Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the term used to describe the phenomenon of differences in general shape and size between human skulls?
What is the term used to describe the phenomenon of differences in general shape and size between human skulls?
Sexual dimorphism
What is the characteristic of the skull features typically associated with females?
What is the characteristic of the skull features typically associated with females?
Gracile (delicate, small)
What is the purpose of analyzing the skull in forensic anthropology?
What is the purpose of analyzing the skull in forensic anthropology?
To determine the sex and age of an individual
What is the term used to describe the robust features of the skull?
What is the term used to describe the robust features of the skull?
What is the significance of Table 8.4 in the context of sex determination from skull analysis?
What is the significance of Table 8.4 in the context of sex determination from skull analysis?
What is the primary function of fontanelles in the infant skull, and how do they facilitate birth?
What is the primary function of fontanelles in the infant skull, and how do they facilitate birth?
What is the significance of the 'cone-shaped' head in newborns?
What is the significance of the 'cone-shaped' head in newborns?
How do the maxillary and frontal sinuses change with age?
How do the maxillary and frontal sinuses change with age?
What happens to the cranial sutures as a person ages?
What happens to the cranial sutures as a person ages?
What is dental attrition, and how does it affect the skull?
What is dental attrition, and how does it affect the skull?
What is the purpose of the posterior and anterior fontanelles, and when do they typically close?
What is the purpose of the posterior and anterior fontanelles, and when do they typically close?
How do the fontanelles facilitate brain growth after birth?
How do the fontanelles facilitate brain growth after birth?
What is the significance of the mastoid and sphenoidal fontanelles, and when do they close?
What is the significance of the mastoid and sphenoidal fontanelles, and when do they close?
What is the main challenge in determining the sex of a skull based on skeletal remains?
What is the main challenge in determining the sex of a skull based on skeletal remains?
Why is it difficult to determine the sex of infant and juvenile remains?
Why is it difficult to determine the sex of infant and juvenile remains?
What is the most accurate method of determining sex based on skeletal remains?
What is the most accurate method of determining sex based on skeletal remains?
What factors contribute to the change in skull features from childhood to adulthood in males?
What factors contribute to the change in skull features from childhood to adulthood in males?
What is the significance of cranial sutures in the development of the skull?
What is the significance of cranial sutures in the development of the skull?
How does the rate of skull growth compare to the rest of the body in early life?
How does the rate of skull growth compare to the rest of the body in early life?
What percentage of brain growth is complete by age 5?
What percentage of brain growth is complete by age 5?
What is the significance of fontanelles in the development of the skull?
What is the significance of fontanelles in the development of the skull?
How do the proportions and size of cranial elements differ between infants and adults?
How do the proportions and size of cranial elements differ between infants and adults?
What are some of the key sexually dimorphic features of the skull?
What are some of the key sexually dimorphic features of the skull?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
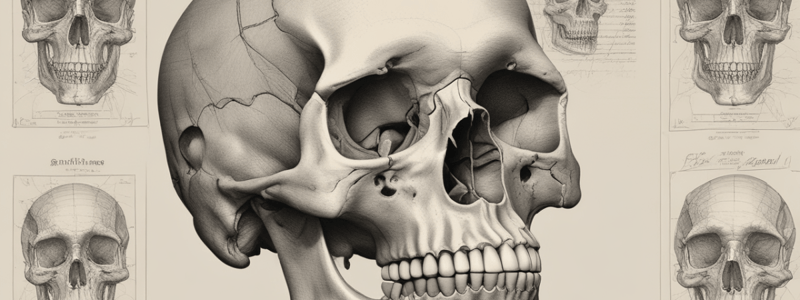
Sex and Age Determination from Analysis of the Skull
Sexually Dimorphic Features of the Skull
- Human skulls display differences in shape and size, known as sexual dimorphism, with "female" features tending to be gracile and "male" features tend to be more robust.
- Sexually dimorphic features of the skull include:
- General size and appearance: females tend to be smaller and more delicate, while males tend to be larger and more robust.
- Nuchal lines and external occipital protuberance: females have a smooth occipital bone with no prominent bony projections, while males have well-demarcated nuchal lines and a prominent bump.
- Mastoid process: females have a relatively small mastoid process, while males have a larger one.
- Squamous part of frontal bone: females tend to have a more vertically oriented and rounded frontal bone, while males have a sloping angle.
- Supraorbital margin: females have a thin, sharp border, while males have a thick, rounded, blunt border.
- Superciliary arches: females have little or no prominence, while males have more prominent and bulky arches.
- Mandible (general features): females tend to have smaller and lighter mandibles, while males have larger and heavier ones.
- Mental protuberance: females have a more pointed and triangular-shaped protuberance with less forward projection, while males have a squarish protuberance with more forward projection.
- Mandibular angle: females tend to have a greater angle (usually more than 125 degrees), while males have a smaller angle (usually less than 125 degrees).
Challenges in Determining Sex
- Determining sex from the skull can be challenging due to variation in size and robusticity among populations.
- Sexually dimorphic characteristics vary along a continuum, making it difficult to determine sex in some cases.
- Infant and juvenile remains are particularly difficult to sex because their skull characteristics appear female-like until well after puberty.
Aging of the Skull
- The shape and structure of cranial elements differ between infants and adults, causing variations in proportions and size.
- The most significant growth in the skull occurs before age 5, when the brain is still growing and exerting pressure against the developing skull bones.
- Brain growth is 90-95% complete by age 5, at which time cranial bone growth is close to completion.
- Early in life, the skull grows at a much faster rate than the rest of the body, making a young child's cranium relatively larger compared to the rest of their body.
- Fontanelles are flexible areas of dense regular connective tissue that connect cranial bones in infants, allowing for flexion during birth.
- The posterior fontanelle normally closes around 9 months of age, while the larger anterior fontanelle doesn't close until about 15 months of age.
- As we age, the maxillary sinus becomes more prominent after age 5, and the frontal sinus is becoming well formed by age 10.
- Cranial sutures start to fuse and ossify with age.
- Dental attrition occurs as teeth wear down from use, and alveolar processes of the maxillae and mandible regress and eventually disappear if an individual loses teeth.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.