfer of Phosphate Group (Pyruvate Kinase): A final ATP molecule is produced when a phosphate group from Phosphoenolpyruvate is transferred to ADP, creating pyruvate. The enzyme catalyzing this step is pyruvate kinase.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.