Podcast
Questions and Answers
What does an energy diagram primarily represent in a chemical reaction?
What does an energy diagram primarily represent in a chemical reaction?
- The speed of molecular collisions
- The amount of reactants in the reaction
- The physical state of reactants and products
- The energy changes during a chemical reaction (correct)
Which factor does activation energy (Ea) directly influence in a chemical reaction?
Which factor does activation energy (Ea) directly influence in a chemical reaction?
- The number of reactants
- The amount of heat released
- The stability of products
- The rate of the reaction (correct)
In the context of an energy diagram, what characterizes an exothermic reaction?
In the context of an energy diagram, what characterizes an exothermic reaction?
- The energy of products is lower than that of reactants (correct)
- The reaction occurs without a transition state
- The energy of products is equal to reactants
- Heat is absorbed during the reaction
What is the transition state in a reaction as per the energy diagram?
What is the transition state in a reaction as per the energy diagram?
What does the heat of reaction, denoted as ΔH, represent?
What does the heat of reaction, denoted as ΔH, represent?
Which of the following best describes a reaction intermediate as shown on an energy diagram?
Which of the following best describes a reaction intermediate as shown on an energy diagram?
How does a large activation energy (Ea) affect the reaction rate?
How does a large activation energy (Ea) affect the reaction rate?
What distinguishes an endothermic reaction from an exothermic one based on energy changes?
What distinguishes an endothermic reaction from an exothermic one based on energy changes?
What best describes the rate-determining step in a multistep reaction?
What best describes the rate-determining step in a multistep reaction?
In the context of proton transfer, which of the following statements is correct?
In the context of proton transfer, which of the following statements is correct?
Which mechanism pattern involves the interaction of an electron-poor and an electron-rich species?
Which mechanism pattern involves the interaction of an electron-poor and an electron-rich species?
What occurs during the mechanism pattern of taking a proton away?
What occurs during the mechanism pattern of taking a proton away?
What is the primary characteristic of intermediates in chemical reactions?
What is the primary characteristic of intermediates in chemical reactions?
Which pattern correctly describes the result of proton addition across a C—C double bond?
Which pattern correctly describes the result of proton addition across a C—C double bond?
Which statement about nucleophiles is accurate?
Which statement about nucleophiles is accurate?
Which of the following is NOT a common mechanism pattern mentioned?
Which of the following is NOT a common mechanism pattern mentioned?
What is the primary reason for the regioselectivity in Markovnikov's rule?
What is the primary reason for the regioselectivity in Markovnikov's rule?
Which type of rearrangement occurs when a methyl group migrates from one carbon to another in a carbocation?
Which type of rearrangement occurs when a methyl group migrates from one carbon to another in a carbocation?
What is the result of the first step of hydration when adding H2O to an alkene?
What is the result of the first step of hydration when adding H2O to an alkene?
What type of rearrangement is commonly observed in carbocations?
What type of rearrangement is commonly observed in carbocations?
What happens during the rearrangement process of a carbocation?
What happens during the rearrangement process of a carbocation?
What does the term 'regioselective' imply in the context of alkene reactions?
What does the term 'regioselective' imply in the context of alkene reactions?
Which reaction is NOT a type that carbocation intermediates undergo?
Which reaction is NOT a type that carbocation intermediates undergo?
In the reaction of HCl with an alkene, what might the addition of hydrogen result in?
In the reaction of HCl with an alkene, what might the addition of hydrogen result in?
What is the result of the addition of Cl2 or Br2 to a cycloalkene?
What is the result of the addition of Cl2 or Br2 to a cycloalkene?
What type of bond is formed when a nucleophile reacts with an electrophile in a carbocation mechanism?
What type of bond is formed when a nucleophile reacts with an electrophile in a carbocation mechanism?
What is the significance of the 3° carbocation in the rearrangement mechanism?
What is the significance of the 3° carbocation in the rearrangement mechanism?
What is the final step in the mechanism of carbocation rearrangement involving an electrophile?
What is the final step in the mechanism of carbocation rearrangement involving an electrophile?
What occurs during the first step of the addition of Br2 to an alkene?
What occurs during the first step of the addition of Br2 to an alkene?
Which of the following best describes the stereochemical outcome of the reaction involving a bromonium ion?
Which of the following best describes the stereochemical outcome of the reaction involving a bromonium ion?
What was the historical industrial use of tert-butylmethyl ether?
What was the historical industrial use of tert-butylmethyl ether?
