Podcast
Questions and Answers
What role do sensory neurons in the myenteric plexus play in the enteric nervous system?
What role do sensory neurons in the myenteric plexus play in the enteric nervous system?
- They transmit impulses exclusively to the brain.
- They connect sensory and motor neurons directly.
- They measure the degree of stretch in smooth muscles. (correct)
- They regulate mucus release into the lumen.
What is the primary function of the submucosal plexus in the enteric nervous system?
What is the primary function of the submucosal plexus in the enteric nervous system?
- To measure the degree of stretch in smooth muscles.
- To measure the chemical composition of the lumen. (correct)
- To coordinate contraction of the smooth muscles.
- To promote peristaltic movement in the gut.
How does the enteric nervous system function regarding brain input?
How does the enteric nervous system function regarding brain input?
- It relies entirely on sympathetic neuron input.
- It operates independently but receives some regulatory input. (correct)
- It does not interact with the autonomic nervous system.
- It functions solely based on brain signals.
What type of neurons are specifically involved in coordinating peristaltic movement within the enteric nervous system?
What type of neurons are specifically involved in coordinating peristaltic movement within the enteric nervous system?
Which anatomical structure is located between the longitudinal and circular smooth muscle layers?
Which anatomical structure is located between the longitudinal and circular smooth muscle layers?
What percentage of postganglionic neurons release noradrenaline as a neurotransmitter?
What percentage of postganglionic neurons release noradrenaline as a neurotransmitter?
Which neurotransmitter is primarily used by postganglionic neurons that project to sweat glands?
Which neurotransmitter is primarily used by postganglionic neurons that project to sweat glands?
Which cranial nerve is associated with the oculomotor nerve?
Which cranial nerve is associated with the oculomotor nerve?
Where are most preganglionic parasympathetic neurons located?
Where are most preganglionic parasympathetic neurons located?
Postganglionic parasympathetic neurons typically have what kind of axons?
Postganglionic parasympathetic neurons typically have what kind of axons?
Which cranial nerve does NOT have postganglionic neurons located in discrete ganglia near their target organs?
Which cranial nerve does NOT have postganglionic neurons located in discrete ganglia near their target organs?
What distinguishes the sympathetic nervous system ganglia location from the parasympathetic system?
What distinguishes the sympathetic nervous system ganglia location from the parasympathetic system?
What roles do cranial nerves VII and IX primarily play in the parasympathetic nervous system?
What roles do cranial nerves VII and IX primarily play in the parasympathetic nervous system?
What primary function does the autonomic nervous system contribute to in the body?
What primary function does the autonomic nervous system contribute to in the body?
What is the main role of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system?
What is the main role of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system?
Which of the following is not a parameter regulated by homeostasis?
Which of the following is not a parameter regulated by homeostasis?
How are preganglionic and postganglionic neurons characterized in the sympathetic nervous system?
How are preganglionic and postganglionic neurons characterized in the sympathetic nervous system?
What effect does the parasympathetic nervous system have on heart rate?
What effect does the parasympathetic nervous system have on heart rate?
Where are the preganglionic neuron cell bodies of the sympathetic nervous system located?
Where are the preganglionic neuron cell bodies of the sympathetic nervous system located?
Which neurotransmitter is released by preganglionic neurons in the sympathetic nervous system?
Which neurotransmitter is released by preganglionic neurons in the sympathetic nervous system?
What is the primary role of the enteric division of the autonomic nervous system?
What is the primary role of the enteric division of the autonomic nervous system?
What pathway does a preganglionic neurone take when traveling to synapse with a postganglionic neurone in the sympathetic chain?
What pathway does a preganglionic neurone take when traveling to synapse with a postganglionic neurone in the sympathetic chain?
Which type of sympathetic ganglia targets the abdomen or pelvis?
Which type of sympathetic ganglia targets the abdomen or pelvis?
What is the primary function of post-ganglionic sympathetic neurones in the cervical ganglion?
What is the primary function of post-ganglionic sympathetic neurones in the cervical ganglion?
Which of the following describes the action of sympathetic post-ganglionic neurones on heart function?
Which of the following describes the action of sympathetic post-ganglionic neurones on heart function?
What is the role of the white ramus in the sympathetic nervous system?
What is the role of the white ramus in the sympathetic nervous system?
Which ramus ultimately leads to the target of a postganglionic neurone after passing through the sympathetic chain?
Which ramus ultimately leads to the target of a postganglionic neurone after passing through the sympathetic chain?
What physiological reaction does the sympathetic nervous system primarily initiate?
What physiological reaction does the sympathetic nervous system primarily initiate?
What is the primary role of the sympathetic trunk below the upper lumbar levels?
What is the primary role of the sympathetic trunk below the upper lumbar levels?
What role do visceral sensory neurons play in the autonomic nervous system?
What role do visceral sensory neurons play in the autonomic nervous system?
Which ganglion is associated with cranial nerve IX?
Which ganglion is associated with cranial nerve IX?
Which region of the nucleus of the solitary tract (NST) is associated with taste sensation?
