Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main function of dendrites in a neuron?
What is the main function of dendrites in a neuron?
- Carry electrical signals away from the cell body
- Hold the nucleus containing genetic material
- Receive signals from other neurons via synapses (correct)
- Release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft
Which type of neuron transmits signals from sensory organs to the central nervous system?
Which type of neuron transmits signals from sensory organs to the central nervous system?
- Sensory neurons (correct)
- Interneurons
- Motor neurons
- Neurotransmitter neurons
Where are neurotransmitters released in a neuron's communication process?
Where are neurotransmitters released in a neuron's communication process?
- Axon
- Axon terminal (correct)
- Dendrites
- Cell body (soma)
Which part of a neuron carries electrical signals away from the cell body?
Which part of a neuron carries electrical signals away from the cell body?
What is the function of motor neurons in the nervous system?
What is the function of motor neurons in the nervous system?
What happens when excitatory neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the adjacent cell's membrane?
What happens when excitatory neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the adjacent cell's membrane?
Which neurotransmitters cause the receiving cell's membrane potential to become more negative?
Which neurotransmitters cause the receiving cell's membrane potential to become more negative?
What process allows the nervous system to adapt to changing conditions and learn new information?
What process allows the nervous system to adapt to changing conditions and learn new information?
Which neurological disorder is characterized by abnormal, excessive, and synchronized electrical activity in the brain?
Which neurological disorder is characterized by abnormal, excessive, and synchronized electrical activity in the brain?
What can dysfunction of neurons lead to, according to the text?
What can dysfunction of neurons lead to, according to the text?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Unraveling the Nervous System: Exploring Neurons
The nervous system is a complex network of specialized cells that transmit and process information, allowing us to perceive, respond, and adapt to our environment. At the core of this system are neurons, often referred to as nerve cells or neurotransmitters. These cells are the building blocks of the nervous system, enabling communication within and between the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system.
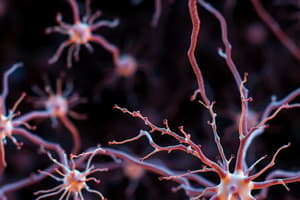
The Basic Structure of a Neuron
A neuron is composed of several distinct parts:
- Cell body (soma): Holds the nucleus, which contains the genetic material.
- Dendrites: Receive signals from other neurons via synapses.
- Axon: A long, slender projection that carries electrical signals away from the cell body.
- Axon terminal: The end of the axon where neurotransmitters are released into the synaptic cleft.
Types of Neurons
Neurons can be classified based on their structural and functional characteristics:
- Sensory neurons: Transmit signals from sensory organs to the central nervous system (CNS).
- Interneurons: Communicate with other neurons within the CNS.
- Motor neurons: Connect the CNS to the muscles and glands, controlling movement and other bodily functions.
The Nervous System's Communication Pathway
When a neuron receives a signal, it generates an electrical impulse—known as an action potential—that travels down the axon towards the axon terminal. Once the impulse reaches the terminal, neurotransmitters are released into the synaptic cleft, where they bind to receptors on the adjacent cell's membrane. This binding either opens or closes ion channels, leading to changes in the cell's electrical potential:
- Excitatory neurotransmitters: Cause the receiving cell's membrane potential to become more positive, increasing the likelihood of the receiving cell generating an action potential.
- Inhibitory neurotransmitters: Cause the receiving cell's membrane potential to become more negative, decreasing the likelihood of the receiving cell generating an action potential.
Neuronal Communication and Signal Integration
The nervous system's complexity comes from the interconnected network of neurons, allowing for vastly different response patterns to the same stimuli. Signal integration occurs when the neuron receives multiple inputs simultaneously, integrating the information to generate an appropriate response. This process is also known as synaptic plasticity, which allows the nervous system to adapt to changing conditions and learn new information.
Neuronal Communication and Disease
Dysfunction of neurons can lead to various neurological diseases and disorders, including:
- Parkinson's disease: A neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra, leading to tremors, muscle stiffness, and difficulties with movement.
- Alzheimer's disease: A progressive neurodegenerative disease that causes the loss of synapses and neurons in several brain regions, leading to memory loss, impaired reasoning, and changes in behavior and mood.
- Epilepsy: A neurological disorder characterized by abnormal, excessive, and synchronized electrical activity in the brain, leading to seizures.
- Multiple sclerosis: An autoimmune disorder that affects the protective covering of nerve fibers, leading to inflammation, scarring, and disruption of nerve impulses.
In the quest to understand the nervous system, scientists study neurons, their communication pathways, and their roles in various diseases to develop new treatments and therapies. As our knowledge expands, so too does our appreciation for the wonders of the nervous system and the intricate, yet delicate, balance of neurons that underpins our thoughts, emotions, and actions.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.