Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which anatomical structure is NOT considered a primary barrier against ascending contamination in the mare's reproductive tract?
Which anatomical structure is NOT considered a primary barrier against ascending contamination in the mare's reproductive tract?
- Cervix
- Oviduct (correct)
- Labia
- Vestibular sphincter
A mare presents with a vulva that is tilted forward at a 20-degree angle from vertical. Based on perineal conformation principles, this finding is most likely to predispose the mare to:
A mare presents with a vulva that is tilted forward at a 20-degree angle from vertical. Based on perineal conformation principles, this finding is most likely to predispose the mare to:
- Increased susceptibility to pneumovagina and ascending infections (correct)
- Reduced risk of uterine infections
- No significant impact on reproductive health
- Improved fertility due to enhanced drainage
During a routine reproductive examination, you are palpating the dorsal fornix of the vagina in a mare. Which anatomical relationship is most critical to consider when accessing this area for a colpotomy?
During a routine reproductive examination, you are palpating the dorsal fornix of the vagina in a mare. Which anatomical relationship is most critical to consider when accessing this area for a colpotomy?
- Lateral adjacency to the broad ligament
- Ventral proximity to the bladder
- Cranial connection to the cervix
- Dorsal covering of the peritoneum (correct)
The cervix of the mare is described as structurally 'more simplistic' compared to other species. Which of the following best characterizes this 'simplicity'?
The cervix of the mare is described as structurally 'more simplistic' compared to other species. Which of the following best characterizes this 'simplicity'?
The mesometrium and mesosalpinx are critical components of the equine reproductive system. What is the primary functional difference between these two structures?
The mesometrium and mesosalpinx are critical components of the equine reproductive system. What is the primary functional difference between these two structures?
The ovulation fossa is a unique anatomical feature of the equine ovary. What is its primary significance in equine reproduction?
The ovulation fossa is a unique anatomical feature of the equine ovary. What is its primary significance in equine reproduction?
Compared to other species, the corpus luteum (CL) in mares has a distinct characteristic. Which statement accurately describes this difference?
Compared to other species, the corpus luteum (CL) in mares has a distinct characteristic. Which statement accurately describes this difference?
The ovarian artery is a primary blood supply to the mare's reproductive tract. From which major vessel does the ovarian artery originate?
The ovarian artery is a primary blood supply to the mare's reproductive tract. From which major vessel does the ovarian artery originate?
The uterine artery is another significant vessel supplying the mare's reproductive tract. From which major vessel does the uterine artery originate?
The uterine artery is another significant vessel supplying the mare's reproductive tract. From which major vessel does the uterine artery originate?
During a standing surgical procedure on a mare, a combination of sedation, epidural analgesia, and local anesthesia is utilized. What is the primary rationale for this multi-modal approach to chemical restraint?
During a standing surgical procedure on a mare, a combination of sedation, epidural analgesia, and local anesthesia is utilized. What is the primary rationale for this multi-modal approach to chemical restraint?
Alpha-2 agonists like xylazine and detomidine are commonly used for sedation in standing equine surgeries. What is a significant physiological effect of these drugs, besides sedation and analgesia, that clinicians must be aware of?
Alpha-2 agonists like xylazine and detomidine are commonly used for sedation in standing equine surgeries. What is a significant physiological effect of these drugs, besides sedation and analgesia, that clinicians must be aware of?
Butorphanol tartrate, an opioid, is used in equine sedation protocols. What is its primary mechanism of action that contributes to its analgesic and sedative effects?
Butorphanol tartrate, an opioid, is used in equine sedation protocols. What is its primary mechanism of action that contributes to its analgesic and sedative effects?
Acepromazine, a phenothiazine tranquilizer, is used in equine sedation. What is a key limitation of acepromazine compared to alpha-2 agonists or opioids in the context of surgical procedures?
Acepromazine, a phenothiazine tranquilizer, is used in equine sedation. What is a key limitation of acepromazine compared to alpha-2 agonists or opioids in the context of surgical procedures?
When performing caudal epidural analgesia in a mare, what is the recommended maximum volume of lidocaine to minimize the risk of hindlimb ataxia?
