Podcast
Questions and Answers
Why should the reported 1% prevalence of lichen planus in the general population be interpreted cautiously?
Why should the reported 1% prevalence of lichen planus in the general population be interpreted cautiously?
- Most epidemiologic studies focus on specific manifestations (oral or cutaneous) rather than the entire ectodermal spectrum. (correct)
- The prevalence is consistent across different age groups.
- There is a clear sexual and racial predilection, making the overall prevalence less reliable.
- Lichen planus is more common at the extremes of age.
Which age range represents the peak onset for most cases of lichen planus?
Which age range represents the peak onset for most cases of lichen planus?
- 30 to 60 years
- 55 to 74 years (correct)
- 75 to 85 years
- 10 to 20 years
Which of the following statements accurately describes sexual or racial predilection in lichen planus?
Which of the following statements accurately describes sexual or racial predilection in lichen planus?
- There is a clear sexual and racial predilection, with males being more affected than females.
- Lichen planus is more common in females and certain racial groups.
- There is no clear sexual or racial predilection, but the age of onset is earlier in women. (correct)
- Lichen planus is more common in males and certain racial groups.
How does the incidence of childhood lichen planus in Pacific Indians compare to that in other populations?
How does the incidence of childhood lichen planus in Pacific Indians compare to that in other populations?
What is a characteristic feature of familial lichen planus that distinguishes it from nonfamilial forms?
What is a characteristic feature of familial lichen planus that distinguishes it from nonfamilial forms?
Which of the following is a common HLA haplotype associated with nonfamilial lichen planus?
Which of the following is a common HLA haplotype associated with nonfamilial lichen planus?
Why is a detailed history and physical examination essential for patients with lichen planus?
Why is a detailed history and physical examination essential for patients with lichen planus?
What factor primarily determines the disease duration of lichen planus?
What factor primarily determines the disease duration of lichen planus?
Which of the following characteristics is LEAST likely to be observed in classic lichen planus?
Which of the following characteristics is LEAST likely to be observed in classic lichen planus?
What histopathological finding is MOST closely associated with the clinical observation of Wickham striae in lichen planus lesions?
What histopathological finding is MOST closely associated with the clinical observation of Wickham striae in lichen planus lesions?
A patient with lichen planus develops new lesions at sites of recent scratches. This is an example of what phenomenon?
A patient with lichen planus develops new lesions at sites of recent scratches. This is an example of what phenomenon?
What immunological process is now understood to underlie the Koebner phenomenon observed in acute lichen planus?
What immunological process is now understood to underlie the Koebner phenomenon observed in acute lichen planus?
Why is postinflammatory hyperpigmentation a common feature in lichen planus?
Why is postinflammatory hyperpigmentation a common feature in lichen planus?
Which of the following statements best describes the reported prevalence of childhood lichen planus?
Which of the following statements best describes the reported prevalence of childhood lichen planus?
A clinician observes hypopigmentation in a patient suspected of having lichen planus. What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A clinician observes hypopigmentation in a patient suspected of having lichen planus. What is the MOST appropriate next step?
Flashcards
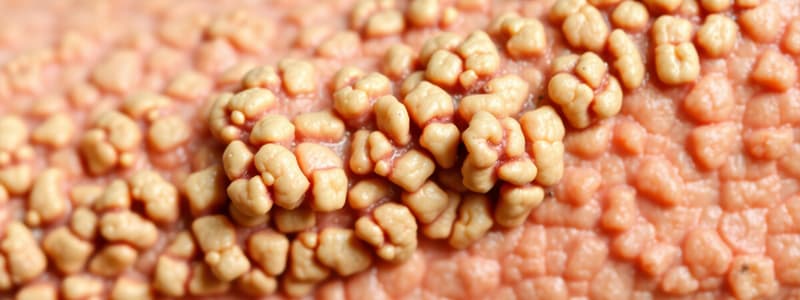
Lichen Planus Lesions
Lichen Planus Lesions
Well-defined, dull red-violet, flat-topped, polygonal papules that may merge into plaques.
Wickham Striae
Wickham Striae
Fine, white, adherent reticulate lines seen on the surface of lichen planus lesions.
Histological Correlation of Wickham Striae
Histological Correlation of Wickham Striae
Orthokeratosis, epidermal thickening, and an increased granular layer in lichen planus lesions.
