Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which cellular structure is primarily responsible for moving mucus along the respiratory tract?
Which cellular structure is primarily responsible for moving mucus along the respiratory tract?
- Brush border
- Cilia (correct)
- Microvilli
- Nucleus
In the small intestine, which of the following is the primary function of microvilli?
In the small intestine, which of the following is the primary function of microvilli?
- Secretion of digestive enzymes
- Increase surface area for absorption of nutrients. (correct)
- Protection of the intestinal lining.
- Propulsion of chyme through the digestive tract.
Which type of epithelial tissue is characterized by a single layer of tall, thin cells with elongated nuclei?
Which type of epithelial tissue is characterized by a single layer of tall, thin cells with elongated nuclei?
- Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
- Simple columnar epithelium (correct)
- Simple cuboidal epithelium
- Simple squamous epithelium
Which of the following best describes pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium?
Which of the following best describes pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium?
Which characteristic is NOT true of epithelial tissue?
Which characteristic is NOT true of epithelial tissue?
What is the primary function of simple squamous epithelium?
What is the primary function of simple squamous epithelium?
Where is simple cuboidal epithelium NOT found?
Where is simple cuboidal epithelium NOT found?
What is a key characteristic of stratified squamous epithelium?
What is a key characteristic of stratified squamous epithelium?
Which type of epithelium is specialized for the stretching and distension seen in the urinary bladder?
Which type of epithelium is specialized for the stretching and distension seen in the urinary bladder?
What is a key feature of pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium?
What is a key feature of pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium?
In which location would you most likely find keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
In which location would you most likely find keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
Which function is NOT typically performed by simple columnar epithelium?
Which function is NOT typically performed by simple columnar epithelium?
Flashcards
Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial Tissue
One of the four basic types of tissue in the body. Forms glands and lines the inside and outside of the body.
Transitional Epithelium (Urothelium)
Transitional Epithelium (Urothelium)
A specialized epithelium found in the urinary system. Cells can stretch and distend, allowing organs to expand.
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Simple Squamous Epithelium
A single layer of flat, scale-like cells. Functions in diffusion, filtration, and lubrication.
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium
Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Keratin
Keratin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cilia
Cilia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Microvilli
Microvilli
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brush Border
Brush Border
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Epithelial Tissue
- One of the four basic tissue types in the body (along with connective tissue, muscle, and nervous tissue).
- Forms glands and lines the inside and outside of the body.
- Epithelial cells are anchored to a basement membrane.
- Epithelial tissue lacks extracellular matrix, meaning the cells are packed closely together.
- Avascular, meaning it does not contain blood vessels. Receives nutrients and oxygen through diffusion from capillaries in the underlying connective tissue.
Classifications of Epithelium
- Simple Squamous Epithelium:
- Single layer of flat, scale-like cells.
- Functions:
- Diffusion
- Filtration
- Lubrication
- Locations:
- Alveoli (for gas exchange)
- Glomerulus (in the kidney, for filtration)
- Lining of blood vessels (endothelial cells)
- Simple Cuboidal Epithelium:
- Single layer of cube-shaped cells.
- Functions:
- Absorption
- Secretion
- Locations:
- Nephron (tubules in the kidney)
- Glands (e.g., sweat glands, liver, pancreas)
- Simple Columnar Epithelium:
- Single layer of tall, thin cells.
- Functions:
- Absorption
- Secretion
- May have cilia for moving fluid across apical surface
- Locations:
- Gastrointestinal tract (stomach to anus)
- Glands
- Airways
- Uterus and uterine tube
- Stratified Squamous Epithelium:
- Multiple layers of cells, with the apical cells being flat.
- Function: Protection against abrasion
- Locations:
- Epidermis (skin)
- Esophagus
- Vagina
- Two types:
- Keratinized: Contains keratin, a tough protein, for added protection against water; apical cells lack nuclei.
- Non-keratinized: Does not contain keratin; apical cells have nuclei.
- Transitional Epithelium (Urothelium):
- Specialized stratified epithelium found only in the urinary system.
- Apical cells are dome-shaped and can stretch and distend.
- Function: Allows for the stretching and distension of the urinary system (e.g., bladder).
- Locations:
- Urinary system (ureter, bladder, proximal urethra)
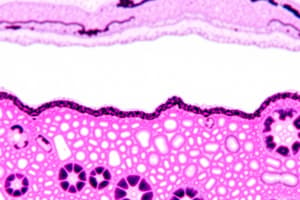
- Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium (Respiratory Epithelium):
- Appears stratified, but all cells are anchored to the basement membrane.
- Ciliated, with cilia projecting from the apical surface.
- Function:
- Secretion (mainly mucus)
- Propulsion of mucus by cilia
- Location:
- Respiratory system (trachea, proximal bronchi)
Cilia and Microvilli
- Cilia:
- Hair-like projections located on the apical surface of cells.
- Function: Move liquid over the surface of the cell (like a crowd surfing at a concert)
- Microvilli:
- Finger-like projections located on the apical surface of cells.
- Function: Increase surface area for absorption.
Surface Area & Absorption
- Microvilli increase surface area for absorption in the jejunum
- Brush border is a term for the appearance of the microvilli which resemble a hairbrush
- The jejunum is where amino acids, simple sugars, and fats are absorbed
Epithelial Tissues
- Simple squamous epithelium is one layer of flat cells (e.g., Bowman's capsule from the glomerulus)
- Simple cuboidal epithelium is one layer of cube-shaped cells (the nucleus rounds out the cell)
- Simple columnar epithelium is one layer of tall, thin cells (the tall nuclei are a key identifier)
- Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium is one layer of cells that appears stratified. The key identifier is the presence of cilia projecting from the cell surface (e.g., Respiratory epithelium)
- Stratified squamous keratinized epithelium is multiple layers of cells with the top layer flat and no nuclei
- Stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium is multiple layers of cells with the top layer containing nuclei.
- Nucleus is located typically in the center of cells.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.