Which region of the nucleus of the solitary tract (NST) is associated with taste sensation?
How do visceral sensory neurons from dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons reach the nucleus of the solitary tract?
How do visceral sensory neurons from dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons reach the nucleus of the solitary tract?
What impact does the processing of visceral sensory information have on the autonomic nervous system?
What impact does the processing of visceral sensory information have on the autonomic nervous system?
Where is most visceral sensory information primarily sent within the brain?
Where is most visceral sensory information primarily sent within the brain?
What is the function of the nucleus of the solitary tract (NST) in relation to autonomic activity?
What is the function of the nucleus of the solitary tract (NST) in relation to autonomic activity?
Which neurotransmitters are primarily involved in the signaling pathways of the autonomic nervous system?
Which neurotransmitters are primarily involved in the signaling pathways of the autonomic nervous system?
What is the primary function of the adrenal medulla during the fight or flight response?
What is the primary function of the adrenal medulla during the fight or flight response?
Which cranial nerve is associated with the otic ganglion that innervates the parotid salivary gland?
Which cranial nerve is associated with the otic ganglion that innervates the parotid salivary gland?
What roles do the different adrenergic receptor types play?
What roles do the different adrenergic receptor types play?
Which G-protein-coupled receptor type is responsible for breaking down lipids in adipose tissue?
Which G-protein-coupled receptor type is responsible for breaking down lipids in adipose tissue?
What is the role of phospholipase C in adrenergic receptor signaling?
What is the role of phospholipase C in adrenergic receptor signaling?
What neurotransmitters are primarily associated with the autonomic nervous system's sympathetic actions?
What neurotransmitters are primarily associated with the autonomic nervous system's sympathetic actions?
Which of the following best describes the nature of adrenergic receptors?
Which of the following best describes the nature of adrenergic receptors?
Which statement accurately reflects the effects of adrenaline and noradrenaline binding to adrenergic receptors?
Which statement accurately reflects the effects of adrenaline and noradrenaline binding to adrenergic receptors?
Flashcards
What is Homeostasis?
What is Homeostasis?
The physiological process that maintains internal systems at equilibrium despite external changes.
Autonomic Nervous System
Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is a part of the peripheral nervous system that controls involuntary bodily functions like heart rate, digestion, and breathing.
Sympathetic Nervous System
Sympathetic Nervous System
The sympathetic nervous system activates the 'fight or flight' response, preparing the body for stressful situations.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Enteric Nervous System
Enteric Nervous System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sympathetic Nervous System Relay
Sympathetic Nervous System Relay
Signup and view all the flashcards
Preganglionic Neuron
Preganglionic Neuron
Signup and view all the flashcards
Postganglionic Neuron
Postganglionic Neuron
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the primary neurotransmitter released by postganglionic sympathetic neurons?
What is the primary neurotransmitter released by postganglionic sympathetic neurons?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the postganglionic neurons that release acetylcholine in the sympathetic nervous system called?
What are the postganglionic neurons that release acetylcholine in the sympathetic nervous system called?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are piloerector muscles?
What are piloerector muscles?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Which cranial nerves are associated with parasympathetic preganglionic neurons?
Which cranial nerves are associated with parasympathetic preganglionic neurons?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where are the parasympathetic preganglionic neurons located in the spinal cord?
Where are the parasympathetic preganglionic neurons located in the spinal cord?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the characteristics of preganglionic parasympathetic axons?
What are the characteristics of preganglionic parasympathetic axons?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the neurotransmitter released by postganglionic parasympathetic neurons?
What is the neurotransmitter released by postganglionic parasympathetic neurons?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the routes taken by preganglionic sympathetic axons?
What are the routes taken by preganglionic sympathetic axons?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the sympathetic chain?
What is the sympathetic chain?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are splanchnic nerves?
What are splanchnic nerves?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are prevertebral ganglia?
What are prevertebral ganglia?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where does the sympathetic chain extend?
Where does the sympathetic chain extend?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the white ramus?
What is the white ramus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the grey ramus?
What is the grey ramus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does the sympathetic nervous system affect the eye?
How does the sympathetic nervous system affect the eye?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does the sympathetic nervous system affect saliva?
How does the sympathetic nervous system affect saliva?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where is the myenteric plexus located?
Where is the myenteric plexus located?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where is the submucosal plexus located?
Where is the submucosal plexus located?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What do the sensory neurons in the myenteric plexus respond to?
What do the sensory neurons in the myenteric plexus respond to?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What do the sensory neurons in the submucosal plexus respond to?
What do the sensory neurons in the submucosal plexus respond to?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How independent is the enteric nervous system?
How independent is the enteric nervous system?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adrenal Medulla
Adrenal Medulla
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sympathetic Neurotransmitters
Sympathetic Neurotransmitters
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adrenergic Receptors
Adrenergic Receptors
Signup and view all the flashcards
α1 Adrenergic Receptor
α1 Adrenergic Receptor
Signup and view all the flashcards
β2 Adrenergic Receptor
β2 Adrenergic Receptor
Signup and view all the flashcards
β1 Adrenergic Receptor
β1 Adrenergic Receptor
Signup and view all the flashcards
α2 Adrenergic Receptor
α2 Adrenergic Receptor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lipolysis
Lipolysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are visceral sensory neurons?
