Podcast
Questions and Answers
What type of forces create faults in the Earth's crust?
What type of forces create faults in the Earth's crust?
- Electromagnetic forces
- Gravitational forces
- Magnetic forces
- Different types of tectonic forces (correct)
What is a key characteristic of a transform fault boundary?
What is a key characteristic of a transform fault boundary?
- It resembles a strike-slip fault in motion (correct)
- It forms new crust material during seismic activity
- It occurs only beneath the Earth's surface
- It has divergent motions between adjacent plates
What did the arrangement of blocks representing divergent plate boundaries indicate?
What did the arrangement of blocks representing divergent plate boundaries indicate?
- The blocks move toward each other
- The plates push against each other
- There are gaps between the blocks representing movement (correct)
- The blocks act independently without interaction
In the activity, what was used to simulate the interaction of lithospheric plates?
In the activity, what was used to simulate the interaction of lithospheric plates?
How do transform faults typically interact with mid-ocean ridges?
How do transform faults typically interact with mid-ocean ridges?
Which type of boundary is created between blocks 1 and 2, and blocks 3 and 4 in the activity?
Which type of boundary is created between blocks 1 and 2, and blocks 3 and 4 in the activity?
What is the primary material found in the continental crust?
What is the primary material found in the continental crust?
What is the purpose of the sandpaper in the simulation activity?
What is the purpose of the sandpaper in the simulation activity?
What effect does pulling the blocks apart simulate in the transform fault boundary activity?
What effect does pulling the blocks apart simulate in the transform fault boundary activity?
What is the average thickness of the oceanic crust?
What is the average thickness of the oceanic crust?
Which of the following correctly describes the density relationship between oceanic and continental crust?
Which of the following correctly describes the density relationship between oceanic and continental crust?
What are the two main regions into which the crust is subdivided?
What are the two main regions into which the crust is subdivided?
What is the maximum thickness the Earth's crust can reach under mountains?
What is the maximum thickness the Earth's crust can reach under mountains?
What represents the source of molten materials that creates volcanic island chains?
What represents the source of molten materials that creates volcanic island chains?
Why do volcanic islands get older as they move away from Hawaii?
Why do volcanic islands get older as they move away from Hawaii?
What geological feature will be formed at the surface of the crust due to continuing plate movement?
What geological feature will be formed at the surface of the crust due to continuing plate movement?
What happens to an island volcano after it becomes extinct?
What happens to an island volcano after it becomes extinct?
Which of the features is expected to be the most active in a chain of volcanic islands?
Which of the features is expected to be the most active in a chain of volcanic islands?
What is likely to occur during the process of oceanic plate movement over a mantle plume?
What is likely to occur during the process of oceanic plate movement over a mantle plume?
What is one consequence of the Pacific plate moving over the mantle plume?
What is one consequence of the Pacific plate moving over the mantle plume?
What natural disasters is the country most susceptible to, according to the content?
What natural disasters is the country most susceptible to, according to the content?
What geological feature is formed by the subduction of the Philippine Sea Plate beneath the Philippines?
What geological feature is formed by the subduction of the Philippine Sea Plate beneath the Philippines?
Which volcanic chain was created by the descent of the West Philippine Sea oceanic lithosphere?
Which volcanic chain was created by the descent of the West Philippine Sea oceanic lithosphere?
What types of earthquakes are primarily induced by the constant dipping movement of slabs in the Philippines?
What types of earthquakes are primarily induced by the constant dipping movement of slabs in the Philippines?
Which of the following volcanoes is NOT mentioned as being part of the volcanic chain formed by the downward movement of oceanic lithospheres?
Which of the following volcanoes is NOT mentioned as being part of the volcanic chain formed by the downward movement of oceanic lithospheres?
What material is primarily used in the described activity involving continental plate convergence?
What material is primarily used in the described activity involving continental plate convergence?
What does the experiment involving the modeling clay and blocks of wood primarily demonstrate?
What does the experiment involving the modeling clay and blocks of wood primarily demonstrate?
How does the downward movement of oceanic lithospheres impact the geography of the Philippines?
How does the downward movement of oceanic lithospheres impact the geography of the Philippines?
What happens to the strips of clay when they are pushed together from opposite ends during the experiment?
What happens to the strips of clay when they are pushed together from opposite ends during the experiment?