When performing caudal epidural analgesia in a mare, what is the recommended maximum volume of lidocaine to minimize the risk of hindlimb ataxia?
Which nerve roots are primarily targeted for blockade when performing a caudal epidural in a mare for perineal analgesia?
Which nerve roots are primarily targeted for blockade when performing a caudal epidural in a mare for perineal analgesia?
During epidural administration, what is the significance of observing a 'hanging drop' of anesthetic in the needle hub before injection?
During epidural administration, what is the significance of observing a 'hanging drop' of anesthetic in the needle hub before injection?
Loss of anal and tail tone is a clinical indicator of successful caudal epidural analgesia. What physiological mechanism directly causes this loss of tone?
Loss of anal and tail tone is a clinical indicator of successful caudal epidural analgesia. What physiological mechanism directly causes this loss of tone?
In pre-operative systemic medication for equine female reproductive surgery, NSAIDs are commonly used. What is the primary rationale for their use?
In pre-operative systemic medication for equine female reproductive surgery, NSAIDs are commonly used. What is the primary rationale for their use?
When are peri-operative antimicrobials generally considered most necessary in equine female reproductive surgeries?
When are peri-operative antimicrobials generally considered most necessary in equine female reproductive surgeries?
Prior to surgery of the external genitalia and vestibule in a mare, fecal evacuation from the rectum is a critical preparatory step. What is the primary reason for this?
Prior to surgery of the external genitalia and vestibule in a mare, fecal evacuation from the rectum is a critical preparatory step. What is the primary reason for this?
Wrapping and securing the tail is a standard part of surgical site preparation for perineal surgeries in mares. What is a critical precaution regarding tail wrapping post-procedure?
Wrapping and securing the tail is a standard part of surgical site preparation for perineal surgeries in mares. What is a critical precaution regarding tail wrapping post-procedure?
In preparing the surgical site for external genitalia surgery, a 'clean hand/dirty hand' technique is mentioned. What does this technique primarily aim to prevent?
In preparing the surgical site for external genitalia surgery, a 'clean hand/dirty hand' technique is mentioned. What does this technique primarily aim to prevent?
Episioplasty (Caslick's procedure) is indicated for mares with compromised vulvar conformation. What is the primary functional outcome sought by performing an episioplasty?
Episioplasty (Caslick's procedure) is indicated for mares with compromised vulvar conformation. What is the primary functional outcome sought by performing an episioplasty?
During an episioplasty, how much of the vulvar mucosa is typically removed to ensure proper healing and apposition?
During an episioplasty, how much of the vulvar mucosa is typically removed to ensure proper healing and apposition?
What is a potential complication of excessive closure during an episioplasty that must be carefully avoided?
What is a potential complication of excessive closure during an episioplasty that must be carefully avoided?
A persistent hymen in a maiden mare may go unnoticed until an attempted breeding. What is the primary clinical sign that would indicate a persistent hymen?
A persistent hymen in a maiden mare may go unnoticed until an attempted breeding. What is the primary clinical sign that would indicate a persistent hymen?
Urine pooling in mares is often associated with poor perineal conformation and aging. What is the primary mechanism by which urine pooling leads to infertility?
Urine pooling in mares is often associated with poor perineal conformation and aging. What is the primary mechanism by which urine pooling leads to infertility?
Urethral extension procedures are performed to treat urine pooling in mares. What is the fundamental principle behind these surgical techniques?
Urethral extension procedures are performed to treat urine pooling in mares. What is the fundamental principle behind these surgical techniques?
Cervical lacerations in mares are often missed at parturition and diagnosed later. When is the most appropriate time post-foaling to detect cervical lacerations during a routine exam?
Cervical lacerations in mares are often missed at parturition and diagnosed later. When is the most appropriate time post-foaling to detect cervical lacerations during a routine exam?
Cervical lacerations are easiest to detect during which phase of the estrous cycle?
Cervical lacerations are easiest to detect during which phase of the estrous cycle?
What percentage of cervical laceration length generally indicates that surgical repair is necessary?
What percentage of cervical laceration length generally indicates that surgical repair is necessary?
