Podcast
Questions and Answers
What primary characteristic is used to classify the different types of epithelium?
What primary characteristic is used to classify the different types of epithelium?
- The shape and arrangement of the cells. (correct)
- The size of the extracellular matrix surrounding the cells.
- The rate at which the cells divide and regenerate.
- The presence or absence of blood vessels within the tissue.
In what types of tissues are simple squamous epithelium typically found?
In what types of tissues are simple squamous epithelium typically found?
- Lining of the bladder
- Lining of air sacs in the lungs and blood vessels (correct)
- Lining of the digestive tract
- Outer layer of skin
Which type of epithelium is best suited for areas of the body where protection from abrasion is important?
Which type of epithelium is best suited for areas of the body where protection from abrasion is important?
- Simple columnar
- Transitional
- Simple cuboidal
- Stratified squamous (correct)
What is the primary function of transitional epithelium?
What is the primary function of transitional epithelium?
Where is pseudostratified columnar epithelium typically found?
Where is pseudostratified columnar epithelium typically found?
Which of the following is NOT a function of epithelial tissue?
Which of the following is NOT a function of epithelial tissue?
How do epithelial cells receive nutrients, considering they are avascular?
How do epithelial cells receive nutrients, considering they are avascular?
What is the role of goblet cells found within some epithelial tissues?
What is the role of goblet cells found within some epithelial tissues?
What is the main difference between keratinized and non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
What is the main difference between keratinized and non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
What is the defining characteristic of cuboidal epithelial cells?
What is the defining characteristic of cuboidal epithelial cells?
How do microvilli contribute to the function of certain epithelial tissues?
How do microvilli contribute to the function of certain epithelial tissues?
In stratified epithelium, how is the tissue classified based on the cell shape?
In stratified epithelium, how is the tissue classified based on the cell shape?
What type of epithelial tissue is found lining kidney tubules, and what is its primary function?
What type of epithelial tissue is found lining kidney tubules, and what is its primary function?
What is a common characteristic among simple epithelia regarding the basement membrane?
What is a common characteristic among simple epithelia regarding the basement membrane?
Which special feature of epithelium acts as sensory structures?
Which special feature of epithelium acts as sensory structures?
Which classification of tissue protects, supports, and binds together?
Which classification of tissue protects, supports, and binds together?
Where can stratified cuboidal epithelium be found?
Where can stratified cuboidal epithelium be found?
What is the function of stratified columnar epithelium?
What is the function of stratified columnar epithelium?
Which of the following is NOT a function of epithelium?
Which of the following is NOT a function of epithelium?
Which of the following tissue types is characterized by cells in a single layer?
Which of the following tissue types is characterized by cells in a single layer?
Which of the following tissues functions in movement?
Which of the following tissues functions in movement?
Which type of cell has approximately equal height and width?
Which type of cell has approximately equal height and width?
Which of the following structures can be found in the tracheal lining?
Which of the following structures can be found in the tracheal lining?
In the digestive tract, which tissue is able to absorb?
In the digestive tract, which tissue is able to absorb?
What is the function of cilia in the respiratory tract?
What is the function of cilia in the respiratory tract?
Which is NOT a function of epithelium?
Which is NOT a function of epithelium?
What does basal lamina do for epithelial tissue?
What does basal lamina do for epithelial tissue?
Which tissue is found in the bladder
Which tissue is found in the bladder
Which of the following functions epithelial tissue does NOT perform.
Which of the following functions epithelial tissue does NOT perform.
Which of the following tissue is avascular but innervated in nature
Which of the following tissue is avascular but innervated in nature
Which tissue helps increase surface area allowing for faster and efficient adsorption
Which tissue helps increase surface area allowing for faster and efficient adsorption
Which of the special features of epithelium lubricates and and protects the surface of an organ
Which of the special features of epithelium lubricates and and protects the surface of an organ
What makes epithelial cells connect and hold the cells together to form a tightly connect layer:
What makes epithelial cells connect and hold the cells together to form a tightly connect layer:
Which best describes the shape of squamous cells?
Which best describes the shape of squamous cells?
Flashcards
What are cells?
What are cells?
The smallest, basic units of living things.
What is tissue?
What is tissue?
A collection of similar cells and extracellular matrix that together perform a specific function.
What is Histology?
What is Histology?
The study of the tissues of the body and how they are arranged to constitute organs.
What is Epithelium?
What is Epithelium?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is epithelium classified?
How is epithelium classified?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are Squamous cells?
What are Squamous cells?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are cuboidal cells?
What are cuboidal cells?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are Columnar cells?
What are Columnar cells?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is simple epithelium?
What is simple epithelium?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is stratified epithelium?
What is stratified epithelium?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is pseudostratified epithelium?
What is pseudostratified epithelium?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is transitional epithelium?
What is transitional epithelium?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is simple squamous epithelium?
What is simple squamous epithelium?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of simple cuboidal epithelium?
What is the function of simple cuboidal epithelium?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of simple columnar epithelium?
What is the function of simple columnar epithelium?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the location and function of Pseudostratified columnar epithelium?
What is the location and function of Pseudostratified columnar epithelium?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of Stratified squamous epithelium?
What is the function of Stratified squamous epithelium?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of Squamous keratinized (dry)?
