Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main purpose of a clutch in a mechanical system?
What is the main purpose of a clutch in a mechanical system?
- To change the direction of rotation of the gearbox shaft
- To connect two shafts when desired (correct)
- To cool down the system during operation
- To increase the speed of the engine shaft
In a single plate clutch, what is the material of the clutch plate usually made of?
In a single plate clutch, what is the material of the clutch plate usually made of?
- Copper
- Rubber
- Steel (correct)
- Aluminum
What component presses the clutch plate against the flywheel when the clutch is engaged?
What component presses the clutch plate against the flywheel when the clutch is engaged?
- Flywheel
- Spring-loaded pressure plate (correct)
- Thrust bearing
- Release lever
When a single plate clutch is disengaged, what component is pulled back to release the clutch?
When a single plate clutch is disengaged, what component is pulled back to release the clutch?
How are the shafts connected in friction clutches?
How are the shafts connected in friction clutches?
What happens when the foot is taken off the clutch pedal in a mechanical system?
What happens when the foot is taken off the clutch pedal in a mechanical system?
What is the formula for the normal load acting on the ring?
What is the formula for the normal load acting on the ring?
In a conical friction clutch, what does the intensity of normal pressure vary inversely with?
In a conical friction clutch, what does the intensity of normal pressure vary inversely with?
What is the formula for finding axial spring force necessary to engage the clutch?
What is the formula for finding axial spring force necessary to engage the clutch?
What is the coefficient of friction in Example 1?
What is the coefficient of friction in Example 1?
What is the face angle in Example 1?
What is the face angle in Example 1?
What is the width of the bearing surface in Example 2?
What is the width of the bearing surface in Example 2?
What is the maximum mean diameter of the clutch face in Example 1?
What is the maximum mean diameter of the clutch face in Example 1?
What does the torque transmitted formula take into account in a conical friction clutch?
What does the torque transmitted formula take into account in a conical friction clutch?
What keeps the shoes of a centrifugal clutch against the boss on the driving shaft?
What keeps the shoes of a centrifugal clutch against the boss on the driving shaft?
What is the formula for calculating the total force on the contact surface in a single plate clutch?
What is the formula for calculating the total force on the contact surface in a single plate clutch?
When does the shoe remain in the same position as when the driving shaft was stationary?
When does the shoe remain in the same position as when the driving shaft was stationary?
In a cone clutch, what holds the clutch faces in contact and maintains the pressure between them?
In a cone clutch, what holds the clutch faces in contact and maintains the pressure between them?
What is the formula for calculating torque transmitted in a cone clutch?
What is the formula for calculating torque transmitted in a cone clutch?
What happens when the centrifugal force exceeds the spring force in a centrifugal clutch?
What happens when the centrifugal force exceeds the spring force in a centrifugal clutch?
What is used for disengagement of the clutch in a cone clutch system?
What is used for disengagement of the clutch in a cone clutch system?
What is the formula for the frictional torque acting on each shoe in a centrifugal clutch?
What is the formula for the frictional torque acting on each shoe in a centrifugal clutch?
What does the area of contact of a shoe in a centrifugal clutch depend on?
What does the area of contact of a shoe in a centrifugal clutch depend on?
What is the formula for calculating the normal load acting on a ring of the friction surface?
What is the formula for calculating the normal load acting on a ring of the friction surface?
How is the total frictional torque transmitted in a centrifugal clutch calculated?
How is the total frictional torque transmitted in a centrifugal clutch calculated?
What does 'R' represent in the formula for torque transmitted in a cone clutch?
What does 'R' represent in the formula for torque transmitted in a cone clutch?
What is used to determine reasonable life intensity in a centrifugal clutch?
What is used to determine reasonable life intensity in a centrifugal clutch?
In a single plate clutch, what should be known to determine the power transmitted by the clutch?
In a single plate clutch, what should be known to determine the power transmitted by the clutch?
What is 'dl' in relation to a small ring of radius 'r' and thickness 'dr'?
What is 'dl' in relation to a small ring of radius 'r' and thickness 'dr'?
What does $P_c - P_s$ represent in a centrifugal clutch?