When is the optimal timing for surgical repair of cervical lacerations post-foaling?
When is the optimal timing for surgical repair of cervical lacerations post-foaling?
In cervical laceration repair, how many layers are typically used to close the cervix?
In cervical laceration repair, how many layers are typically used to close the cervix?
After cervical laceration repair, what is the recommended minimum period mares should not be bred to allow for adequate healing?
After cervical laceration repair, what is the recommended minimum period mares should not be bred to allow for adequate healing?
Which of the following is NOT a typical surgical procedure discussed for the equine female reproductive tract in the provided content?
Which of the following is NOT a typical surgical procedure discussed for the equine female reproductive tract in the provided content?
Vaginal neoplasia and vaginal polyps are mentioned in the context of equine female reproductive surgery. What is a key differentiating factor between these two conditions in terms of prognosis and management?
Vaginal neoplasia and vaginal polyps are mentioned in the context of equine female reproductive surgery. What is a key differentiating factor between these two conditions in terms of prognosis and management?
Uterine leiomyoma is briefly mentioned. What is the general nature of a leiomyoma?
Uterine leiomyoma is briefly mentioned. What is the general nature of a leiomyoma?
In the context of standing surgery, the content emphasizes the importance of surgeon preference in drug selection for chemical restraint. What is the most likely reason for this emphasis on surgeon preference?
In the context of standing surgery, the content emphasizes the importance of surgeon preference in drug selection for chemical restraint. What is the most likely reason for this emphasis on surgeon preference?
The content mentions 'dosages not on the exam' in relation to specific drug dosages. What is the most probable reason for this disclaimer?
The content mentions 'dosages not on the exam' in relation to specific drug dosages. What is the most probable reason for this disclaimer?
A maiden mare exhibits signs of infertility during breeding attempts. Upon examination, a band of tissue is found obstructing the cervix. While a persistent hymen is suspected, which diagnostic step most accurately confirms the condition and differentiates it from other potential obstructive abnormalities?
A maiden mare exhibits signs of infertility during breeding attempts. Upon examination, a band of tissue is found obstructing the cervix. While a persistent hymen is suspected, which diagnostic step most accurately confirms the condition and differentiates it from other potential obstructive abnormalities?
An older, multiparous mare is diagnosed with urine pooling. The veterinarian elects to perform a urethral extension procedure. Postoperatively, the mare develops a persistent fistula at the cranial aspect of the extended urethral opening. What is the most critical factor in determining the optimal timing for surgical revision of this complication?
An older, multiparous mare is diagnosed with urine pooling. The veterinarian elects to perform a urethral extension procedure. Postoperatively, the mare develops a persistent fistula at the cranial aspect of the extended urethral opening. What is the most critical factor in determining the optimal timing for surgical revision of this complication?
A mare presents with a third-degree cervical laceration detected 45 days post-foaling. The laceration involves over 50% of the cervical length, extending deeply into the cervical stroma. Before surgical intervention, which diagnostic modality provides the MOST critical information for pre-operative planning and predicting the mare's future fertility?
A mare presents with a third-degree cervical laceration detected 45 days post-foaling. The laceration involves over 50% of the cervical length, extending deeply into the cervical stroma. Before surgical intervention, which diagnostic modality provides the MOST critical information for pre-operative planning and predicting the mare's future fertility?
During a cervical laceration repair, after resecting the scar tissue, the veterinarian aims to close the defect in three layers. What is the MOST important consideration when closing the cervical muscle layer to optimize tissue apposition and minimize the risk of post-operative complications?
During a cervical laceration repair, after resecting the scar tissue, the veterinarian aims to close the defect in three layers. What is the MOST important consideration when closing the cervical muscle layer to optimize tissue apposition and minimize the risk of post-operative complications?
A mare undergoing a standing perineal surgery exhibits significant discomfort despite adequate sedation with an alpha-2 agonist and local anesthesia. The veterinarian decides to perform a caudal epidural. What is the MOST important parameter to monitor DURING the epidural injection to prevent potential complications such as hindlimb ataxia or recumbency?
