Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which characteristic is specifically referred to as a dop burn?
Which characteristic is specifically referred to as a dop burn?
- A small dot that results from pinpoint inclusions
- A haze caused by excessive heat during polishing
- A surface burn due to excessive heat at the contact point of the dop (correct)
- Burn marks caused by a jeweler’s torch
What is the primary cause of lizard skin on a polished diamond?
What is the primary cause of lizard skin on a polished diamond?
- Excessive heat from the polishing process
- Rubbing against another diamond during cutting
- Polishing too closely to the octahedral plane (correct)
- Inclusion marks that break the surface
Which type of mark might occur during polishing that resembles an extra facet?
Which type of mark might occur during polishing that resembles an extra facet?
- Pit
- Scratch
- Polish mark (correct)
- Polish line
Which term describes the surface irregularity similar to the surface of a sugar cube?
Which term describes the surface irregularity similar to the surface of a sugar cube?
What is the outcome when pinpoint inclusions are removed during the polishing process?
What is the outcome when pinpoint inclusions are removed during the polishing process?
What is an extra facet primarily used for in diamond cutting?
What is an extra facet primarily used for in diamond cutting?
Which characteristic is specifically created during a laser manufacturing process?
Which characteristic is specifically created during a laser manufacturing process?
Which defect is caused by excessive heat during polishing?
Which defect is caused by excessive heat during polishing?
What does a scratch on a diamond primarily appear as?
What does a scratch on a diamond primarily appear as?
What feature shows growth marks and remains from the original diamond surface?
What feature shows growth marks and remains from the original diamond surface?
Which term refers to any break in a diamond?
Which term refers to any break in a diamond?
What appearance does a heavily bearded girdle have?
What appearance does a heavily bearded girdle have?
How is cleavage defined in the context of diamonds?
How is cleavage defined in the context of diamonds?
What type of inclusion consists of tight clusters of pinpoints that can affect a diamond's transparency?
What type of inclusion consists of tight clusters of pinpoints that can affect a diamond's transparency?
What can the appearance of internal graining resemble?
What can the appearance of internal graining resemble?
Which feature is defined as appearing flat and ribbon-like, radiating from the diamond's center?
Which feature is defined as appearing flat and ribbon-like, radiating from the diamond's center?
What aspect does internal graining that appears colorless or transparent not affect?
What aspect does internal graining that appears colorless or transparent not affect?
What is an etch channel?
What is an etch channel?
Which term is used for a small concentrated area of crystal growth distortion within a diamond?
Which term is used for a small concentrated area of crystal growth distortion within a diamond?
What is the term for a break in any crystal direction other than a cleavage plane?
What is the term for a break in any crystal direction other than a cleavage plane?
What is a key difference between inclusions and blemishes in gemstones?
What is a key difference between inclusions and blemishes in gemstones?
Which of the following best describes a blemish in the context of gemstone clarity?
Which of the following best describes a blemish in the context of gemstone clarity?
When examining gemstones, which of the following instruments is emphasized for clarity grading?
When examining gemstones, which of the following instruments is emphasized for clarity grading?
What effect does chromatic aberration have when viewing a gemstone?
What effect does chromatic aberration have when viewing a gemstone?
How can one differentiate between a blemish and an inclusion when examining a stone?
How can one differentiate between a blemish and an inclusion when examining a stone?
What happens to the depth of field as magnification increases?
What happens to the depth of field as magnification increases?
What is the significance of recognizing prism images in diamond clarity evaluations?
What is the significance of recognizing prism images in diamond clarity evaluations?
Which characteristic is NOT associated with internal inclusions in diamonds?
Which characteristic is NOT associated with internal inclusions in diamonds?
What type of mineral crystal is most commonly found in diamonds?
What type of mineral crystal is most commonly found in diamonds?
Which type of illumination helps to make inclusions stand out against the background of a gemstone?
Which type of illumination helps to make inclusions stand out against the background of a gemstone?
Which of the following descriptions accurately represents a bruise on a diamond?
Which of the following descriptions accurately represents a bruise on a diamond?
What distinguishes a knot from other inclusions in a diamond?
What distinguishes a knot from other inclusions in a diamond?
Which statement about a patch of color on a diamond is true?
Which statement about a patch of color on a diamond is true?
Which of the following describes a cavity in a diamond?
Which of the following describes a cavity in a diamond?
What is the key characteristic of an indented natural on a diamond?
What is the key characteristic of an indented natural on a diamond?
How does a laser drill-hole impact a diamond?
How does a laser drill-hole impact a diamond?
Which option best defines a chip on a diamond?
Which option best defines a chip on a diamond?
What distinguishes fracture filling treatment in diamonds?
What distinguishes fracture filling treatment in diamonds?
What is the effect of the flash phenomenon in a treated diamond?
What is the effect of the flash phenomenon in a treated diamond?
Which of the following best identifies a nick on a diamond?
Which of the following best identifies a nick on a diamond?
What does spherical aberration cause?
What does spherical aberration cause?
Flashcards
Clarity Characteristics in Gemstones
Clarity Characteristics in Gemstones
Features within or on a gemstone that affect its clarity, graded by their size, number, and position.
Inclusions
Inclusions
Features inside a gemstone, either completely enclosed or extending into it from the surface.