What are visceral sensory neurons?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where are visceral sensory neurons located?
Where are visceral sensory neurons located?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are afferent neurons?
What are afferent neurons?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the nucleus of the solitary tract (NST)?
What is the nucleus of the solitary tract (NST)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does the NST receive information?
How does the NST receive information?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does the autonomic nervous system use visceral sensory information?
How does the autonomic nervous system use visceral sensory information?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does sensory feedback regulate the autonomic nervous system?
How does sensory feedback regulate the autonomic nervous system?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What do preganglionic neurons do?
What do preganglionic neurons do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Autonomic Nervous System Organization
- The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates internal body functions to maintain homeostasis.
- Homeostasis is the physiological process keeping internal body systems in equilibrium despite external changes.
Examples of Homeostatically Regulated Parameters
- Body temperature
- Blood pressure
- Hydration levels
- Acid-base balance
Autonomic Nervous System Structure
- The ANS is involuntary; we have no conscious control over its actions.
- It has three divisions: sympathetic, parasympathetic, and enteric.
Sympathetic Nervous System
- Active Division ("fight or flight"): involved in active or stressful situations.
- Increased heart rate: enhances blood flow to muscles.
- Pupil dilation: allows more light into the eyes.
- Bronchodilation: increases air intake.
- Redirected blood flow: prioritizes striated and cardiac muscles.
- Neurotransmitter: primarily norepinephrine (noradrenaline), with some acetylcholine use in sweat glands and piloerector muscles.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
- Passive division ("rest and digest"): involved in maintaining the body's everyday functions.
- Decreased heart rate: conserves energy.
- Pupil constriction: reduces light intake.
- Bronchoconstriction: reduces air intake.
- Blood flow redirection: directs blood to internal organs.
- Neurotransmitter: acetylcholine.
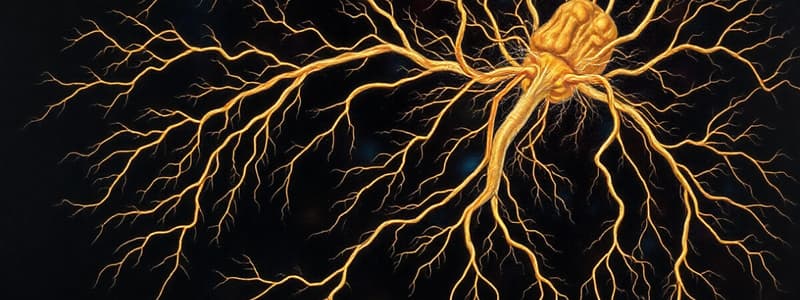
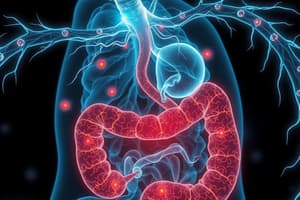
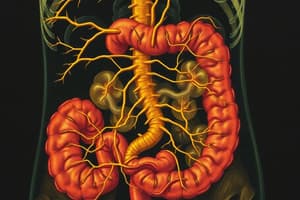
Enteric Nervous System
- Embedded in the digestive tract lining.
- Regulates gut motility and secretions such as:
- Increased motility (peristalsis)
- Mucus secretion
- Digestive enzyme secretion
Sympathetic Nervous System Pathway
- Two-neuron relay: preganglionic and postganglionic neurons.
- Preganglionic neurons originate in the spinal cord (T1-L2).
- They project to ganglia (paravertebral or prevertebral)
- Postganglionic neurons project to target tissues (smooth muscle, glands, cardiac muscle).
- Primarily releases norepinephrine (noradrenaline) as a neurotransmitter.
Parasympathetic Nervous System Pathway
- Two-neuron relay: preganglionic and postganglionic neurons.
- Preganglionic neurons in the brain stem (cranial nerves III, VII, IX, X) and sacral spinal cord (S2-S4).
- Postganglionic neurons are located in ganglia close to or within target organs.
- Primarily releases acetylcholine as a neurotransmitter.
ANS Neurotransmitters
- Sympathetic: norepinephrine (primarily) and (occasionally) acetylcholine.
- Parasympathetic: acetylcholine.
Multiple Receptors
- Multiple types of receptors for neurotransmitters (e.g., adrenergic and cholinergic receptors) lead to various effects on target tissues. Receptor type determines extent of effect.
Enteric Nervous System Organization
- The enteric nervous system (ENS) contains sensory (stretch, chemical), interneurons, and autonomic motor (visceromotor) neurons.
- Controls peristalsis (gut movement
- Regulates secretions
Regulation of ANS Activity
- Sensory feedback from target tissues regulates ANS activity.
- Visceral sensory neurons carry sensory information to brainstem nuclei that modulate ANS activity.
- Higher brain areas also influence the ANS.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.