Common Sites of Lichen Planus
Common Sites of Lichen Planus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Koebner Phenomenon in Lichen Planus
Koebner Phenomenon in Lichen Planus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Postinflammatory Hyperpigmentation
Postinflammatory Hyperpigmentation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Childhood Lichen Planus
Childhood Lichen Planus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epidemiology
Epidemiology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lichen Planus Prevalence
Lichen Planus Prevalence
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lichen Planus Onset Age
Lichen Planus Onset Age
Signup and view all the flashcards
Familial Lichen Planus
Familial Lichen Planus
Signup and view all the flashcards
HLA Associations with LP
HLA Associations with LP
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sites affected by Lichen Planus
Sites affected by Lichen Planus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Progression of Lichen Planus
Progression of Lichen Planus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Epidemiology of Lichen Planus
- The actual incidence and prevalence are not precisely known.
- Existing studies often focus on oral or cutaneous aspects, underrepresenting the full ectodermal range.
- A general estimated prevalence of 1% should be regarded cautiously.
- Prevalence geographically ranges from 0.1% to 4%.
- Most cases (around two thirds) manifest between ages 30 to 60, with peak onset between 55 and 74 years.
- The condition is less prevalent in very young or old age groups.
- There is no observed inclination towards any sex or race, although women tend to experience an earlier onset.
Childhood Lichen Planus
- Accounts for 1% to 5% of all lichen planus cases.
- More frequent in Pacific Indians, comprising around 20% of cases.
- Possibly more common in African American children in the United States.
- Displays no significant sexual predilection.
- Onset typically occurs between 8 and 12 years of age.
Familial Lichen Planus
- Fewer than 100 cases have been reported.
- A strong family history exists in 1.5% of adult cases and 3.8% of pediatric cases.
- Familial forms are characterized by early onset, widespread and often erosive or ulcerative disease, mucosal involvement, and frequent relapses.
- This has led some to classify it as a distinct condition.
- Multiple HLA haplotypes have been identified, including HLA-B27, Aw19, -B18, and -Cw8.
- Nonfamilial cases commonly show HLA-A3, -A5, -A28, -B8, -B16, and Bw35.
- HLA-B8 is more frequent in cases of oral lichen planus alone, while HLA-Bw35 is more frequent in cutaneous lichen planus alone.
Clinical Features of Lichen Planus
- Skin and oral mucosa are most commonly affected.
- It can affect any ectodermal tissue including hair, nails, internal and external genitalia, eyes, and esophagus.
- A detailed history and examination is required to guide therapy, referrals, and monitoring.
- Skin lesions usually develop over several weeks.
- Disease duration depends on lesion location, morphology, and histological pattern.
- Classic cutaneous lesions are well-defined, dull red-violet, flat-topped, polygonal papules.
- Papules often cluster and merge into plaques.
- Wickham striae, which are fine, white, adherent reticulate scales, are seen in developed lesions.
- Wickham striae are highly characteristic and best viewed with dermoscopy.
- Clinical and dermoscopic features correlate with histological findings.
- Wickham striae correspond with orthokeratosis, epidermal thickening, and an increased granular layer.
- The red-violet color results from vascular dilation combined with pigment incontinence.
- Lesions tend to be symmetrically distributed, commonly on the flexural wrists, arms, and legs.
- Other common sites include proximal thighs, trunk, and neck, commonly spares the face and palms.
- Inverse lichen planus affects the axillae, groin, and inframammary region.
- The condition is often extremely pruritic, with the degree of itching related to the extent of involvement.
- A major exception is hypertrophic lichen planus, commonly on the lower extremities, which is intensely pruritic.
- In the acute phase, lichen planus exhibits an isomorphic (Koebner) phenomenon, where trauma induces disease.
- Trauma induces exposure of plasmacytoid DCs to endogenous peptides, such as cathelicidin LL-37, and endogenous antigens, such as DNA and RNA, which stimulate the release of type I IFNs (-α and -β), which propagates disease.
- Usually resolves with postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, more common in darker-skinned individuals.
- Hypopigmentation is rare and warrants considering other diagnoses.
Childhood Lichen Planus in Specific Populations
- Frequent reports originate from the Indian subcontinent.
- This may be due to genetic predisposition, infectious exposures, and social stigma related to pigmentary changes.
- The largest U.S. study found a predominance in African American children, supporting the social implications of pigmentary changes.
- Has similar clinical and histological features to adult lichen planus.
- Skin and oral involvement occur in 42% to 60% and 17% to 30% of cases, respectively.
- Hair and nail involvement are rare, at 2% to 6% and 0% to 19% of cases, respectively.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.