Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of bile in fat digestion?
What is the primary function of bile in fat digestion?
- To transport nutrients
- To emulsify fats (correct)
- To digest proteins
- To store carbohydrates
What triggers the secretion of cholecystokinin (CCK)?
What triggers the secretion of cholecystokinin (CCK)?
- Food entering the stomach
- Enzymes secreted by the pancreas
- Chyme entering the small intestine (correct)
- Bile entering the gallbladder
Which of the following is NOT a type of enzyme secreted by the pancreas?
Which of the following is NOT a type of enzyme secreted by the pancreas?
- Proteins (correct)
- Amylases
- Nucleases
- Lipases
What role does the ileocecal sphincter play in digestion?
What role does the ileocecal sphincter play in digestion?
What effect does a blockage in the pancreatic duct have on digestion?
What effect does a blockage in the pancreatic duct have on digestion?
What type of muscle contraction characterizes peristalsis?
What type of muscle contraction characterizes peristalsis?
Which structure is NOT propelled by smooth muscle contractions during peristalsis?
Which structure is NOT propelled by smooth muscle contractions during peristalsis?
What is a consequence of dysfunction in the ileocecal sphincter?
What is a consequence of dysfunction in the ileocecal sphincter?
Which process is utilized to transport sperm from the testicles to the urethra?
Which process is utilized to transport sperm from the testicles to the urethra?
What distinguishes arteries from structures that utilize peristalsis?
What distinguishes arteries from structures that utilize peristalsis?
Where are goblet cells primarily located?
Where are goblet cells primarily located?
What is the primary function of mucus secreted by goblet cells?
What is the primary function of mucus secreted by goblet cells?
Which enzyme initiates starch breakdown in the mouth?
Which enzyme initiates starch breakdown in the mouth?
What role does cholecystokinin (CCK) play in digestion?
What role does cholecystokinin (CCK) play in digestion?
What is the primary function of bile in the small intestine?
What is the primary function of bile in the small intestine?
Which of the following organs does not produce vitamins?
Which of the following organs does not produce vitamins?
What crucial role do gut bacteria play in the human body?
What crucial role do gut bacteria play in the human body?
Which statement about bile is true?
Which statement about bile is true?
What is the role of enteropeptidase in digestion?
What is the role of enteropeptidase in digestion?
What is the function of Kupffer cells within the liver?
What is the function of Kupffer cells within the liver?
Which structure connects the gallbladder to the liver?
Which structure connects the gallbladder to the liver?
What is a key difference between goblet cells and mucous cells?
What is a key difference between goblet cells and mucous cells?
What is the primary function of microvilli in the small intestine?
What is the primary function of microvilli in the small intestine?
Which enzyme is responsible for protein digestion in the small intestine?
Which enzyme is responsible for protein digestion in the small intestine?
What triggers the secretion of gastrin in the stomach?
What triggers the secretion of gastrin in the stomach?
What is the role of lacteals in the digestive process?
What is the role of lacteals in the digestive process?
Which substance is essential for activating trypsin from trypsinogen?
Which substance is essential for activating trypsin from trypsinogen?
What role does hydrochloric acid (HCl) play in protein digestion?
What role does hydrochloric acid (HCl) play in protein digestion?
What initiates the release of pancreatic bicarbonate into the small intestine?
What initiates the release of pancreatic bicarbonate into the small intestine?
Which two enzymes are secreted by the pancreas for protein digestion?
Which two enzymes are secreted by the pancreas for protein digestion?
What is the primary function of G cells in the stomach?
What is the primary function of G cells in the stomach?
Which enzyme breaks down triglycerides in the digestive process?
Which enzyme breaks down triglycerides in the digestive process?
Which of the following is a vestigial organ in humans?
Which of the following is a vestigial organ in humans?
What substance is secreted by the pancreas to neutralize acidic chyme?
What substance is secreted by the pancreas to neutralize acidic chyme?
What is formed when food exits the stomach?
What is formed when food exits the stomach?
Where are lacteals located?
Where are lacteals located?
What is the primary function of glycogenesis in liver metabolism?
What is the primary function of glycogenesis in liver metabolism?
What is converted into urea by the liver?
What is converted into urea by the liver?
Which process allows the liver to synthesize glucose from non-carbohydrate sources?
Which process allows the liver to synthesize glucose from non-carbohydrate sources?
What is the primary role of Kupffer cells in the liver?
What is the primary role of Kupffer cells in the liver?
Which organ is primarily responsible for enzymatic digestion of proteins?
Which organ is primarily responsible for enzymatic digestion of proteins?
The destruction of symbiotic bacteria due to prolonged antibiotic use primarily affects which vitamin production?
The destruction of symbiotic bacteria due to prolonged antibiotic use primarily affects which vitamin production?
What mechanism allows trypsinogen to become active trypsin?
What mechanism allows trypsinogen to become active trypsin?
What is a function of zymogens like trypsinogen in the pancreas?
