Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of glomerular filtration?
What is the primary function of glomerular filtration?
- Collecting urine in the bladder
- Moving dissolved solutes from blood plasma into nephron (correct)
- Reabsorbing water and ions from filtrate
- Secreting additional wastes into blood
Which substance does not pass into Bowman’s capsule during glomerular filtration?
Which substance does not pass into Bowman’s capsule during glomerular filtration?
- Urea
- Water
- Plasma proteins (correct)
- Dissolved solutes
What percentage of filtrate is typically reabsorbed in the proximal tubule?
What percentage of filtrate is typically reabsorbed in the proximal tubule?
- 50%
- 80%
- 65% (correct)
- 25%
How does water primarily move from the filtrate into the blood in the descending limb of the Loop of Henle?
How does water primarily move from the filtrate into the blood in the descending limb of the Loop of Henle?
Which ions are actively secreted into the distal tubule to help maintain blood pH?
Which ions are actively secreted into the distal tubule to help maintain blood pH?
What characteristic of the ascending limb of the Loop of Henle affects water permeability?
What characteristic of the ascending limb of the Loop of Henle affects water permeability?
What happens to the permeability of the distal tubule and collecting duct when dehydrated?
What happens to the permeability of the distal tubule and collecting duct when dehydrated?
What role do carrier molecules in the thick-walled portion of the ascending limb play?
What role do carrier molecules in the thick-walled portion of the ascending limb play?
Flashcards
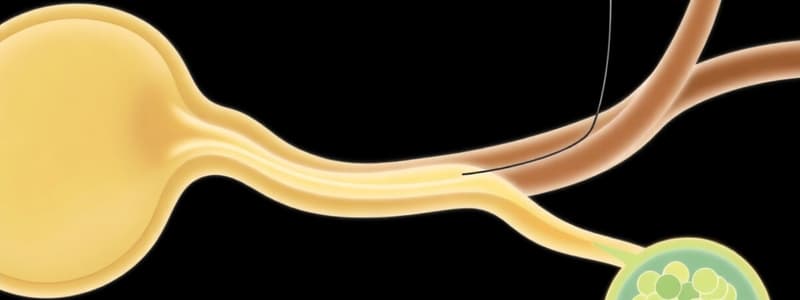
Glomerular Filtration
Glomerular Filtration
The process where water and small solutes move from blood plasma into the nephron.
Filtration
Filtration
The liquid part of blood that passes through the filter into the nephron.
Tubular Reabsorption
Tubular Reabsorption
The process of reclaiming useful substances from the filtrate and returning them to the blood.
Loop of Henle Function
Loop of Henle Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tubular Secretion
Tubular Secretion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Collecting Duct
Collecting Duct
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proximal Tubule
Proximal Tubule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Active Transport
Active Transport
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Formation of Urine
- Urine formation involves three processes: glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption, and tubular secretion.
Glomerular Filtration
- Blood enters the glomerulus, acting as a high-pressure filter.
- Dissolved solutes pass through the glomerulus walls into Bowman's capsule, creating a filtrate similar to blood plasma.
- Plasma proteins, platelets, and red blood cells don't pass through the membrane, as they are too large.
Tubular Reabsorption
- Approximately 65% of the filtrate passes through the proximal tubule (including the loop of Henle).
- This process returns useful substances to the blood.
- Involves both active and passive transport mechanisms.
- Loop of Henle's function is to reabsorb water and ions from the glomerular filtrate.
- Water diffuses from filtrate into capillaries by osmosis.
- Cells of the descending limb are permeable to water.
- Near the bottom of the loop, the permeability to water and ions changes, now impermeable to water and slightly permeable to ions.
- Na+ ions diffuse from the filtrate into surrounding blood vessels.
- At the thick-walled portion of the ascending limb, carrier molecules actively transport Na+ ions, followed by Cl⁻ and bicarbonate ions passively.
- This replenishes the salty environment in the medulla, aiding in water absorption from the filtrate in the descending limb.
- Nutrients (e.g., glucose, amino acids, Na+, K+) are actively reabsorbed.
- Negatively charged ions (e.g., Cl⁻) are passively reabsorbed due to electrical attraction.
- Water is reabsorbed by osmosis.
Tubular Secretion
- Potassium (K⁺) and hydrogen (H⁺) ions are actively secreted from capillaries into the distal tubule to maintain blood pH.
- Drugs and substances not normally part of the body are secreted into the distal tubule.
- Filtrate is collected in the collecting duct, still containing a large amount of water.
- Passive reabsorption of water from filtrate through osmosis occurs
- If dehydrated, the permeability to water in the distal and collecting ducts increases, causing more water to be reabsorbed.
- The filtrate, now 4x more concentrated is called urine, representing only 1% of the original filtrate volume.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.