What does $P_c - P_s$ represent in a centrifugal clutch?
What is used to calculate the area of contact of a shoe pressing against a rim in a centrifugal clutch?
What is used to calculate the area of contact of a shoe pressing against a rim in a centrifugal clutch?
What does 'µ' represent in the context of cone clutches?
What does 'µ' represent in the context of cone clutches?
What holds the driven member in place on the driven shaft in a cone clutch?
What holds the driven member in place on the driven shaft in a cone clutch?
What does $l \times b \times p$ represent in a centrifugal clutch?
What does $l \times b \times p$ represent in a centrifugal clutch?
What is the value of the frictional force acting tangentially on each shoe?
What is the value of the frictional force acting tangentially on each shoe?
What is the formula to calculate the torque transmitted (T)?
What is the formula to calculate the torque transmitted (T)?
What is the size of the shoes in mm?
What is the size of the shoes in mm?
What is the principle difference between absorption dynamometers and transmission dynamometers?
What is the principle difference between absorption dynamometers and transmission dynamometers?
What is the Prony brake dynamometer primarily used for?
What is the Prony brake dynamometer primarily used for?
In a Prony brake dynamometer, what balances the brake when unloaded?
In a Prony brake dynamometer, what balances the brake when unloaded?
What is required to prevent slipping of the rope over the flywheel in a Rope Brake Dynamometer?
What is required to prevent slipping of the rope over the flywheel in a Rope Brake Dynamometer?
'N-m' represents which unit in engineering?
'N-m' represents which unit in engineering?
What does a torsion dynamometer measure?
What does a torsion dynamometer measure?
In a torsion dynamometer, what does the amount of twist in the shaft depend on?
In a torsion dynamometer, what does the amount of twist in the shaft depend on?
What is the formula for power transmitted by a shaft according to the text?
What is the formula for power transmitted by a shaft according to the text?
What does the torsion equation represent?
What does the torsion equation represent?
Why is the turning moment diagram plotted for a single cylinder double-acting steam engine?
Why is the turning moment diagram plotted for a single cylinder double-acting steam engine?
When is the turning moment zero in a single cylinder double-acting steam engine?
When is the turning moment zero in a single cylinder double-acting steam engine?
What does a negative turning moment signify in an engine according to the text?
What does a negative turning moment signify in an engine according to the text?
'Accelerating torque on the rotating parts of the engine' is calculated as:
'Accelerating torque on the rotating parts of the engine' is calculated as:
'Flywheel accelerates' when:
'Flywheel accelerates' when:
What type of engine has a turning moment diagram shown after two revolutions of the crankshaft?
What type of engine has a turning moment diagram shown after two revolutions of the crankshaft?
What does the coefficient of fluctuation of energy represent?
What does the coefficient of fluctuation of energy represent?
How is the mean torque calculated in terms of the angle turned in one revolution for a four-stroke internal combustion engine?
How is the mean torque calculated in terms of the angle turned in one revolution for a four-stroke internal combustion engine?
What does the maximum fluctuation of energy equal to?
What does the maximum fluctuation of energy equal to?
What represents the maximum energy in the flywheel?
What represents the maximum energy in the flywheel?
What is the cycle repeat point after which energy at G equals energy at A?
What is the cycle repeat point after which energy at G equals energy at A?
Which engine type has an angle turned of $2π$ in one revolution?
Which engine type has an angle turned of $2π$ in one revolution?
What is the formula for net load on the brake in a rope brake system?
What is the formula for net load on the brake in a rope brake system?
In an epicyclic-train dynamometer, what is equal to the tangential effort exerted by the spur gear on the pinion?
In an epicyclic-train dynamometer, what is equal to the tangential effort exerted by the spur gear on the pinion?
What is used to balance the total upward force on the lever in an epicyclic-train dynamometer?
What is used to balance the total upward force on the lever in an epicyclic-train dynamometer?
What is the formula for torque transmitted in an epicyclic-train dynamometer?
What is the formula for torque transmitted in an epicyclic-train dynamometer?
In a belt transmission dynamometer, what causes movement about the pivot E?
In a belt transmission dynamometer, what causes movement about the pivot E?
