Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the acrosome in spermatozoa during fertilization?
What is the primary function of the acrosome in spermatozoa during fertilization?
- To provide energy for motility
- To store genetic material
- To facilitate the fusion with the oocyte (correct)
- To assist in the capacitation process
Which part of the spermatozoon is primarily responsible for motility?
Which part of the spermatozoon is primarily responsible for motility?
- Tail (flagellum) (correct)
- Head
- Middle piece
- Neck
What is the significance of the mitochondrial sheath in the spermatozoon?
What is the significance of the mitochondrial sheath in the spermatozoon?
- It protects the genetic material
- It enables the sperm to enter the oocyte
- It assists in fertilization by regulating temperature
- It provides energy necessary for sperm motility (correct)
Where does fertilization predominantly take place in the female reproductive system?
Where does fertilization predominantly take place in the female reproductive system?
What is the main reason that mitochondria are inherited only from the mother?
What is the main reason that mitochondria are inherited only from the mother?
What occurs during the capacitation phase of spermatozoa?
What occurs during the capacitation phase of spermatozoa?
Which of the following statements best describes the structure of spermatozoa?
Which of the following statements best describes the structure of spermatozoa?
What is the primary outcome if the neural tube does not fuse properly during the period of organogenesis?
What is the primary outcome if the neural tube does not fuse properly during the period of organogenesis?
Which of the following describes the development of the chorion during the early weeks of pregnancy?
Which of the following describes the development of the chorion during the early weeks of pregnancy?
What developmental stage is critical for the formation of major organs and organ systems?
What developmental stage is critical for the formation of major organs and organ systems?
Which of the following best describes the change in the villous structure from primary to tertiary villi?
Which of the following best describes the change in the villous structure from primary to tertiary villi?
What is the role of neuroectodermal cells during the fusion of neural folds?
What is the role of neuroectodermal cells during the fusion of neural folds?
What is the primary layer of the uterine endometrium called after the implantation of the blastocyst?
What is the primary layer of the uterine endometrium called after the implantation of the blastocyst?
At what approximate age does the blastocyst undergo implantation?
At what approximate age does the blastocyst undergo implantation?
Which structure provides nourishment to the blastocyst while it is floating freely in the uterus?
Which structure provides nourishment to the blastocyst while it is floating freely in the uterus?
What is the sequence of the embryonic stages in the first week following fertilization, starting with the oocyte?
What is the sequence of the embryonic stages in the first week following fertilization, starting with the oocyte?
Which layer of the trophoblast is responsible for the rapid expansion and the formation of finger-like processes?
Which layer of the trophoblast is responsible for the rapid expansion and the formation of finger-like processes?
What happens when the implantation of the blastocyst extends deeper into the uterine tissue?
What happens when the implantation of the blastocyst extends deeper into the uterine tissue?
What is the function of the syncytiotrophoblast after implantation?
What is the function of the syncytiotrophoblast after implantation?
What marks the transition from a primary follicle to a preovulatory follicle?
What marks the transition from a primary follicle to a preovulatory follicle?
What is the maximum number of blastomeres in a morula stage, approximately 3 days after fertilization?
What is the maximum number of blastomeres in a morula stage, approximately 3 days after fertilization?
What characterizes placenta previa during delivery?
What characterizes placenta previa during delivery?
What is the primary function of the syncytiotrophoblast during the second week of development?
What is the primary function of the syncytiotrophoblast during the second week of development?
Which layers differentiate from the inner cell mass of the blastocyst?
Which layers differentiate from the inner cell mass of the blastocyst?
What initiates the maternal blood supply to the lacunae in the syncytiotrophoblast?
What initiates the maternal blood supply to the lacunae in the syncytiotrophoblast?
What structure fills the space between the trophoblast and the amnion during the second week of development?
What structure fills the space between the trophoblast and the amnion during the second week of development?
What is primarily formed by the cytotrophoblast during the second week?
What is primarily formed by the cytotrophoblast during the second week?
What process occurs to create a primitive uteroplacental circulation during the second week of development?
What process occurs to create a primitive uteroplacental circulation during the second week of development?
What is the function of amnioblasts that arise from the epiblast?
What is the function of amnioblasts that arise from the epiblast?
What is a consequence of the embryo being completely embedded by the end of the second week?
What is a consequence of the embryo being completely embedded by the end of the second week?
How do epiblast and hypoblast contribute to the structure of the blastocyst?
How do epiblast and hypoblast contribute to the structure of the blastocyst?
Which structure is formed from the cranial part of the embryo during head fold development?
Which structure is formed from the cranial part of the embryo during head fold development?
What does the term 'vitellointestinal duct' refer to in the context of lateral folding?