Blemishes
Blemishes
Features on the surface of a gemstone.
Clarity Grading
Clarity Grading
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gemological Loupe
Gemological Loupe
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chromatic Aberration
Chromatic Aberration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spherical Aberration
Spherical Aberration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Internal crystal inclusion
Internal crystal inclusion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Depth of Field
Depth of Field
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prism Images
Prism Images
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bruise (Br)
Bruise (Br)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Knot (K)
Knot (K)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Patch of Color (Patch)
Patch of Color (Patch)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chip (Ch)
Chip (Ch)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cavity (Cav)
Cavity (Cav)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Indented Natural (IN)
Indented Natural (IN)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Laser Drill-hole (LDH)
Laser Drill-hole (LDH)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Internal Laser Drilling (ILD)
Internal Laser Drilling (ILD)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nick (Nck)
Nick (Nck)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fracture Filling
Fracture Filling
Signup and view all the flashcards
Abrasion (Abr)
Abrasion (Abr)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scratch (Scr)
Scratch (Scr)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Extra Facet (EF)
Extra Facet (EF)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lizard Skin (LS)
Lizard Skin (LS)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Polish Lines (PL)
Polish Lines (PL)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Burn (Brn)
Burn (Brn)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dop Burn
Dop Burn
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rough Girdle (RG)
Rough Girdle (RG)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pit (Pit)
Pit (Pit)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Laser Manufacturing Remnant (LMR)
Laser Manufacturing Remnant (LMR)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Needle (Ndl)
Needle (Ndl)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pinpoint (Pp)
Pinpoint (Pp)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cloud (Cld)
Cloud (Cld)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Twinning Wisp (TW)
Twinning Wisp (TW)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Internal Graining (IG)
Internal Graining (IG)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Grain Center (GC)
Grain Center (GC)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Feather (Ftr)
Feather (Ftr)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cleavage
Cleavage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Etch Channel (EC)
Etch Channel (EC)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bearded Girdle (BG)
Bearded Girdle (BG)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Clarity Grading in Gemstones
- Clarity grading is a crucial aspect of gemstone evaluation.
- Clarity characteristics are sometimes called flaws or imperfections.
- Two types of clarity characteristics exist: inclusions and blemishes.
- Inclusions are features within a gemstone, possibly extending to the surface.
- Blemishes are surface-confined features.
- Gemstone clarity is assessed systematically.
Examining Gemstones
- Initial inspection is through a corrected loupe (10x magnification).
- Types of corrected loupes include triplets (to correct color and linear distortions, chromatic and spherical aberration).
- Gemstone examination should use achromatic or aplanatic lenses.
- Darkfield illumination emphasizes inclusions.
- Brightfield illumination highlights inclusions as noticeable dark objects.
- Depth of field changes with magnification.
- Closeness to a surface reflection indicates proximity to the surface for inclusions.
- Prism images, multiple images of inclusions, can arise from strong diamond refraction.
- Identifying inclusions vs. blemishes can involve positioning the stone to utilize light from a different angle.
Types of Clarity Characteristics
Internal Inclusions
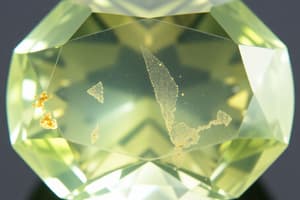
- Minerals (crystals) found within diamonds, with more than 24 identified.
- Common crystals include smaller diamond crystals, olivine, and garnet.
- Needle-like crystals appear as tiny rods.
- Pinpoint inclusions resemble tiny dots.
- Clouds are tightly grouped pinpoints, varying in density from hazy to dense.
- Twinning wisps are pinpoint groupings in twinning planes.
- Internal graining shows crystal growth irregularities, visible in lines or angles, or like transparent threads.
- Grain centers are concentrated crystal growth areas.
Surface Reaching Inclusions
- Feathers are breaks in the diamond (also called glets in some regions).
- Cleavage describes breaks along crystal planes, and fractures are breaks in other directions.
- Etch channels are angular openings extending into the diamond.
- Bruises resemble tiny impacts with radiating feathers.
- Knots are included crystals partially visible on the polished surface.
- Patches are naturally occurring radiation stains.
- Chips are shallow surface openings.
- Cavities are surface openings due to feather or crystal loss during polishing.
- Indented naturals are portions of the original surface, with or without growth markings.
- Laser drill holes are created by laser beams.
- Internal laser drilling expands existing feathers or creates new ones.
Blemishes
- Rough girdles are irregular or granular girdles.
- Pits are tiny white dots (result from polishing).
- Laser manufacturing remnants (LMRs) are surface marks from fabrication processes.
- Naturals are original rough diamond surface residue.
- Surface graining are transparent surface lines, indicating internal irregularities.
- Nicks are small notches.
- Abrasions are surface scratches.
- Scratches are thin lines.
- Extra facets are non-required facets.
- Polish marks are feature-like extra facets.
- Lizard skin is a wavy surface.
- Polishing lines are parallel surface grooves.
- Burns are surface haziness from excessive heat.
- Dop burns are surface damage from excessive dop (a molten glass substance) heat.
Other Features
- Inscriptions on the surface, like logos or text, don't affect clarity unless viewed in 3D.
- Surface grooves can be used to mount the diamond.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.