What is used to balance the movement about pivot E in a belt transmission dynamometer?
What is used to balance the movement about pivot E in a belt transmission dynamometer?
In a belt transmission dynamometer, what are pulleys C and D connected by?
In a belt transmission dynamometer, what are pulleys C and D connected by?
What is used to measure the difference between the tensions of the belt in a belt transmission dynamometer?
What is used to measure the difference between the tensions of the belt in a belt transmission dynamometer?
What causes the clutch plate and the driven shaft to rotate?
What causes the clutch plate and the driven shaft to rotate?
When does clutch slip occur?
When does clutch slip occur?
What is the purpose of using a multi-plate clutch?
What is the purpose of using a multi-plate clutch?
What happens when the actuating force on the pedal is removed in a multi-plate clutch?
What happens when the actuating force on the pedal is removed in a multi-plate clutch?
What is considered when pressure is uniformly distributed over the entire area of a friction face?
What is considered when pressure is uniformly distributed over the entire area of a friction face?
What does 'R' represent in the total frictional torque equation for a multi-plate clutch?
What does 'R' represent in the total frictional torque equation for a multi-plate clutch?
How is 'p' related to 'r' in a case of uniform wear?
How is 'p' related to 'r' in a case of uniform wear?
What happens to a multi-plate clutch when there are more friction rings and metal plates?
What happens to a multi-plate clutch when there are more friction rings and metal plates?
What causes a spring in a multi-plate clutch to press discs into contact with friction rings?
What causes a spring in a multi-plate clutch to press discs into contact with friction rings?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Transmission Dynamometers
- Classification of transmission dynamometers:
- Epicyclic-train dynamometer
- Belt transmission dynamometer (also known as Froude or Throneycroft transmission dynamometer)
- Torsion dynamometer
Epicyclic-train Dynamometer
- Consists of a simple epicyclic train of gears:
- Spur gear
- Annular gear (with internal teeth)
- Pinion (intermediate gear)
- Pinion revolves freely on a lever pivoted to the common axis of the driving and driven shafts
- Weight (w) is placed at the smaller end of the lever to keep it in position
- Tangential effort (P) exerted by the spur gear on the pinion is equal to the tangential reaction of the annular gear on the pinion
- Total upward force on the lever acting through the axis of the pinion is 2P
- Balanced by a dead weight (W) at the end of the lever
Belt Transmission Dynamometer
- Measures the difference between the tensions of the tight and slack sides of the belt
- Consists of a pulley (A) rigidly fixed to the shaft of an engine, and another pulley (B) mounted on another shaft
- Pulleys are connected by a continuous belt passing round two loose pulleys (C and D) mounted on a T-shaped frame
- Frame is pivoted at E and its movement is controlled by two stops (S, S)
- Tension in the tight side of the belt (T1) is greater than the tension in the slack side of the belt (T2)
Friction Clutches
- Types of friction clutches:
- Single plate clutch (also known as disc clutch)
- Cone clutch
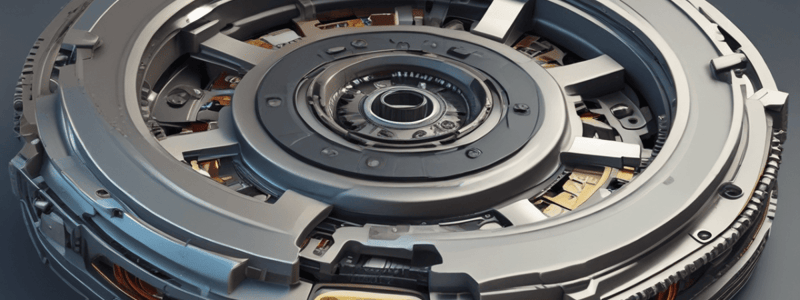
- Single plate clutch:
- Consists of a clutch plate attached to a splined hub which is free to slide axially on splines cut on the driven shaft
- Clutch plate is made of steel and has a ring of friction lining on each side
- Engine shaft supports a rigidly fixed flywheel
- Spring-loaded pressure plate presses the clutch plate firmly against the flywheel when the clutch is engaged
- Cone clutch:
- Consists of one pair of friction surface only
- Driver is keyed to the driving shaft by a sunk key and has an inside conical surface or face which exactly fits into the outside conical surface of the driven
- Driven member resting on the feather key in the driven shaft may be shifted along the shaft by a forked lever provided at B, in order to engage the clutch by bringing the two conical surfaces in contact
Centrifugal Clutch
- Consists of a number of shoes on the inside of a rim of the pulley
- Shoes are covered with a friction material
- Shoes can move radially in guides and are held against the boss (or spider) on the driving shaft by means of springs
- Centrifugal force acting on each shoe at the running speed is proportional to the mass of the shoe and the square of the angular running speed
- Frictional torque acting on each shoe is proportional to the coefficient of friction and the radius of the pulley
Problems and Examples
- Examples of problems and solutions related to brake power, transmission dynamometers, friction clutches, and centrifugal clutches
- Solutions involve calculations of torque, power, and axial load acting on the clutch or brake### Centrifugal Clutch
- A centrifugal clutch is a type of clutch that uses centrifugal force to engage and disengage the clutch.