What does the term 'vitellointestinal duct' refer to in the context of lateral folding?
During the head fold process, which structure is positioned ventrally to the embryo after folding?
During the head fold process, which structure is positioned ventrally to the embryo after folding?
What structure is formed from the terminal part of the hind gut during development?
What structure is formed from the terminal part of the hind gut during development?
What is the primary result of cephalocaudal folding on the embryo?
What is the primary result of cephalocaudal folding on the embryo?
Which of the following structures is located at the caudal part of the embryo before folding?
Which of the following structures is located at the caudal part of the embryo before folding?
What happens to the allantois during the tail fold process?
What happens to the allantois during the tail fold process?
Which embryonic structure develops from the area around the buccopharyngeal membrane?
Which embryonic structure develops from the area around the buccopharyngeal membrane?
What triggers the lateral folding of the embryo?
What triggers the lateral folding of the embryo?
Which embryonic cavity increases in size at the expense of the extraembryonic coelom during lateral folding?
Which embryonic cavity increases in size at the expense of the extraembryonic coelom during lateral folding?
Which decidua serves as the maternal origin of the placenta?
Which decidua serves as the maternal origin of the placenta?
What is the role of the syncytiotrophoblast during early pregnancy?
What is the role of the syncytiotrophoblast during early pregnancy?
Where is an ectopic pregnancy most commonly located?
Where is an ectopic pregnancy most commonly located?
What ultimately happens to the decidua capsularis, parietalis, and marginalis during pregnancy?
What ultimately happens to the decidua capsularis, parietalis, and marginalis during pregnancy?
What is a potential result of abnormal implantation in the uterus?
What is a potential result of abnormal implantation in the uterus?
What primarily characterizes the syncytiotrophoblast during the second week of development?
What primarily characterizes the syncytiotrophoblast during the second week of development?
What is the primary significance of the primitive uteroplacental circulation established by the end of the second week?
What is the primary significance of the primitive uteroplacental circulation established by the end of the second week?
Which cells contribute to the formation of the bilaminar disc during the second week of development?
Which cells contribute to the formation of the bilaminar disc during the second week of development?
What is the expected result of the blastocyst being completely embedded by the end of the second week?
What is the expected result of the blastocyst being completely embedded by the end of the second week?
What primary role does the extraembryonic mesoderm play during the second week of development?
What primary role does the extraembryonic mesoderm play during the second week of development?
What is the primary role of the notochord during embryonic development?
What is the primary role of the notochord during embryonic development?
Which cell layer contributes to the formation of the definitive endoderm during gastrulation?
Which cell layer contributes to the formation of the definitive endoderm during gastrulation?
What structure is formed from the primitive pit during gastrulation?
What structure is formed from the primitive pit during gastrulation?
Which statement accurately describes the formation of the intraembryonic mesoderm?
Which statement accurately describes the formation of the intraembryonic mesoderm?
What is the significance of the area of the oral membrane during the formation of the germ layers?
What is the significance of the area of the oral membrane during the formation of the germ layers?
What is the primary role of anchoring villi in placental development?
What is the primary role of anchoring villi in placental development?
Which of the following factors is implicated in the development of preeclampsia?
Which of the following factors is implicated in the development of preeclampsia?
What is the primary source of amniotic fluid during the first trimester of pregnancy?
What is the primary source of amniotic fluid during the first trimester of pregnancy?
Which function is NOT associated with the amniotic fluid surrounding the embryo?
Which function is NOT associated with the amniotic fluid surrounding the embryo?
What is the composition of amniotic fluid at the end of pregnancy?
What is the composition of amniotic fluid at the end of pregnancy?
Flashcards
Fertilization definition
Fertilization definition
The process of sperm and ovum joining to form a zygote.
Fertilization site
Fertilization site
The ampullary part of the uterine tube (lateral third).
Mitochondria inheritance
Mitochondria inheritance
Inherited only from the mother.
Sperm structure for motility
Sperm structure for motility
Signup and view all the flashcards
Capacitation
Capacitation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acrosome function
Acrosome function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sperm head function
Sperm head function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oocyte Stage
Oocyte Stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Implantation Definition
Implantation Definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fertilization Timeline
Fertilization Timeline
Signup and view all the flashcards
Two-Cell Stage
Two-Cell Stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Morula Stage
Morula Stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blastocyst Stage
Blastocyst Stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Implantation Timeline
Implantation Timeline
Signup and view all the flashcards
Implantation Site
Implantation Site
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decidua Definition
Decidua Definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neural Tube Formation
Neural Tube Formation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neural Crest Cells
Neural Crest Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Organogenesis
Organogenesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neural Tube Defects
Neural Tube Defects
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chorion Frondosum
Chorion Frondosum
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is head folding?
