Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which function is NOT associated with epithelial tissues?
Which function is NOT associated with epithelial tissues?
- Energy storage (correct)
- Protection
- Absorption
- Secretion
What best describes the vascularity of epithelial tissues?
What best describes the vascularity of epithelial tissues?
- Highly vascularized
- Only vascular in certain areas
- Avascular (correct)
- Moderately vascularized
What specialized structure do epithelial cells use for cell-to-cell communication?
What specialized structure do epithelial cells use for cell-to-cell communication?
- Desmosomes
- Adherens junctions
- Tight junctions
- Gap junctions (correct)
Which of the following is a characteristic feature of epithelial cells?
Which of the following is a characteristic feature of epithelial cells?
How are epithelial tissues classified?
How are epithelial tissues classified?
What is a primary role of epithelial tissues in exocrine glands?
What is a primary role of epithelial tissues in exocrine glands?
Which of the following structures primarily functions to move mucus and particles over epithelial surfaces in the respiratory epithelium?
Which of the following structures primarily functions to move mucus and particles over epithelial surfaces in the respiratory epithelium?
What is the characteristic arrangement of microtubules in cilia called?
What is the characteristic arrangement of microtubules in cilia called?
What feature is common in epithelial cells involved in ion transport?
What feature is common in epithelial cells involved in ion transport?
What role does the basement membrane play for epithelial tissues?
What role does the basement membrane play for epithelial tissues?
Which of the following ions are necessary for ciliary movement?
Which of the following ions are necessary for ciliary movement?
Which type of epithelial cells contains a brush border for enhanced absorption?
Which type of epithelial cells contains a brush border for enhanced absorption?
Kartagener’s syndrome is associated with malfunctions in which structure?
Kartagener’s syndrome is associated with malfunctions in which structure?
What is a key characteristic of endocrine glands?
What is a key characteristic of endocrine glands?
Which type of secretion involves the entire cell breaking apart?
Which type of secretion involves the entire cell breaking apart?
Which of the following are examples of exocrine glands?
Which of the following are examples of exocrine glands?
What is the primary structural classification of exocrine glands based on duct structure?
What is the primary structural classification of exocrine glands based on duct structure?
What characterizes merocrine glands?
What characterizes merocrine glands?
Which type of surface specialization is primarily involved in absorption?
Which type of surface specialization is primarily involved in absorption?
What type of gland is the goblet cell classified as?
What type of gland is the goblet cell classified as?
What is the primary function of cilia?
What is the primary function of cilia?
What is the primary function of stereocilia?
What is the primary function of stereocilia?
Which of the following statements about mammalian sperm is true?
Which of the following statements about mammalian sperm is true?
What percentage of all thyroid cancers does papillary thyroid carcinoma represent?
What percentage of all thyroid cancers does papillary thyroid carcinoma represent?
Which condition is NOT associated with adenocarcinoma?
Which condition is NOT associated with adenocarcinoma?
Which of the following is a common test for examining epithelial cells?
Which of the following is a common test for examining epithelial cells?
What type of epithelial tissue is characterized by a single layer of flattened cells and is often found in sites of filtration and diffusion?
What type of epithelial tissue is characterized by a single layer of flattened cells and is often found in sites of filtration and diffusion?
Which type of epithelial tissue is primarily involved in secretion and absorption and has cube-shaped cells?
Which type of epithelial tissue is primarily involved in secretion and absorption and has cube-shaped cells?
Which epithelial tissue has cells that appear stratified due to varying nucleus levels but is actually a single layer?
Which epithelial tissue has cells that appear stratified due to varying nucleus levels but is actually a single layer?
Which type of epithelial tissue consists of multiple layers of cells and provides protection from abrasion?
Which type of epithelial tissue consists of multiple layers of cells and provides protection from abrasion?
Which type of epithelial tissue is found lining parts of the urinary bladder and allows for stretching?
Which type of epithelial tissue is found lining parts of the urinary bladder and allows for stretching?
What distinguishes exocrine glands from endocrine glands?
What distinguishes exocrine glands from endocrine glands?
What is the primary function of simple columnar epithelium?
What is the primary function of simple columnar epithelium?
Which type of epithelial tissue is characterized by its rare occurrence and typically consists of two layers of cells?
Which type of epithelial tissue is characterized by its rare occurrence and typically consists of two layers of cells?
The presence of cilia and goblet cells is characteristic of which type of epithelial tissue?
The presence of cilia and goblet cells is characteristic of which type of epithelial tissue?
Which type of epithelial tissue contains dome-shaped surface cells and allows for stretching?
Which type of epithelial tissue contains dome-shaped surface cells and allows for stretching?