- The clutch consists of a spider, shoes, and a pressure plate.
- At engagement speed, the shoes move outward and contact the pressure plate, engaging the clutch.
- The frictional force acting tangentially on each shoe is calculated using the formula: F = (Pc - Ps)
- The torque transmitted (T) is calculated using the formula: T = n.F.R
Dynamometers
- A dynamometer is a device that measures the torque and power output of an engine.
- Types of dynamometers: absorption dynamometers and transmission dynamometers.
- Absorption dynamometers absorb the energy produced by the engine and convert it into heat.
- Transmission dynamometers transmit the energy produced by the engine to another machine, where it is measured.
Prony Brake Dynamometer
- A Prony brake dynamometer is a type of absorption dynamometer.
- It consists of two wooden blocks placed around a pulley fixed to the engine shaft.
- The blocks are clamped by means of two bolts and nuts.
- A helical spring is provided between the nut and the upper block to adjust the pressure on the pulley.
- The upper block has a long lever attached to it, which carries a weight at its outer end.
Rope Brake Dynamometer
- A rope brake dynamometer is another type of absorption dynamometer.
- It consists of one or more ropes wound around a flywheel or pulley fixed to the engine shaft.
- The upper end of the ropes is attached to a spring balance, while the lower end is kept in position by applying a dead weight.
- Wooden blocks are placed at intervals around the circumference of the flywheel to prevent the rope from slipping.
Torsion Dynamometer
- A torsion dynamometer is used to measure large powers, particularly in turbine or motor vessels.
- It measures the twist of the shaft, which is proportional to the torque acting on the shaft.
- The power transmitted (P) is calculated using the formula: P = 2πNT/60
Turning Moment and Flywheel
- The turning moment diagram is a graphical representation of the turning moment or crank-effort for various positions of the crank.
- It is plotted on cartesian coordinates, with the turning moment as the ordinate and crank angle as the abscissa.
- The turning moment diagram for a single cylinder double acting steam engine shows that the turning moment is zero when the crank angle is zero, maximum when the crank angle is 90°, and again zero when the crank angle is 180°.
Turning Moment Diagram for a Four Stroke Cycle Internal Combustion Engine
- The turning moment diagram for a four stroke cycle internal combustion engine shows that there is one working stroke after the crank has turned through two revolutions.
- The turning moment diagram for a multi-cylinder engine shows that the fluctuation of energy is reduced with the increase in the number of cylinders.
Coefficient of Fluctuation of Energy
- The coefficient of fluctuation of energy is defined as the ratio of the maximum fluctuation of energy to the work done per cycle.
- It is calculated using the formula: coefficient of fluctuation of energy = maximum fluctuation of energy / work done per cycle
Plate and Disc Clutch
- A plate and disc clutch is a type of clutch that uses frictional forces to transmit torque.
- The torque transmitted (T) is calculated using the formula: T = µ.W.R
- The mean radius of the friction surfaces (R) is calculated using the formula: R = (r1 + r2)/2
- In a multi-plate clutch, the number of frictional linings and metal plates is increased, which increases the capacity of the clutch to transmit torque.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.