Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which organ is not fully functional in a fetus?
Which organ is not fully functional in a fetus?
- Placenta
- Liver (correct)
- Heart
- Lungs
What is the main function of the placenta in a fetus?
What is the main function of the placenta in a fetus?
- To provide oxygen and nutrients (correct)
- To filter waste products
- To produce red blood cells
- To pump blood
Which blood vessel carries oxygenated blood from the placenta to the liver in a fetus?
Which blood vessel carries oxygenated blood from the placenta to the liver in a fetus?
- Umbilical vein (correct)
- Ductus venosus
- Superior vena cava
- Inferior vena cava
What is the pathway of most of the blood entering the right atrium (RA) in a fetus?
What is the pathway of most of the blood entering the right atrium (RA) in a fetus?
What type of blood mainly enters the right atrium (RA) from the superior vena cava (SVC) in a fetus?
What type of blood mainly enters the right atrium (RA) from the superior vena cava (SVC) in a fetus?
Where does most of the well-oxygenated blood from the placenta enter in a fetus after reaching the right atrium?
Where does most of the well-oxygenated blood from the placenta enter in a fetus after reaching the right atrium?
What is the purpose of the ductus venosus in a fetus?
What is the purpose of the ductus venosus in a fetus?
Which blood vessel carries deoxygenated blood from the head region of the fetus to the right atrium (RA)?
Which blood vessel carries deoxygenated blood from the head region of the fetus to the right atrium (RA)?
What does the foramen ovale connect in a fetus?
What does the foramen ovale connect in a fetus?
Which vessel does blood mainly flow through after leaving the pulmonary artery?
Which vessel does blood mainly flow through after leaving the pulmonary artery?
What happens to systemic vascular resistance (SVR) at birth?
What happens to systemic vascular resistance (SVR) at birth?
What happens to pulmonary vascular resistance at birth?
What happens to pulmonary vascular resistance at birth?
What is the result of the expansion of the lungs at birth?
What is the result of the expansion of the lungs at birth?
What happens to the resistance to blood flow in the lungs when they expand?
What happens to the resistance to blood flow in the lungs when they expand?
What happens to the right atrial pressure at birth?
What happens to the right atrial pressure at birth?
What happens to the left atrial pressure at birth?
What happens to the left atrial pressure at birth?
What happens if the closure of the valve between the left and right atria does not occur?
What happens if the closure of the valve between the left and right atria does not occur?
What causes the closure of the ductus arteriosus?
What causes the closure of the ductus arteriosus?
Which structure prevents blood from flowing backwards from the left atrium into the right atrium in a fetus?
Which structure prevents blood from flowing backwards from the left atrium into the right atrium in a fetus?
What is the term used to describe the permanent closure of the foramen ovale?
What is the term used to describe the permanent closure of the foramen ovale?
What causes the closure of the ductus arteriosus?
What causes the closure of the ductus arteriosus?
What is the term used to describe the failure of the ductus arteriosus to close?
What is the term used to describe the failure of the ductus arteriosus to close?
What is the main function of the placenta in a fetus?
What is the main function of the placenta in a fetus?
What happens to the systemic vascular resistance (SVR) at birth?
What happens to the systemic vascular resistance (SVR) at birth?
What happens to the resistance to blood flow in the lungs when they expand?
What happens to the resistance to blood flow in the lungs when they expand?
What happens to the right atrial pressure at birth?
What happens to the right atrial pressure at birth?
What happens to the left atrial pressure at birth?
What happens to the left atrial pressure at birth?
Which type of congenital malformation is the most common at birth?
Which type of congenital malformation is the most common at birth?
What happens to ventricular septal defects (VSDs) over time, during childhood in most cases?
What happens to ventricular septal defects (VSDs) over time, during childhood in most cases?
What is the consequence of a large ventricular septal defect (VSD)?
What is the consequence of a large ventricular septal defect (VSD)?
What is the consequence of a persistent ostia/defect in atrial septal defects (ASDs)?
What is the consequence of a persistent ostia/defect in atrial septal defects (ASDs)?
What is the main consequence of a left-to-right shunt in atrial septal defects (ASDs)?
What is the main consequence of a left-to-right shunt in atrial septal defects (ASDs)?
When do most cases of atrial septal defects (ASDs) become significant?
When do most cases of atrial septal defects (ASDs) become significant?
What is the main purpose of surgical correction for atrial septal defects (ASDs)?
What is the main purpose of surgical correction for atrial septal defects (ASDs)?
Which of the following is true about congenital heart disease?
Which of the following is true about congenital heart disease?
What is the main function of the ductus venosus in a fetus?
What is the main function of the ductus venosus in a fetus?
What happens to the left atrial pressure at birth?
What happens to the left atrial pressure at birth?
Where does most of the well-oxygenated blood from the placenta enter in a fetus after reaching the right atrium?
Where does most of the well-oxygenated blood from the placenta enter in a fetus after reaching the right atrium?
What type of blood mainly enters the right atrium (RA) from the superior vena cava (SVC) in a fetus?
What type of blood mainly enters the right atrium (RA) from the superior vena cava (SVC) in a fetus?
Which vessel carries most of the portal blood in a fetus?
Which vessel carries most of the portal blood in a fetus?
When does most congenital heart disease arise?
