Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the fetal component of the placenta derived from?
What is the fetal component of the placenta derived from?
- Trophoblast and extraembryonic mesoderm (correct)
- Uterine endometrium and chorionic plate
- Decidua basalis and junctional zone
- Amnion and blood vessels
Which measurement is NOT typically determined using ultrasound in gestational assessments?
Which measurement is NOT typically determined using ultrasound in gestational assessments?
- Chorionic plate thickness (correct)
- Crown-rump length (CRL)
- Head circumference
- Biparietal diameter (BPD)
Which structure is formed from the maternal contribution to the placenta?
Which structure is formed from the maternal contribution to the placenta?
- Chorionic plate
- Umbilical cord
- Decidua basalis (correct)
- Chorion frondosum
What is the average weight range of a newborn considered healthy?
What is the average weight range of a newborn considered healthy?
Which of the following structures connects the fetus to the placenta?
Which of the following structures connects the fetus to the placenta?
At the beginning of the third month, what proportion of the crown-rump length (CRL) does the head constitute?
At the beginning of the third month, what proportion of the crown-rump length (CRL) does the head constitute?
What happens to the size of the head by the fifth month of fetal development?
What happens to the size of the head by the fifth month of fetal development?
Which measurement is correlated with the age of the fetus in weeks?
Which measurement is correlated with the age of the fetus in weeks?
What characterizes the fetal period from the 9th week to birth?
What characterizes the fetal period from the 9th week to birth?
What is the maximum crown-rump length (CRL) for a full-term baby around 37-38 weeks?
What is the maximum crown-rump length (CRL) for a full-term baby around 37-38 weeks?
During what stage of development does the majority of bodily growth accelerates while head growth slows down?
During what stage of development does the majority of bodily growth accelerates while head growth slows down?
Which length measurement refers specifically to the sitting height from the vertex of the skull to the heel?
Which length measurement refers specifically to the sitting height from the vertex of the skull to the heel?
What structural component of pregnancy is responsible for nutrient and gas exchange between the mother and fetus?
What structural component of pregnancy is responsible for nutrient and gas exchange between the mother and fetus?
What is the significance of the swelling at the base of the umbilical cord in an 11-week fetus?
What is the significance of the swelling at the base of the umbilical cord in an 11-week fetus?
At what stage does the amnion and chorion fuse, resulting in the obliteration of the uterine cavity?
At what stage does the amnion and chorion fuse, resulting in the obliteration of the uterine cavity?
How are infants identified as having Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR)?
How are infants identified as having Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR)?
What overall age of gestation is taken into account for measuring fetal development?
What overall age of gestation is taken into account for measuring fetal development?
What developmental feature is observed in the skull of an 11-week fetus?
What developmental feature is observed in the skull of an 11-week fetus?
What characteristic is notable about the face of a 12-week fetus?
What characteristic is notable about the face of a 12-week fetus?
What happens to the chorionic villi at the abembryonic pole by the end of the second month?
What happens to the chorionic villi at the abembryonic pole by the end of the second month?
When do fetal movements typically begin during gestation?
When do fetal movements typically begin during gestation?
At what stage of pregnancy can the testicles of a male fetus be seen within the scrotum via ultrasound?
At what stage of pregnancy can the testicles of a male fetus be seen within the scrotum via ultrasound?
What is the characteristic that allows determination of the fetus's sex by external examination during the third month?
What is the characteristic that allows determination of the fetus's sex by external examination during the third month?
What fetal development milestone occurs between the fourth and fifth month?
What fetal development milestone occurs between the fourth and fifth month?
Which feature becomes pronounced by the end of the third month of fetal development?
Which feature becomes pronounced by the end of the third month of fetal development?
What physical characteristic is notable about the skin of the fetus during the third month?
What physical characteristic is notable about the skin of the fetus during the third month?
What factor can be used by a doctor to determine the month of pregnancy during a prenatal check-up?
What factor can be used by a doctor to determine the month of pregnancy during a prenatal check-up?
What embryonic characteristic is evident as the fetus develops between the third and fourth months?
What embryonic characteristic is evident as the fetus develops between the third and fourth months?
What happens to the intestines by the sixth week of fetal development?
What happens to the intestines by the sixth week of fetal development?
What is the average length of pregnancy in days considered from the last normal menstrual period?
What is the average length of pregnancy in days considered from the last normal menstrual period?
During which months does growth in length particularly accelerate for a fetus?
During which months does growth in length particularly accelerate for a fetus?
What is the specific structure of the chorion that has many villi known as?
What is the specific structure of the chorion that has many villi known as?
What is the primary change in weight during the stages of gestation?
What is the primary change in weight during the stages of gestation?
How long is age typically calculated from fertilization in days?
How long is age typically calculated from fertilization in days?
What does the yolk sac and long vitelline duct indicate in a fetus?
What does the yolk sac and long vitelline duct indicate in a fetus?
What is the maximum crown-heel length (CHL) noted in the content for a fetus?
What is the maximum crown-heel length (CHL) noted in the content for a fetus?
In terms of fetal development, what is a notable feature of the chorionic cavity during the gestational period?
In terms of fetal development, what is a notable feature of the chorionic cavity during the gestational period?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Fetal Development Overview
- Begins at 9 weeks and continues to birth, characterized by rapid growth and maturation of tissues and organs.
- Fetal size is measured as Crown-Rump Length (CRL) and Crown-Heel Length (CHL).
- CRL can reach approximately 36 cm by weeks 37-38.
- CHL can reach up to 51 cm in full-term babies.
- Growth speed fluctuates: significant length increase in the 3rd to 5th months, weight gain peaks in the last two months.
Armamentarium for Assessing Fetal Age
- Age is typically calculated based on the last normal menstrual period (LNMP) or fertilization date.
- Average pregnancy length is 280 days (40 weeks) from LNMP or 266 days (38 weeks) post-fertilization.
- Ultrasound imaging is central to determining gestational age using CRL, biparietal diameter (BPD), and other size metrics.
Physical Development Milestones
- By the end of the 3rd month, primary ossification centers emerge, and external genitalia can be identified through ultrasound.
- Body proportions shift: head is large compared to body at 9 weeks; by the 5th month, head is about one-third of body size.
- Skin remains thin and transparent, making underlying blood vessels visible.
- Fetal movement begins around the 4th month and may be felt by the mother.
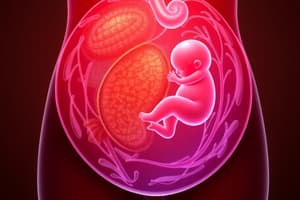
Placenta Overview
- The placenta consists of fetal (derived from trophoblast and mesoderm) and maternal components (derived from uterine endometrium).
- The fetal side has blood vessels covered with the chorionic plate, while the maternal side includes the decidua basalis and decidual plate.
- Functions to provide nutrients, gas exchange, and waste elimination between mother and fetus.
Umbilical Cord and Amniotic Fluid
- Connects the fetus to the placenta, essential for nutrient transport and waste removal.
- Amniotic fluid serves as a protective cushion for the developing fetus and aids in growth and movement.
Parturition (Birth)
- Birth occurs in three stages, with successful delivery of a healthy infant being the goal.
- Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR) refers to infants who do not achieve normal growth; these infants may be at risk for health complications.
- Low Birth Weight (LBW) classification is essential for identifying babies at risk for adverse outcomes.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.