A mare undergoing a standing perineal surgery exhibits significant discomfort despite adequate sedation with an alpha-2 agonist and local anesthesia. The veterinarian decides to perform a caudal epidural. What is the MOST important parameter to monitor DURING the epidural injection to prevent potential complications such as hindlimb ataxia or recumbency?
Post-operatively, following an episioplasty, a mare develops significant swelling and edema at the surgical site despite appropriate anti-inflammatory medications. Palpation reveals crepitus in the subcutaneous tissues. What is the MOST appropriate next step to address this complication?
Post-operatively, following an episioplasty, a mare develops significant swelling and edema at the surgical site despite appropriate anti-inflammatory medications. Palpation reveals crepitus in the subcutaneous tissues. What is the MOST appropriate next step to address this complication?
You are preparing a mare for a standing surgical procedure involving the external genitalia. After sedation but prior to the local or regional anesthesia, which of the following steps is MOST crucial to perform to minimize potential surgical site contamination?
You are preparing a mare for a standing surgical procedure involving the external genitalia. After sedation but prior to the local or regional anesthesia, which of the following steps is MOST crucial to perform to minimize potential surgical site contamination?
A veterinarian is performing an episioplasty on a mare with poor perineal conformation. During the procedure, the veterinarian inadvertently removes an excessive amount of vulvar mucosa, resulting in significant tension during closure. What is the PRIMARY long-term concern associated with this complication?
A veterinarian is performing an episioplasty on a mare with poor perineal conformation. During the procedure, the veterinarian inadvertently removes an excessive amount of vulvar mucosa, resulting in significant tension during closure. What is the PRIMARY long-term concern associated with this complication?
A mare is undergoing a standing surgical procedure with sedation including an alpha-2 agonist. Post-operatively, the mare exhibits profuse sweating, muscle tremors, and increased urination. What is the MOST likely underlying cause of these clinical signs related to the sedation protocol?
A mare is undergoing a standing surgical procedure with sedation including an alpha-2 agonist. Post-operatively, the mare exhibits profuse sweating, muscle tremors, and increased urination. What is the MOST likely underlying cause of these clinical signs related to the sedation protocol?
A veterinarian is preparing to perform a Caslick's procedure on a mare. What is the MOST important anatomical landmark to consider when determining the extent of vulvar closure to prevent future complications?
A veterinarian is preparing to perform a Caslick's procedure on a mare. What is the MOST important anatomical landmark to consider when determining the extent of vulvar closure to prevent future complications?
During a standing surgical procedure, a mare suddenly becomes agitated and attempts to kick despite the administration of xylazine and butorphanol. What is the MOST appropriate immediate step to ensure the safety of the surgical team and the mare?
During a standing surgical procedure, a mare suddenly becomes agitated and attempts to kick despite the administration of xylazine and butorphanol. What is the MOST appropriate immediate step to ensure the safety of the surgical team and the mare?
Why is a multimodal approach of sedation, epidural, and local/regional anesthesia preferred for standing surgical procedures in mares?
Why is a multimodal approach of sedation, epidural, and local/regional anesthesia preferred for standing surgical procedures in mares?
Prior to performing surgery on the external genitalia of a mare, the surgical site is prepared using a 'clean hand/dirty hand' technique. What is the MOST significant advantage of employing this technique in this specific anatomical location?
Prior to performing surgery on the external genitalia of a mare, the surgical site is prepared using a 'clean hand/dirty hand' technique. What is the MOST significant advantage of employing this technique in this specific anatomical location?
When performing a caudal epidural, what factor has the MOST influence on the cranial extent of the analgesia?
When performing a caudal epidural, what factor has the MOST influence on the cranial extent of the analgesia?
You are called to examine a multiparous mare displaying signs of vaginitis and infertility. Upon vaginal speculum examination, you observe a pool of urine in the cranial vagina. How does chronic urine pooling MOST directly contribute to infertility in mares?
You are called to examine a multiparous mare displaying signs of vaginitis and infertility. Upon vaginal speculum examination, you observe a pool of urine in the cranial vagina. How does chronic urine pooling MOST directly contribute to infertility in mares?
Flashcards
What is the perineum?
What is the perineum?
