Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which tissue type covers the body's surfaces and lines its cavities?
Which tissue type covers the body's surfaces and lines its cavities?
- Muscle tissue
- Epithelial tissue (correct)
- Connective tissue
- Nervous tissue
What is the primary function of connective tissue?
What is the primary function of connective tissue?
- To cover the body's surfaces
- To transmit nerve impulses
- To control body movements
- To support the body (correct)
Which type of tissue is responsible for body movements?
Which type of tissue is responsible for body movements?
- Epithelial tissue
- Nervous tissue
- Connective tissue
- Muscle tissue (correct)
What is the role of nervous tissue in the body?
What is the role of nervous tissue in the body?
What does SEM provide?
What does SEM provide?
What are the steps for preparing tissue for microscopic viewing?
What are the steps for preparing tissue for microscopic viewing?
What are the functions of epithelium?
What are the functions of epithelium?
What are the distinguishing characteristics of epithelial tissues?
What are the distinguishing characteristics of epithelial tissues?
How are epithelial tissues supported?
How are epithelial tissues supported?
What is the regenerative capacity of epithelium?
What is the regenerative capacity of epithelium?
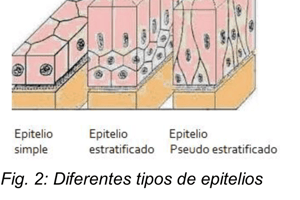
How is epithelial tissue classified?
How is epithelial tissue classified?
What are the common shapes of epithelial cells?
What are the common shapes of epithelial cells?
What do glandular epithelia consist of?
What do glandular epithelia consist of?
How are glands classified?
How are glands classified?
Which type of tissue is responsible for body movement?
Which type of tissue is responsible for body movement?
Which type of tissue forms delicate networks around small blood vessels and supports the soft tissue of organs?
Which type of tissue forms delicate networks around small blood vessels and supports the soft tissue of organs?
What are the three kinds of muscle tissue?
What are the three kinds of muscle tissue?
What is the main component of the nervous system?
What is the main component of the nervous system?
Which membrane consists of a keratinized stratified squamous epithelium firmly attached to a thick layer of connective tissue?
Which membrane consists of a keratinized stratified squamous epithelium firmly attached to a thick layer of connective tissue?
Where are mucous membranes found?
Where are mucous membranes found?
What brings about movement or contraction in all cell types?
What brings about movement or contraction in all cell types?
What is skeletal muscle often referred to as?
What is skeletal muscle often referred to as?
What are the resident cell types in each major class of connective tissue?
What are the resident cell types in each major class of connective tissue?
Which type of tissue is home to cell types such as adipocytes, white blood cells, mast cells, and macrophages?
Which type of tissue is home to cell types such as adipocytes, white blood cells, mast cells, and macrophages?
What are the moist membranes found in closed ventral body cavities called?
What are the moist membranes found in closed ventral body cavities called?
What is an exception to the generalization of resident cell type in blood, a major class of connective tissue?
What is an exception to the generalization of resident cell type in blood, a major class of connective tissue?
Which type of glands release hormones into the blood or lymphatic fluid to prompt specific target organs to respond?
Which type of glands release hormones into the blood or lymphatic fluid to prompt specific target organs to respond?
What is the main function of connective tissue?
What is the main function of connective tissue?
Which type of glands release their products onto body surfaces or into body cavities?
Which type of glands release their products onto body surfaces or into body cavities?
What is the only true example of holocrine glands?
What is the only true example of holocrine glands?
Which type of glands secrete products by exocytosis?
Which type of glands secrete products by exocytosis?
What is the most abundant and widely distributed tissue in the body?
What is the most abundant and widely distributed tissue in the body?
What separates the living cells of connective tissue?
What separates the living cells of connective tissue?
From which embryonic tissue do all connective tissues arise?
From which embryonic tissue do all connective tissues arise?
What are the main components of connective tissues?
What are the main components of connective tissues?
Which type of glands accumulate products until they rupture?
Which type of glands accumulate products until they rupture?
Which type of glands release their products through unicellular or multicellular glands?
Which type of glands release their products through unicellular or multicellular glands?
What is the range of secretions from endocrine glands?
What is the range of secretions from endocrine glands?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Endocrine Glands and Exocrine Glands
- Endocrine glands release hormones into the blood or lymphatic fluid to prompt specific target organs to respond.
- Endocrine glands are structurally diverse and their secretions range from modified amino acids to steroids.
- Exocrine glands release their products onto body surfaces or into body cavities through unicellular or multicellular glands.
- Glandular epithelia can be simple or compound and are further categorized by their secretory units as tubular, alveolar, or tubuloalveolar.
- Merocrine glands secrete products by exocytosis, while holocrine glands accumulate products until they rupture.
- Sebaceous (oil) glands are the only true example of holocrine glands.
- Connective tissue is the most abundant and widely distributed tissue in the body.
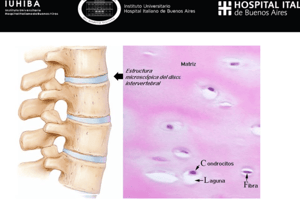
- There are four main classes of connective tissue: connective tissue proper, cartilage, bone, and blood.
- Connective tissue functions include binding and supporting, protecting, insulating, storing reserve fuel, and transporting substances within the body.
- Connective tissues consist largely of nonliving extracellular matrix, which separates the living cells of the tissue.
- All connective tissues arise from mesenchyme, an embryonic tissue.
- Connective tissues have three main components: ground substance, fibers, and cells. Ground substance has interstitial fluid, cell adhesion proteins, and proteoglycans.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.