What is a function of zymogens like trypsinogen in the pancreas?
What is the primary function of gastric hormone gastrin?
What is the primary function of gastric hormone gastrin?
Which nutrient is absorbed in the small intestine?
Which nutrient is absorbed in the small intestine?
Antibiotic resistance in bacteria can primarily be attributed to what process?
Antibiotic resistance in bacteria can primarily be attributed to what process?
Which sphincter controls the exit of chyme from the stomach to the small intestine?
Which sphincter controls the exit of chyme from the stomach to the small intestine?
Which enzyme class is responsible for the breakdown of fats?
Which enzyme class is responsible for the breakdown of fats?
What is the role of intestinal enzymes in digestion?
What is the role of intestinal enzymes in digestion?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Fat Absorption Process
- Bile, produced by the liver, is critical for fat digestion and is stored in the gallbladder.
- Chyme entering the small intestine triggers the release of cholecystokinin (CCK), stimulating bile release.
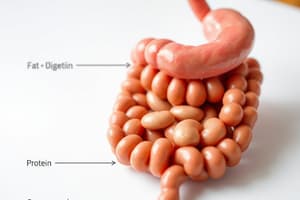
- Bile emulsifies fats in the duodenum, breaking them into smaller droplets to aid digestion.
- Lipases from the pancreas digest the emulsified fats, enabling nutrient absorption by the small intestine.
Pancreatic Function and Enzyme Pathway
- The pancreas secretes essential digestive enzymes: amylases for carbohydrates, proteases for proteins, and nucleases for nucleic acids.
- Digestive enzymes travel from the pancreas via the pancreatic duct to the small intestine.
- Blockages in the pancreatic duct hinder enzyme delivery, impairing digestion.
Common Bile Duct and Bile Function
- The common bile duct transports bile from the liver to the small intestine, but does not carry enzymes.
- Bile enhances fat digestion through emulsification, although this process is mechanical, not chemical.
Ileocecal Sphincter Role
- The ileocecal sphincter controls material transfer from the small to the large intestine.
- Dysfunction can lead to uncontrolled movements, disrupting digestion.
Peristalsis Overview
- Peristalsis involves coordinated contractions and relaxations of smooth muscle, moving contents through digestive tubes.
- Esophagus, stomach, and vas deferens utilize peristalsis to propel food and sperm.
Structures Utilizing Peristalsis
- Esophagus: Combines skeletal and smooth muscles for food transport via peristaltic action.
- Stomach: Features a muscular wall for mixing food with gastric juice, moving it to the small intestine.
- Vas deferens: Uses peristaltic contractions to transport sperm.
Exception to Peristalsis
- Arteries use heart pumping, not peristalsis, to circulate blood.
Structure and Function of Goblet Cells
- Goblet cells secrete mucus that protects epithelial linings from damage, particularly in acidic environments.
- Primarily located in the intestines and respiratory system, aiding in the smooth passage of contents.
Enzymes and Secretions in Digestion
- Salivary amylase begins starch digestion in the mouth.
- Gastrin stimulates gastric juice secretion in response to food intake, aiding protein and fat digestion.
- Secretin triggers bicarbonate release from the pancreas, neutralizing stomach acid.
- Cholecystokinin (CCK) promotes bile and enzyme release, facilitating fat digestion.
Bile Production and Function
- Bile is continuously produced by the liver, primarily for lipid emulsification in the small intestine.
- Bile travels through hepatic ducts to the common bile duct, where it enters the small intestine.
Vitamin K Production
- Vitamin K is synthesized by symbiotic bacteria in the large intestine, not produced by the human body.
- The large intestine is crucial for vitamin production, along with water and mineral absorption.
Liver Functions Overview
- The liver maintains blood via detoxification and filtering through the hepatic portal system.
- It also metabolizes glucose, synthesizes plasma proteins, and produces bile necessary for digestion.
Digestion and Absorption Structures
- Microvilli in the small intestine enhance nutrient absorption by increasing surface area.
- Lacteals absorb dietary fats from the intestinal villi.
Effects of Prolonged Antibiotic Use
- Long-term antibiotic use destroys beneficial gut bacteria, leading to decreased vitamin K production.
- Antibiotics can inadvertently harm non-pathogenic bacteria, reducing microbiota diversity.
Clarification of Functions
- Lacteals absorb dietary fats and do not neutralize acidic chyme; this role is performed by pancreatic bicarbonate.
Gastrin Release and Function
- Gastrin is released when food enters the stomach, stimulating acid secretion and digestive enzyme release.
- It plays a vital role in protein digestion by activating pepsin.
Activation of Trypsin
- Trypsinogen, released by the pancreas, is activated by enteropeptidase in the small intestine to facilitate protein digestion.
Key Processes
- The digestive process transitions from mechanical breakdown in the stomach to detailed enzymatic digestion in the small intestine, involving various enzymes and hormones for optimal nutrient partitioning.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.