Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following is NOT one of the three main physiographic divisions of India?
Which of the following is NOT one of the three main physiographic divisions of India?
- The alluvial plains along the Indus and Gangetic rivers
- The peninsula
- The western coastal plains (correct)
- The northern mountain ranges
Which of the following statements about the Himalayas is correct?
Which of the following statements about the Himalayas is correct?
- The Himalayas are located in the southern part of India.
- The Himalayas are home to some of the world's tallest peaks, including Mount Everest and K2. (correct)
- The Himalayas are the lowest mountain range in India.
- The Himalayas stretch for approximately 1,000 kilometers.
What is the southernmost tip of the peninsula (Deccan plateau) called?
What is the southernmost tip of the peninsula (Deccan plateau) called?
- Kanyakumari (correct)
- Kodaikanal
- Ooty
- Coimbatore
Which of the following states is NOT located in the alluvial plains along the Indus and Gangetic rivers?
Which of the following states is NOT located in the alluvial plains along the Indus and Gangetic rivers?
Which of the following landscapes is NOT mentioned as characterizing the peninsula (Deccan plateau)?
Which of the following landscapes is NOT mentioned as characterizing the peninsula (Deccan plateau)?
Which of the following is not a major river in India?
Which of the following is not a major river in India?
What type of vegetation is found in the arid regions of India?
What type of vegetation is found in the arid regions of India?
Which of the following is not a major challenge related to water resource management in India?
Which of the following is not a major challenge related to water resource management in India?
Which of the following is not one of the major metropolitan areas in India?
Which of the following is not one of the major metropolitan areas in India?
What is the dominant religion in India?
What is the dominant religion in India?
Study Notes
India: An Intricate Tapestry of Nature's Artistry and Cultural Heritage
Introduction
India, a land of vibrant colors, cultures, and traditions, is characterized by its rich geographical diversity. From the frozen peaks of the Himalayas in the north to the serene backwaters of Kerala in the south, and from the arid deserts of Rajasthan to the lush rainforests of the Western Ghats, India's geography is a testament to nature's creativity.
Physical Geography
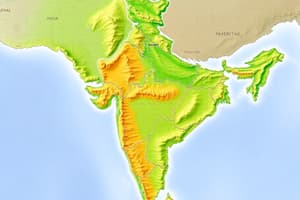
India is divided into three main physiographic divisions: the northern mountain ranges, the peninsula, and the alluvial plains along the Indus and Gangetic rivers. The Himalayas are the highest mountain range, stretching for nearly 2,400 kilometers. They are home to some of the world's tallest peaks, including Mount Everest and K2.
The peninsula, also known as the Deccan plateau, is a large, flat region that covers most of India. It is characterized by its diverse landscapes, including plateaus, valleys, and coastal strips. The southernmost tip of the peninsula is Kanyakumari.
The alluvial plains, mainly along the Indus and Gangetic rivers, are fertile and support a significant portion of India's population. These plains are primarily found in Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal, Assam, Punjab, and part of Haryana.
Climate
India experiences a diverse range of climates due to its extensive geographical area. The country has distinct seasons, including summer, monsoon, autumn, winter, and pre-monsoon. The monsoon season, lasting from July to November, brings heavy rains to most parts of the country, while the summer season is characterized by hot temperatures and minimal rainfall.
Vegetation and Wildlife
India's diverse geography supports a wide range of vegetation types, from tropical evergreen forests in the northeast to thorny scrublands in the arid regions. The country is home to various wildlife habitats, such as national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and biosphere reserves, which protect endemic and migratory fauna.
Water Resources
India's water resources are abundant, with numerous rivers, lakes, and aquifers. Some of the major rivers in India include the Ganga (Ganges), Yamuna, Brahmaputra, Godavari, Krishna, Tungabhadra, and Kaveri. However, the country faces several challenges related to water resource management, including floods, droughts, water pollution, and inequitable distribution.
Human Geography
India's human geography reflects the complex interplay between diverse cultures, languages, religions, and societal structures. The country is home to 24 recognized national languages and over 3,000 dialects. Religion plays a crucial role in shaping the sociocultural landscape, with Hinduism being the dominant religion. Other significant religions include Christianity, Islam, Sikhism, and Buddhism.
Urbanization is rapidly transforming India's landscape, with cities playing a vital role in driving economic growth and social change. Some of the major metropolitan areas in India include New Delhi, Kolkata, Chennai, Mumbai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad, and Surat.
Geopolitics and International Relations
Geography has played a significant role in shaping India's geopolitical position and international relations. Located in South Asia and bordered by the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal, India is strategically positioned in relation to the Persian Gulf and the Indian Ocean, making it a key player in regional and global security dynamics.
Environmental Challenges
Climate change, habitat loss, and resource depletion are some of the pressing environmental challenges facing India. These issues require urgent attention and collaboration between researchers, policymakers, and stakeholders to ensure sustainable solutions and maintain ecological balance.
In conclusion, India's geography is a rich tapestry of natural and cultural elements that contribute to its unique identity and character. Understanding the country's geographical diversity and the interconnections between its physical, social, and economic aspects is essential for appreciating India's complexity and significance on the global stage.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Explore the intricate tapestry of India's geographical features, from the towering Himalayas to the lush backwaters of Kerala. Learn about the country's diverse climate, unique vegetation and wildlife, major rivers, rich human geography, urbanization trends, geopolitical significance, and environmental challenges.