When does most congenital heart disease arise?
What causes bluish skin (cyanosis) in a patient with a right-to-left shunt?
What causes bluish skin (cyanosis) in a patient with a right-to-left shunt?
What initially happens in a left-to-right shunt in congenital heart disease?
What initially happens in a left-to-right shunt in congenital heart disease?
What is the consequence of increased pulmonary blood flow in congenital heart disease?
What is the consequence of increased pulmonary blood flow in congenital heart disease?
What causes late onset cyanosis in congenital heart disease?
What causes late onset cyanosis in congenital heart disease?
What is the most common type of congenital malformation?
What is the most common type of congenital malformation?
What happens to ventricular septal defects (VSDs) over time, during childhood in most cases?
What happens to ventricular septal defects (VSDs) over time, during childhood in most cases?
Which structure is responsible for shunting blood from the pulmonary artery to the aorta in fetal life?
Which structure is responsible for shunting blood from the pulmonary artery to the aorta in fetal life?
What happens to the ductus arteriosus after birth?
What happens to the ductus arteriosus after birth?
What happens if the ductus arteriosus remains patent after birth?
What happens if the ductus arteriosus remains patent after birth?
What is the consequence of a patent ductus arteriosus after birth?
What is the consequence of a patent ductus arteriosus after birth?
Which condition is characterized by a right-to-left shunt that recirculates venous blood back into the systemic circulation?
Which condition is characterized by a right-to-left shunt that recirculates venous blood back into the systemic circulation?
What is the most common cause of a right-to-left shunt in congenital heart disease?
What is the most common cause of a right-to-left shunt in congenital heart disease?
What happens in tetralogy of Fallot if the obstruction is mild?
What happens in tetralogy of Fallot if the obstruction is mild?
What is the term used to describe the discordant connection of the ventricles to their vascular outflow?
What is the term used to describe the discordant connection of the ventricles to their vascular outflow?
What happens if there is complete transposition of the great arteries?
What happens if there is complete transposition of the great arteries?
What is the purpose of a shunt in the context of transposition of great arteries?
What is the purpose of a shunt in the context of transposition of great arteries?
What is the prognosis of a patient with a shunt-related congenital heart disease?
What is the prognosis of a patient with a shunt-related congenital heart disease?
What is the narrowing or constriction of the aorta?
What is the narrowing or constriction of the aorta?
What are the two forms of coarctation of the aorta?
What are the two forms of coarctation of the aorta?
What are the consequences of coarctation of the aorta without a PDA?
What are the consequences of coarctation of the aorta without a PDA?
What is the recommended treatment for coarctation of the aorta?
What is the recommended treatment for coarctation of the aorta?
What is the consequence of a large ventricular septal defect (VSD)?
What is the consequence of a large ventricular septal defect (VSD)?
What is the frequency rank of coarctation of the aorta among common anomalies?
What is the frequency rank of coarctation of the aorta among common anomalies?
What are the symptoms of a patient with transposition of great arteries?
What are the symptoms of a patient with transposition of great arteries?
What determines the severity of coarctation of the aorta?
What determines the severity of coarctation of the aorta?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
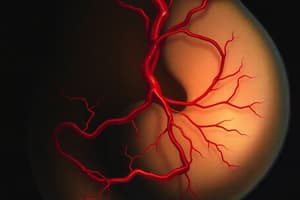
Fetal Circulation
- The liver is not fully functional in a fetus.
- The placenta is responsible for oxygenation and nutrient supply to the fetus.
- The umbilical vein carries oxygenated blood from the placenta to the liver in a fetus.
Fetal Blood Flow
- Most of the blood entering the right atrium (RA) comes from the inferior vena cava (IVC).
- The ductus venosus carries oxygenated blood from the placenta to the liver.
- The foramen ovale connects the right and left atria.
- The ductus arteriosus connects the pulmonary artery to the aorta.
Transition from Fetal to Neonatal Circulation
- At birth, systemic vascular resistance (SVR) increases.
- At birth, pulmonary vascular resistance decreases.
- Expansion of the lungs at birth leads to increased oxygenation and decreased pulmonary resistance.
- Right atrial pressure decreases at birth.
- Left atrial pressure increases at birth.
Congenital Heart Disease
- The most common type of congenital malformation is ventricular septal defects (VSDs).
- VSDs often close spontaneously over time during childhood.
- Large VSDs can lead to pulmonary hypertension and right heart failure.
- Atrial septal defects (ASDs) can cause left-to-right shunts, leading to increased pulmonary blood flow.
- ASDs can become significant if the defect persists over time.
- The main purpose of surgical correction for ASDs is to prevent complications.
Ductus Arteriosus
- The ductus arteriosus shunts blood from the pulmonary artery to the aorta in fetal life.
- After birth, the ductus arteriosus normally closes.
- If the ductus arteriosus remains patent after birth, it can lead to complications.
Other Congenital Heart Defects
- Tetralogy of Fallot is characterized by a right-to-left shunt that recirculates venous blood back into the systemic circulation.
- Transposition of the great arteries is a condition where the ventricles are connected to the wrong great arteries.
- Coarctation of the aorta is the narrowing or constriction of the aorta.
- Coarctation of the aorta can lead to hypertension and heart failure if left untreated.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.