Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is formed by the cytotrophoblastic cells that penetrate into the syncytium?
What is formed by the cytotrophoblastic cells that penetrate into the syncytium?
- An outer cytotrophoblast shell (correct)
- A vascular network
- The chorionic cavity
- The umbilical cord
Which type of villi are responsible for the direct exchange of nutrients?
Which type of villi are responsible for the direct exchange of nutrients?
- Free (terminal) villi (correct)
- Cytotrophoblastic villi
- Stem villi
- Anchoring villi
What is the significance of the connecting stalk during embryo development?
What is the significance of the connecting stalk during embryo development?
- It connects the embryo to the yolk sac.
- It initiates heartbeat.
- It becomes the umbilical cord. (correct)
- It forms the placenta.
At what stage of development does the heart begin to beat, coinciding with the readiness of the villous system?
At what stage of development does the heart begin to beat, coinciding with the readiness of the villous system?
What connects the placenta to where it forms on the maternal endometrium?
What connects the placenta to where it forms on the maternal endometrium?
What is the primary event that occurs during gastrulation in the embryo?
What is the primary event that occurs during gastrulation in the embryo?
During gastrulation, which structure forms at the cephalic end of the primitive streak?
During gastrulation, which structure forms at the cephalic end of the primitive streak?
What is the term for the inward migration of cells during gastrulation?
What is the term for the inward migration of cells during gastrulation?
Which growth factor is involved in the cell migration and specification during gastrulation?
Which growth factor is involved in the cell migration and specification during gastrulation?
What forms the embryonic endoderm during gastrulation?
What forms the embryonic endoderm during gastrulation?
Which structure determines the cranial end of the embryo during the third week of development?
Which structure determines the cranial end of the embryo during the third week of development?
What happens to the cells remaining in the epiblast after invagination occurs?
What happens to the cells remaining in the epiblast after invagination occurs?
What does the primitive streak eventually give rise to during the process of gastrulation?
What does the primitive streak eventually give rise to during the process of gastrulation?
What is the primary function of the notochord during embryonic development?
What is the primary function of the notochord during embryonic development?
At what stage does the notochordal canal communicate with the yolk sac?
At what stage does the notochordal canal communicate with the yolk sac?
What structure forms at the caudal end of the embryonic disc?
What structure forms at the caudal end of the embryonic disc?
Which cells contribute to the formation of the definitive notochord?
Which cells contribute to the formation of the definitive notochord?
How does the notochord influence the development of the neural tube?
How does the notochord influence the development of the neural tube?
What is the significance of the allantoenteric diverticulum during embryonic development?
What is the significance of the allantoenteric diverticulum during embryonic development?
Which membrane is formed where ectoderm and endoderm are adherent without mesoderm?
Which membrane is formed where ectoderm and endoderm are adherent without mesoderm?
What is the shape of the embryonic disc at the beginning of its development?
What is the shape of the embryonic disc at the beginning of its development?
What is the primary source of new cells during the fourth week of embryonic development?
What is the primary source of new cells during the fourth week of embryonic development?
At what stage does the differentiation of germ layers begin in the caudal part of the embryonic disc?
At what stage does the differentiation of germ layers begin in the caudal part of the embryonic disc?
Which structure do cells that migrate through the cranial region of the node ultimately form?
Which structure do cells that migrate through the cranial region of the node ultimately form?
What characterizes the tertiary villus by the end of the third week?
What characterizes the tertiary villus by the end of the third week?
During which week does the primitive streak show regressive changes and begin to shrink?
During which week does the primitive streak show regressive changes and begin to shrink?
What is the starting structure of the villus at the beginning of the third week?
What is the starting structure of the villus at the beginning of the third week?
What tissue is formed from cells migrating through the lateral edges of the node?
What tissue is formed from cells migrating through the lateral edges of the node?
What additional source provides extraembryonic mesoderm besides the primitive streak?
What additional source provides extraembryonic mesoderm besides the primitive streak?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Gastrulation
- Gastrulation is the process of formation of the three germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm
- Occurs during the third week of gestation
- Begins with the formation of the primitive streak and primitive node
- Primitive streak is a groove on the surface of the epiblast
- Primitive node is the cephalic end of the streak with a primitive pit in its center
- Epiblast cells migrate toward the primitive streak, detach, and slip beneath it, a process called invagination
- Invaginated cells displace the hypoblast forming the endoderm
- Cells remaining in the epiblast form ectoderm
- Cells between the newly formed endoderm and epiblast form the mesoderm
- FGF8 controls cell migration and specification
Notochord
- The notochord is a midline structure that develops from the primitive streak
- It extends from the upper end of the primitive streak to the lower end of the prochordal plate
- Notochordal process forms when cells multiply in the midline between the ectoderm and endoderm
- Notochordal canal forms when the primitive pit extends into the notochordal process
- The notochord forms as a solid cord of cells, the definitive notochord, which underlies the neural tube
- Notochord acts as a forerunner in the development of the vertebral column
- Notochord induces the formation of the neural tube
Embryonic Disc Growth
- The embryonic disc is initially flat and round
- It gradually becomes elongated with a broad cephalic and narrow caudal end
- Expansion occurs mainly by continuous migration of cells from the primitive streak in the cephalic region
- Primitive streak regresses and disappears by the end of the fourth week
- Differentiation of germ layers in the cephalic region begins by the middle of the third week
- Differentiation of germ layers in the caudal region begins by the end of the fourth week
- This causes the embryo to develop cephalocaudally
Fate Map Established During Gastrulation
- Cells that ingress through the cranial region of the primitive node become prechordal plate and notochord
- Cells at the lateral edges of the node and cranial end of the streak become paraxial mesoderm
- Cells that migrate through the midstreak region become intermediate mesoderm
- Cells migrating through the more caudal part of the streak form lateral plate mesoderm
- Cells migrating through the caudal most part of the streak contribute to the extraembryonic mesoderm
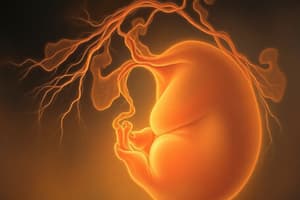
Further Development of the Trophoblast
- The trophoblast is characterized by primary villi that consist of a cytotrophoblastic core covered by a syncytial layer
- Secondary villi form when mesodermal cells penetrate the core of primary villi
- Tertiary villi (definitive placental villi) form when mesodermal cells differentiate into blood cells and blood vessels
- Capillaries in tertiary villi connect with capillaries in the chorionic plate and the connecting stalk
- This establishes a connection between the placenta and the embryo
- Cytotrophoblastic cells in villi penetrate the syncytium and establish contact with neighboring villous stems, forming a thin outer cytotrophoblast shell
- The outer cytotrophoblast shell surrounds the trophoblast, firmly attaching the chorionic sac to the maternal endometrial tissue
- Stem villi extend from the chorionic plate to the decidua basalis
- Free villi branch from the sides of stem villi
- The connecting stalk develops into the umbilical cord
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.