The region within the base of the tail, semimembranosus muscle, and ventral commissure of the vulva.
What is the vulva?
What is the vulva?
The external genitalia including the 2 labia, dorsal and ventral commissures, and the clitoris ventrally.
What is the vestibule?
What is the vestibule?
It connects the vagina to the vulva, beginning at the transverse fold of the external urethral orifice
What is the mare's reproductive tract?
What is the mare's reproductive tract?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the cervix?
What is the cervix?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the uterus?
What is the uterus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the infundibulum?
What is the infundibulum?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the ovaries?
What are the ovaries?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Ovarian artery & vein?
What is the Ovarian artery & vein?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Name some udder issues.
Name some udder issues.
Signup and view all the flashcards
3 components for standing sx.
3 components for standing sx.
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is caudal epidural anesthesia?
What is caudal epidural anesthesia?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Indication for Episioplasty.
Indication for Episioplasty.
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Caslick's Procedure?
What is Caslick's Procedure?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Persistent Hymen?
What is Persistent Hymen?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Urethral Extension?
What is Urethral Extension?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are cervix lacerations?
What are cervix lacerations?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Describe Cervical Laceration Repair.
Describe Cervical Laceration Repair.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Equine Female Reproductive Surgery
- Dylan Lutter DVM, MS, DACVS-LA, from Kansas State University, presents equine female reproductive surgery.
Learning Objectives
- Recall the relevant anatomy to the region.
- Describe the methods used for chemical restraint in standing surgeries.
- Describe the indications for the surgeries covered.
Overview
- The lecture covers reproductive system anatomy, chemical restraint for standing surgery, surgery of the external genitalia, surgery of the vestibule, vagina, & cervix, and surgery of the uterus & ovaries, which is covered in the second lecture.
Female Reproductive System
- Structures include the external genitalia (vulva & perineum), vestibule, vagina, cervix, uterus, ovaries, and oviduct.
- The mare's reproductive tract is a series of cavities consisting of the vestibule, vagina, and uterus.
- The tract is partitioned by constrictions that act as barriers that consist of the labia, vestibular sphincter, and cervix.
External Genitalia
- The perineum is the region within the base of the tail, semimembranosus muscle, and ventral commissure of the vulva.
- The vulva includes 2 labia, dorsal and ventral commissures, and ventrally located clitoris.
- The vestibule connects the vagina to the vulva, beginning at the transverse fold of the external urethral orifice.
- Ideally, the labia should be vertical and able to resist manual separation.
- Approximately 2/3 of the vulva should be ventral to the ischial arch; upright conformation shows less than 10° vertical tilt.
- Poor conformation can compromise the protective vulvar seal, increasing contamination and infertility.
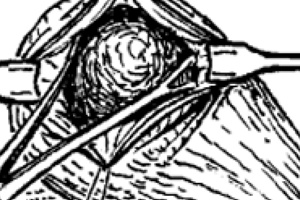
Vagina
- The vagina begins at the transverse fold of the external urethral orifice.
- It extends cranially to the vaginal fornix, bordered dorsally by the rectum and ventrally by the bladder/urethra.
- The dorsal fornix is always covered by peritoneum and can be accessed for colpotomy ovariectomy.
Cervix
- The cervix is a tubular, densely muscular structure with many longitudinal mucosal folds.
- It acts as a sphincter, is more simplistic compared to other species.
- The cervix combines with labia and vestibular constrictor muscles as 3 protective barriers to minimize uterine contamination.
Uterus & Oviducts
- The uterus is suspended by the mesometrium (broad ligament).
- Its blood supply comes from the uterine branches of the vaginal and ovarian arteries and uterine artery and vein.
- The Uterus contains 2 relatively short and large horns.
- The ovaries and oviduct are suspended by the mesosalpinx, with the oviduct consisting of the infundibulum (funnel near the ovulation fossa), a tortuous tube ampulla, and a straight, narrow isthmus that enters to uterine horn.
Ovaries
- The ovaries are kidney-shaped, with the ovulation fossa located along the ventral "free" border.
- They are suspended by the mesovarium, contiguous with the mesometrium (broad ligament of the uterus).