What is the function of Squamous keratinized (dry)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are Goblet cells?
What are Goblet cells?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of Cilia?
What is the function of Cilia?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of Villi?
What is the function of Villi?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of Microvilli?
What is the function of Microvilli?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the functions of Epithelium?
What are the functions of Epithelium?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Orientation of epithelial cell
Orientation of epithelial cell
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Epithelium is under CLO 1.
Learning Objectives
- Explain the ways epithelia are classified.
- Distinguish between simple, stratified, and pseudostratified epithelia.
- List characteristics of squamous, cuboidal, columnar, and transitional epithelia.
- Identify common surface specializations of epithelia.
- Discuss how organization, thickness, surface specializations, and turnover of an epithelial layer might reflect its function.
- Identify different types of epithelial specimens.
Cells
- Cells represent the smallest and most basic living units.
Tissues and Histology
- A tissue constitutes a collection of similar cells and the extracellular matrix.
- Tissues work together to perform a specific function.
- Histology involves studying the tissues of the body and how they are arranged to form organs.
Classification of Tissues
- The human body consists of four basic tissue types: epithelium, connective, muscular, and nervous.
- Epithelium lines and covers surfaces.
- Connective tissue offers protection, support, and binds structures together.
- Muscular tissue produces movement.
- Nervous tissue responds to stimuli and conducts impulses.
Epithelium
- Epithelium covers the body's surface and serves purposes like protection, adsorption, excretion, secretion, filtration, and sensory reception.
- Epithelium classification is based on cell shape and cell arrangement within the tissue.
Classification Based on Shape
- Squamous (Latin, Squamous-Scale) cells are flat and thin, resembling scales.
- Cuboidal cells possess a basic cube shape, with approximately equal height and width.
- Columnar cells are tall and rectangular, typically taller than they are wide.
Classification Based on Arrangement
- Simple cells exist in a single layer attached to a basement membrane.
- Stratified cells are found in two or more layers stacked.
- Pseudostratified cells appear as multiple layers due to varying cell heights and nucleus positions, even though it's a single layer.
- Transitional cells are rounded and can slide over one another, which allows stretching.
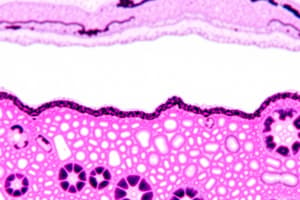
Simple Squamous Epithelium
- This epithelium consists of a single layer of thin, flattened cells that fit tightly together.
- It is located in the serous lining of air sacs in the lungs (alveoli), the lining of the heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels.
- Simple squamous enables materials to pass through via diffusion and filtration and secretes lubricating substances.
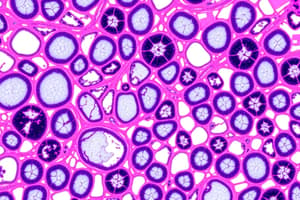
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
- It surrounds the ovary and thyroid.
- It secretes, covers, and absorbs.
Simple Columnar Epithelium
- Ciliated tissues are found in the bronchi, uterine tubes, and uterus.
- Smooth (nonciliated) tissues are in the digestive tract and bladder.
- It provides protection, absorption, secretes mucus (lubrication), and enzymes.
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
- Ciliated tissues of this type line the trachea, nasal cavity, and bronchi.
- It provides protection, secretes mucus and ciliated tissue moves particles trapped in mucus out of the airways.
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
- It lines the esophagus, mouth, and vagina.
- It protects against abrasion.
Squamous Keratinized (Dry)
- This is found in the epidermis.
- It provides protection and prevents water loss.
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
- Sweat glands, salivary glands, and mammary glands contain this tissue type.
- It functions as protective tissue, secretion.
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
- It is located in the male urethra, ducts of some glands, and the conjunctiva.
- Functions include secretion and protection .
Transitional Epithelium
- This epithelium lines the bladder, urethra, and ureters.
- It supports protection and distensibility, which allows urinary organs to expand and stretch.
Special Features of Epithelium
- Cilia are hair-like appendages attached to the apical surface of cells, acting as sensory structures or producing movement.
- Goblet cells are specialized to produce mucus to lubricate and protect organ surfaces.
- Villi are finger-like projections from the epithelial layer that increase surface area for faster, more efficient adsorption.
- Microvilli are smaller projections increasing surface area and have a bushy appearance.
Functions of Epithelium
- Epithelial tissue forms boundaries between different environments.
- It provides protection from radiation, desiccation, toxins, and physical trauma.
- It supports the absorption of substances in the digestive tract lining.
- It aids regeneration and excretion of chemicals between underlying tissues and body cavities.
- It assists in secretion of hormones into the blood vascular system, including sweat, mucus, and enzymes.
- It is used in the detection of sensation.
Characteristics of Epithelial Layers
- Epithelial tissue consists of cells laid out in sheets with cell-to-cell attachments, forming a tightly connected, avascular, yet innervated layer.
- Nourishment comes from substances diffusing from blood vessels of underlying connective tissue.
- Epithelial cells feature orientation: one side faces the tissue surface, body cavity, or external environment, and the other joins to a basement membrane.
- The basement membrane is non-cellular and helps cement epithelial tissue to underlying structures.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.