How do you compare the densities of the Earth’s crust, mantle, and core?
How do you compare the densities of the Earth’s crust, mantle, and core?
Which layer is described as a soft, weak, and plastic-like layer that facilitates the movement of lithospheric plates?
Which layer is described as a soft, weak, and plastic-like layer that facilitates the movement of lithospheric plates?
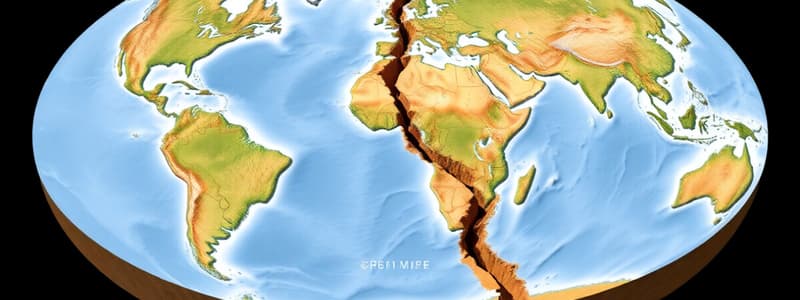
What theory did Alfred Wegener propose regarding the continents?
What theory did Alfred Wegener propose regarding the continents?
Which observation suggests that the continents were once joined?
Which observation suggests that the continents were once joined?
Which observation was NOT instrumental in formulating the hypothesis of seafloor spreading?
Which observation was NOT instrumental in formulating the hypothesis of seafloor spreading?
What process describes how the oceanic crust plunges into the Earth and is destroyed at the mantle?
What process describes how the oceanic crust plunges into the Earth and is destroyed at the mantle?
What is a key characteristic of the asthenosphere?
What is a key characteristic of the asthenosphere?
What evidence supports the existence of the boundary between the crust and the mantle?
What evidence supports the existence of the boundary between the crust and the mantle?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Faults and Plate Boundaries
- Faults are fractures in the Earth's crust caused by various forces on the lithosphere.
- Transform fault boundaries are similar to strike-slip faults, involving horizontal movement of adjacent rock slabs.
- Transform boundaries often connect segments of mid-ocean ridges, showing major geological activity.
Transform Fault Boundaries Simulation
- An experiment using blocks of wood and sandpaper demonstrates the effects of transform fault boundaries.
- Blocks represent lithospheric plates, with divergent boundaries forming between them.
- Movement of blocks simulates the interaction at transform faults, leading to observations of friction and displacement.
Subduction Zones and Geological Features
- The Philippine Trench and East Luzon Trough are results of the subduction of the Philippine Sea Plate.
- Subduction leads to the formation of trenches and volcanic chains, like those from the Manila Trench to Mindoro.
- Major active volcanoes in this chain include Pinatubo and Taal, resulting from descending tectonic plates.
Volcanic Activity and Tectonic Movements
- The downward movement of oceanic lithospheres generates earthquakes and shapes landforms in the Philippine Archipelago.
- Hot spots in the mantle create volcanic chains as tectonic plates move over stationary molten material.
- Over time, as plates shift, volcanic islands become dormant, resulting in a trail of volcanic activity across the ocean floor.
Earth’s Structural Composition
- Earth's layers: crust, mantle, outer core, inner core.
- The crust is the thin, outermost layer averaging 32 km, up to 72 km beneath mountains.
- Two types of crust:
- Continental crust: 35-40 km thick, composed of less dense rocks (granite).
- Oceanic crust: 7-10 km thick, composed of denser rocks (basalt).
Key Scientific Concepts and Theories
- Alfred Wegener's Continental Drift Theory posits all landmasses were once a single supercontinent, Pangaea.
- Evidence for continental connections includes matching shapes of coastlines and similar fossil findings.
- Earth’s tectonic activity influences geological features, including mountains, earthquakes, and volcanic eruptions.
Importance of Studying Earth's Layers
- Understanding Earth's composition provides insights into its geological history and processes.
- Identifying different layers and compositions aids in predicting natural disasters like earthquakes and volcanism.
Conclusion
- The dynamic processes of tectonics and subduction play crucial roles in shaping the Earth’s landscape.
- Continuous plate movements lead to the formation of various geological features and influence seismic activity.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.