What is head folding?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the foregut?
What is the foregut?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the tail fold?
What is the tail fold?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the hindgut?
What is the hindgut?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the cloaca?
What is the cloaca?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is lateral folding?
What is lateral folding?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the midgut?
What is the midgut?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the vitellointestinal duct?
What is the vitellointestinal duct?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the amniotic cavity?
What is the amniotic cavity?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the results of folding?
What are the results of folding?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Placenta previa
Placenta previa
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blastocyst implantation
Blastocyst implantation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trophoblast differentiation
Trophoblast differentiation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cytotrophoblast role
Cytotrophoblast role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Syncytiotrophoblast function
Syncytiotrophoblast function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lacunae formation
Lacunae formation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Primitive uteroplacental circulation
Primitive uteroplacental circulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Primary villi formation
Primary villi formation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Embryoblast differentiation
Embryoblast differentiation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amnioblasts function
Amnioblasts function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decidua Basalis
Decidua Basalis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decidua Capsularis
Decidua Capsularis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decidua Parietalis
Decidua Parietalis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Abnormal Implantation
Abnormal Implantation
Signup and view all the flashcards
What happens to the trophoblast during the second week?
What happens to the trophoblast during the second week?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of the syncytiotrophoblast?
What is the role of the syncytiotrophoblast?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are primary villi?
What are primary villi?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the embryoblast?
What is the embryoblast?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trilaminar Germ Disc
Trilaminar Germ Disc
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gastrulation
Gastrulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Primitive Streak
Primitive Streak
Signup and view all the flashcards
Notochord
Notochord
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the germ layers?
What are the germ layers?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anchoring Villi
Anchoring Villi
Signup and view all the flashcards
Free Villi
Free Villi
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amniotic Cavity
Amniotic Cavity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amniotic Fluid
Amniotic Fluid
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Fertilization, Cleavage & Implantation
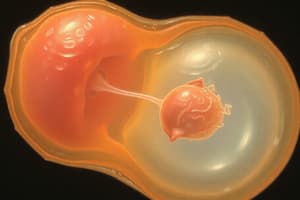
- Fertilization is the process of a mature sperm and ovum fusing to form a zygote
- Fertilization occurs in the ampullary part of the uterine tube
- Spermatozoa require capacitation and acrosome reaction prior to fertilization
- Spermatozoa consists of a head, neck, middle piece, and tail
- The head houses the nucleus and acrosome
- The middle piece contains mitochondria for energy
- The tail (flagellum) is responsible for motility
- The acrosome contains enzymes to penetrate the zona pellucida
Stages of fertilization
- Phase 1: Sperm penetrates the corona radiata
- Phase 2: Sperm penetrates the zona pellucida
- Phase 3: Fusion of sperm and egg cell membranes
Results of fertilization
- Restoration of diploid chromosome number
- Determination of the sex of the zygote
- Initiation of cleavage
Cleavage
- A series of mitotic divisions increasing the number of cells
- Occurs in the uterine tube, medial to the ampulla
- Morula stage is an early stage of cleavage
Blastocyst Formation
- Fluid from the uterine cavity penetrates the zona pellucida forming a blastocele
- Blastomeres are divided into inner cell mass and outer cells
- The inner cell mass forms the embryo proper
- The outer cells form the trophoblast
Implantation
- Penetration of the blastocyst into the uterine endometrium
- Occurs around the 6th to 11th day post-fertilization.
- Normal implantation sites are in the anterior or posterior wall of the uterine body
- Implantation involves the trophoblast proliferating and differentiating into cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast
- The syncytiotrophoblast erodes maternal tissues enabling the blastocyst to burrow and implant
The Decidua
- The endometrium after implantation
- Decidua basalis: part of the endometrium lying between the blastocyst and myometrium, forming the maternal part of the placenta
- Decidua capsularis: part of the endometrium covering the implanted blastocyst, lying between the blastocyst and uterine cavity
- Decidua parietalis: part of the endometrium lining the rest of the uterine cavity
- Decidua marginalis: part of the endometrium lying at the junction of decidua capsularis and parietalis
Clinical Correlates
- Abnormal implantation (ectopic pregnancy): implantation outside the uterus
- Placenta previa: implantation of the blastocyst in the lower segment of the uterus close to the internal os
- Hydatidiform mole: abnormal placental development
- Preeclampsia: Insufficient invasion of trophoblast cells into spiral arteries
The Embryonic Period
- The period of organogenesis (3-8 weeks)
- The flat trilaminar embryonic disc becomes a cylindrical embryo through folding
- The epiblast and hypoblast form layers of the embryonic disc
- Processes like gastrulation and neurulation occur resulting in the formation of the three germ layers
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.