- Ovaries contain innervation and blood supply via the ovarian artery and vein.
Functional States of the Ovary
- The ovary contains corpora lutea and small follicles.
- There are sections of the ovary containing a developing corpus luteum, a fully developed corpus luteum, and large follicles.
- The equine corpus luteum does not protrude from the ovary unlike other species.
Ultrasound of the Ovary
- The ultrasound highlights the interstitial and luteal tissues, central blood clot, follicles, and ovarian fossa.
- The tongue of the corpus luteum shows the direction of the released oocyte from the ovarian fossa.
Blood Supply of the Reproductive Tract
- The blood supply to the reproductive tract comes from the ovarian and uterine arteries and veins
- These originate from the aorta, vena cava, and external iliac artery, and are analogous to the testicular and cremasteric vessels.
- Additional blood supply is provided by the internal pudendal artery, vaginal artery, and pudendoepigastic trunk.
Udder
- The blood supply for the udder is from the external pudendal vessels.
- The mammary gland is firmly adhered to the ventral body wall and is rarely problematic in horses.
- Issues include mastitis, squamous cell carcinoma, and external infection/abscessation.
Chemical Restraint for Standing Surgery
- Most female reproductive procedures can be performed standing, and is the preferred approach
- Successful standing anesthetic management includes sedation, epidural, and local/regional anesthesia
- Drug combinations are utilized for multi-modal restraint
- Based on patient temperament, procedure duration/difficulty, and surgeon preference
- Combinations should involve sedative/hypnotic, tranquilizing, and analgesic effects.
Chemical Restraint: Standing Sedation
- Alpha-2 agonists are used as sedative/hypnotic agents to produce sedation, analgesia, muscle relaxation, and ataxia.
- Xylazine hydrochloride (100 mg/ml), dosage between 0.2 to 1 mg/kg IV, with duration of action 15 to 20 minutes.
- Detomidine hydrochloride (10 mg/ml), dosage between 0.01-0.02 mg/kg IV bolus; 0.02 mg/kg/hr CRI with duration of action 30 to 45 minutes.
- Opioids, such as Butorphanol tartrate, can be used for sedation.
- It's a к-agonist/µ-antagonist with a duration of action lasting about 30-60 minutes.
- Acepromazine is a phenothiazine tranquilizer and anxiolytic without analgesia which has a duration of action lasting 6-10 hours.
Chemical Restraint: Epidural
- 18 ga, 1.5" needle used for epidural, maximum volume of lidocaine = 7 ml, max total volume = 10 ml, Know the proper location & volume limits for epidural use.
- Caudal epidural anesthesia deposits local anesthetic extra-durally within the spinal canal and blocks conduction of caudal nerve roots.
- Can affect hind limb motor control & volume should not exceed 7 ml; larger volumes (over 10 ml for a 500 kg horse) risk ataxia.
- Femoral (L1/L2) and sciatic nerve (L4/5/6) can be affected.
- Palpate C1 space (preferred) or C2 for epidural location.
- Clip a square centered over injection site to aseptically prepare.
Chemical Restraint: Epidural
- Sterilize gloves and draw medication from previously unopened bottles.
- An assistant moves tail & anesthetist palpates space between vertebrae with the thumb nail and insert 18-20g needled through skin over the space.
- The needle hub is filled with anesthetic- hanging drop technique and advanced slowly at ~ 75° angle to the skin (tip directed cranially).
- The user will be able to aspirate fluid and hear a sucking sound once epidural space is entered with minimal resistance.
- Inject anesthetic slowly and steadily after needle is placed properly.
- Time of onset & duration depends on the anesthetic chosen by vet.
- Monitor for loss of anal & tail tone as well as perineal sensation to indicate successful epidural.
Pre-operative Systemic Medications
- NSAIDS provide anti-inflammatory/analgesic effects.
- Antimicrobials are indicated for internal procedures: peri-operative antibiotics, but may not be indicated for an external procedure in a clean, healthy surgical site.
Common Equine Antibiotics
- Procaine Penicillin G; 300,000 IU/ml, administered 22,000-44,000 IU/kg IM BID.
