Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which part of the eye is responsible for focusing light onto the retina?
Which part of the eye is responsible for focusing light onto the retina?
- Sclera
- Iris
- Cornea
- Lens (correct)
The pupil is responsible for giving color to the eye.
The pupil is responsible for giving color to the eye.
False (B)
What is the term for the condition where the eyeball is too long, causing nearsightedness?
What is the term for the condition where the eyeball is too long, causing nearsightedness?
Myopia
The __________ is a part of the retina that contains a high concentration of cones for detailed vision.
The __________ is a part of the retina that contains a high concentration of cones for detailed vision.
Match the following eye parts with their functions:
Match the following eye parts with their functions:
What is the function of the ciliary body?
What is the function of the ciliary body?
The optic disc has photoreceptor cells that form images.
The optic disc has photoreceptor cells that form images.
What is the jelly-like substance that maintains the shape of the eye called?
What is the jelly-like substance that maintains the shape of the eye called?
What role does the cornea play in vision?
What role does the cornea play in vision?
Describe the function of rods and cones in the retina.
Describe the function of rods and cones in the retina.
How does the ciliary body contribute to focusing light on the retina?
How does the ciliary body contribute to focusing light on the retina?
What is the purpose of the choroid layer in the eye?
What is the purpose of the choroid layer in the eye?
Explain the significance of the fovea centralis.
Explain the significance of the fovea centralis.
What is a common vision problem associated with aging and how does it affect vision?
What is a common vision problem associated with aging and how does it affect vision?
How does the iris control the amount of light entering the eye?
How does the iris control the amount of light entering the eye?
Differentiate between myopia and hyperopia.
Differentiate between myopia and hyperopia.
Match the following parts of the eye with their descriptions:
Match the following parts of the eye with their descriptions:
Match the following types of vision problems with their characteristics:
Match the following types of vision problems with their characteristics:
Match the following components of the eye with their main functions:
Match the following components of the eye with their main functions:
Match the following components with their associated characteristics:
Match the following components with their associated characteristics:
Match the following descriptors to the lens configurations:
Match the following descriptors to the lens configurations:
Match the following structures to their locations:
Match the following structures to their locations:
Match the following parts of the eye with their roles in vision:
Match the following parts of the eye with their roles in vision:
Match the following terms related to eye structure with their definitions:
Match the following terms related to eye structure with their definitions:
Flashcards
Sclera
Sclera
The outermost layer of the eye, providing support and attachment for muscles.
Retina
Retina
The layer of the eye containing photoreceptor cells (rods and cones) that convert light into signals.
Rods
Rods
Retinal photoreceptor cells that detect black and white.
Cones
Cones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myopia
Myopia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyperopia
Hyperopia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ciliary body
Ciliary body
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lens
Lens
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the cornea?
What is the function of the cornea?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the choroid's role in the eye?
What is the choroid's role in the eye?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the key differences between rods and cones?
What are the key differences between rods and cones?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the 'blind spot' in the eye?
What is the 'blind spot' in the eye?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the aqueous humor?
What is the function of the aqueous humor?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does the lens adjust for near and far vision?
How does the lens adjust for near and far vision?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the iris?
What is the function of the iris?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the difference between myopia and hyperopia?
What is the difference between myopia and hyperopia?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the sclera?
What is the sclera?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the cornea do?
What does the cornea do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What's the choroid's function?
What's the choroid's function?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are rods and cones?
What are rods and cones?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the fovea centralis?
What is the fovea centralis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the optic disc?
What is the optic disc?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of the lens?
What is the role of the lens?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the ciliary body?
What is the ciliary body?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
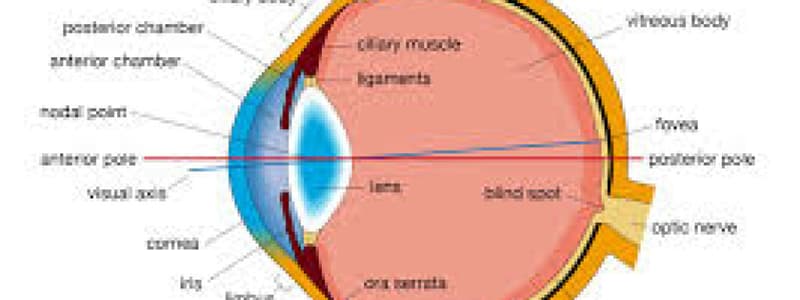
Eye Structure and Function
- Sclera: Outermost layer, opaque, supports the eye and is the site of attachment for oculomotor muscles
- Cornea: Transparent, allows light to enter the eye, helps focus the light. It's avascular
- Choroid: Lies deep to the sclera, contains richly pigmented melanocytes and is highly vascularized to absorb light
- Retina: Deep to the choroid, captures image-forming rays and converts them into action potentials
- Rods: Photoreceptor cells detecting black and white
- Cones: Photoreceptor cells detecting color and providing high acuity vision
- Fovea Centralis: Center of retina, high concentration of cones for detailed vision
- Optic Disc: Where optic nerve exits, no photoreceptors ("blind spot")
- Anterior Cavity: Space between cornea and iris, contains aqueous humor secreted by the ciliary body
- Posterior Cavity: Filled with vitreous humor, a gelatinous substance maintaining the eye's shape
- Lens: Transparent, flexible disc behind the iris, focuses light onto retina
- Suspensory Ligaments: Connect lens to ciliary body, changing lens shape for far/near vision
- Ciliary Body: Ring of smooth muscles surrounding the lens; contraction changes lens shape
- Iris: Colored part of the eye, controls the size of the pupil
- Pupil: Central opening in the iris that allows light into the eye
- Pupillary Sphincter: Muscle constricting the pupil (reducing light intake)
- Pupillary Dilator: Muscle enlarging the pupil (increasing light intake)
Visual Acuity and Eye Defects
- Emmetropia: Normal vision
- Myopia: "Nearsightedness" - Eyeball too long, image focused in front of retina
- Hyperopia: "Farsightedness" - Eyeball too short, image focused behind the retina
- Presbyopia: Age-related farsightedness, common in older individuals
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.