Flashcards
Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial Tissue
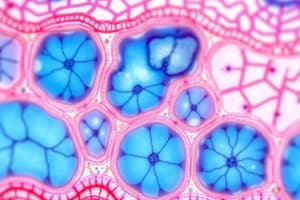
Epithelial tissue is a type of tissue that covers and lines surfaces of the body, acting as a protective barrier and facilitating various functions.
Avascular Epithelium
Avascular Epithelium
Epithelial tissue is avascular, meaning it lacks its own blood vessels, relying on diffusion from underlying connective tissue for nutrients and waste removal.
Regenerative Epithelium
Regenerative Epithelium
Epithelial tissue is highly regenerative, constantly renewing itself and capable of repairing injuries quickly.
Epithelial Tissue Morphology
Epithelial Tissue Morphology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tightly Packed Epithelium
Tightly Packed Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epithelial Cell Junctions
Epithelial Cell Junctions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epithelial Tissue Functions
Epithelial Tissue Functions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epithelial Tissue Types
Epithelial Tissue Types
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endocrine Glands
Endocrine Glands
Signup and view all the flashcards
Exocrine Glands
Exocrine Glands
Signup and view all the flashcards
Merocrine Gland
Merocrine Gland
Signup and view all the flashcards
Apocrine Gland
Apocrine Gland
Signup and view all the flashcards
Holocrine Gland
Holocrine Gland
Signup and view all the flashcards
Microvilli
Microvilli
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stereocilia
Stereocilia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cilia
Cilia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transitional Epithelium
Transitional Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glandular Epithelium
Glandular Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Axoneme
Axoneme
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kartagener's Syndrome
Kartagener's Syndrome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Flagella
Flagella
Signup and view all the flashcards
Undulating Wave Movement
Undulating Wave Movement
Signup and view all the flashcards
9+9+2 Arrangement
9+9+2 Arrangement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dynein
Dynein
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adenocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Epithelial Tissue: Overview
- Epithelial tissue is a sheet of cells that covers body surfaces, lines body cavities, forms glands, and lines hollow organs
- It has a free surface exposed to the exterior or an internal space
- It rests on connective tissue, anchored by a basement membrane
- It's avascular (does not have blood vessels) but is richly innervated
- Cells are tightly packed with minimal extracellular space
- It has specialized cell-cell junctions that adhere cells and allow communication
- The shape and function of the cells are related to the amount of cytoplasm and organelles
- Some epithelial cells contain pigments
- Epithelial tissue involved in secretion, absorption, filtration, excretion, diffusion, sensory reception, and sometimes contraction
- Classified by number of layers and shape of cells
Types of Epithelial Tissues
- Simple squamous epithelium: single layer of flattened cells; permits exchange of gases, nutrients, and wastes
- Lines blood vessels, air sacs of lungs, and serous membranes
- Simple cuboidal epithelium: single layer of cube-shaped cells; involved in secretion and absorption
- Found in kidney tubules, ducts of glands, and surface of ovaries
- Simple columnar epithelium: single layer of tall cells; involved in absorption and secretion
- Lines digestive tract, parts of uterus, and stomach
- Pseudostratified columnar epithelium: appears stratified due to varying cell heights, but all cells touch the basement membrane; involved in secretion and movement of mucus
- Found in trachea and parts of male reproductive system
- Stratified squamous epithelium: multiple layers of flattened cells; provides protection against abrasion
- Keratinized type found in skin, non-keratinized type in mouth and esophagus
- Stratified cuboidal epithelium: two or more layers of cube-shaped cells; involved in protection, secretion, and absorption
- Found in some ducts of glands (rare)
- Transitional epithelium: cells can change shape from cuboidal or columnar to squamous-like; accommodates stretching
- Found in urinary bladder, ureters, and part of urethra
Glands
- Glands are epithelial tissue specialized for secretion
- Two types: unicellular (e.g., goblet cells) or multicellular
- Multicellular glands are classified by their duct structure (simple vs. compound) and secretory unit shape (tubular vs. acinar, or a combination)
- Classified by method of secretion (merocrine, apocrine, holocrine)
- Two types: unicellular (e.g., goblet cells) or multicellular
Surface Specializations
- Microvilli: tiny projections that increase surface area for absorption (e.g., in the intestines)
- Cilia: hair-like projections that move fluids or substances across the surface (e.g., in respiratory tract)
- Stereocilia: long, immotile projections that increase surface area for absorption (e.g., in the male reproductive system)
- Flagella: whip-like structures used for movement (e.g., sperm)
Epithelial Tissue in Health and Disease
- Various types of cancers arise from epithelial cells
- Conditions like Asthma, Celiac disease, and HPV (Human Papillomavirus) can affect epithelial tissues
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.