- Potassium Penicillin; reconstitute per bottle instructions, administered 22,000-44,000 IU/kg IV QID
- Ceftiofur Sodium; reconstitute to 50mg/ml, Naxcel is a trade name, administered 2.2 mg/kg IM or IV BID for adults; larger dosage for foals
- Gentamicin; 100mg/ml, administered 6.6 mg/kg IV SID
- Trimethoprim Sulfadiazine (TMS), Equisul, administered 24 mg/kg PO BID
- Sulfamethoxazole/Trimethoprim (SMZ), administer 30 mg/kg PO BID
- Oxytetracycline; LA-200 = 200 mg/ml, administered 6.6 mg/kg IV BID
- Doxycycline & Minocycline tablets adminsitered PO BID
Surgical Site Preparation for External Genitalia & Vestibular Surgery
- Includes Tetanus prophylaxis & pre-operative anti-inflammatories.
- Antibiotics at surgeon discretion depending on the procedure being performed.
- Restrain mare in stocks, sedate at clinician discretion, and evacuate feces from the rectum.
- Wrap & secure the tail, fully fold the hair to the tail & wrap with brown gauze.
- Clean the perineum & surrounding area with mild soap applying clean hand/dirty hand technique and clean vestibule & vagina (if necessary).
- Wipe vulva & vestibule from cranially to caudally with dilute betadine-soaked gauze/cotton and evacuate all fluid (urine or cleansing water).
Surgery of the External Genitalia
- Indications for Episioplasty: compromise of the vulvar seal resulting in vaginal contamination, poor perineal conformation, maintaining pregnancy, presence of pneumovagina (windsucking), and reconstruction following foaling injury.
- Episioplasty (Caslick’s procedure).
- Close the dorsal 2/3 of the vulva; up to the level of the ischial arch.
Caslick's Procedure
- Restrain in stocks, wrap tail, perform aersptic prep, and apply local anaesthesia.
- Remove 1-2 mm mucosa in dorsal 2/3 of the vulva, and perform appositional suture closure.
Surgery of the Vestibule, Vagina, & Cervix
- Persistent hymen is a congenital band of tissue running the course of the vagina & obscuring the cervix.
- Usually seen in maiden mares, can be complete or perforated, and requires a blunt breakdown or surgical removal to resolve the obstruction.
- Urine pooling occurs most commonly in older, multiparous mares with poor vulvar conformation.
- Causes accumulation of urine in cranial vagina.
- A differential diagnoses of infertility.
Urine Pooling Treatment
- A Urethral Extension Procedure involves multiple techniques that create lateral flaps of vestibular mucosa, and these are sutured to create a tunnel with the urethral opening at the cranial aspect.
- High incidence of partial failure is common; Fistula formation at cranial aspect of tunnel and the surgery is not repaired until around 4-6 weeks following procedure.
Cervix Lacerations
- Can occur during foaling, sometimes detected at 30-day post foaling exam with a speculum exam or manually.
- Cervix is firm and typically closed, may go unnoticed until mares present for infertility.
- Cervix lacerations: Criteria for repair
- < 25% of cervix length may not require repair.
- 25-50% of cervix length may benefit from repair.
- 50% of cervix length or greater requires repair.
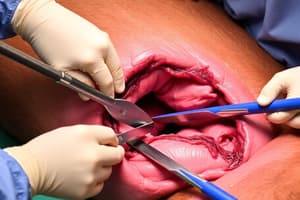
Cervical Laceration Repair
- The repair should not occur sooner than 3 weeks post-foaling and is preferred in diestrus.
- Finochietto rib spreaders & stay sutures (#2 USP suture) are used to retract the cervix.
- Resect scar & freshen edges, close cervix in 3 layers.
- Close Cervical mucosa (0 or 1 absorbable), performing continuous horizontal mattress and checking lumen is patent after every bite.
- Cervical muscle is closed using (#1 suture) in a simple continuous pattern, and the vaginal mucosa is closed similarly.
- After surgery, mares should not be bred for 30-45 days, and has 65-75% successful breeding post operation.
- Vaginal neoplasia or polyp, and uterine leiomyoma are vaginal and uterine tissue related medical conditions.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.