What modification to carbocations increases their stability?
What modification to carbocations increases their stability?
What type of product is formed when chlorine or bromine adds to cyclohexene?
What type of product is formed when chlorine or bromine adds to cyclohexene?
In hydroboration-oxidation reactions, which of the following statements is true regarding the addition of –H and –OH to the double bond?
In hydroboration-oxidation reactions, which of the following statements is true regarding the addition of –H and –OH to the double bond?
Which catalysts are most commonly used for the catalytic reduction of alkenes?
Which catalysts are most commonly used for the catalytic reduction of alkenes?
What is the predominant stereochemical characteristic of catalytic hydrogenation?
What is the predominant stereochemical characteristic of catalytic hydrogenation?
How does the degree of substitution of a double bond affect its heat of hydrogenation?
How does the degree of substitution of a double bond affect its heat of hydrogenation?
Which statement explains the relationship between the stability of a trans alkene compared to a cis alkene?
Which statement explains the relationship between the stability of a trans alkene compared to a cis alkene?
In the addition of hydrogens to alkenes via a transition metal catalyst, which facet of the double bond do both hydrogens add to?
In the addition of hydrogens to alkenes via a transition metal catalyst, which facet of the double bond do both hydrogens add to?
What conformation is initially created during the addition of halogens to cyclohexene before reaching equilibrium?
What conformation is initially created during the addition of halogens to cyclohexene before reaching equilibrium?
Which catalyst is commonly used to achieve syn stereoselective reduction of alkynes?
Which catalyst is commonly used to achieve syn stereoselective reduction of alkynes?
What product is formed when acetylene is reduced with one mole of H2 using the Lindlar catalyst?
What product is formed when acetylene is reduced with one mole of H2 using the Lindlar catalyst?
Which of the following compounds can be synthesized from acetylene using the appropriate reactions?
Which of the following compounds can be synthesized from acetylene using the appropriate reactions?
What is the definitive characteristic of the stereoselectivity when reducing alkynes with the Lindlar catalyst?
What is the definitive characteristic of the stereoselectivity when reducing alkynes with the Lindlar catalyst?
What type of alcohol can be produced by the reduction of 1-Butene?
What type of alcohol can be produced by the reduction of 1-Butene?
Which compound could serve as a starting material for creating cis-3-Hexene?
Which compound could serve as a starting material for creating cis-3-Hexene?
In the reduction of alkynes to alkenes, the intermediate produced before hydrogenation is typically considered to be what?
In the reduction of alkynes to alkenes, the intermediate produced before hydrogenation is typically considered to be what?
Which reagent is necessary in addition to acetylene to synthesize 3,4-Dibromohexane?
Which reagent is necessary in addition to acetylene to synthesize 3,4-Dibromohexane?
Flashcards
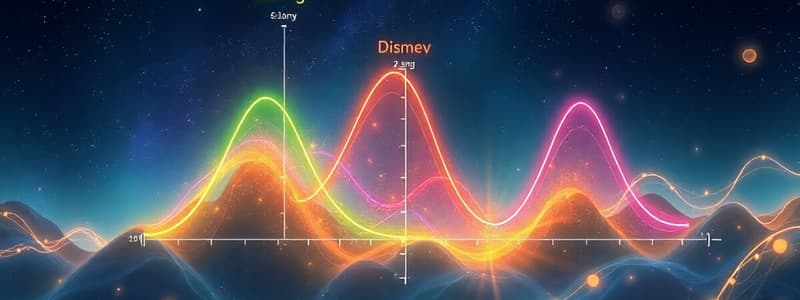
Energy Diagram
Energy Diagram
A graph showing energy changes during a chemical reaction.
Transition State
Transition State
Unstable, high-energy species formed during a reaction. It's the peak on an energy diagram.
Activation Energy (Ea)
Activation Energy (Ea)
Energy difference between reactants and the transition state; controls reaction rate.
Exothermic Reaction
Exothermic Reaction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endothermic Reaction
Endothermic Reaction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reaction Intermediate
Reaction Intermediate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Heat of Reaction (ΔH)
Heat of Reaction (ΔH)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reaction Rate
Reaction Rate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rate-determining step
Rate-determining step
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intermediate
Intermediate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Electrophile
Electrophile
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nucleophile
Nucleophile
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proton transfer
Proton transfer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mechanism pattern 1
Mechanism pattern 1
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mechanism pattern 2
Mechanism pattern 2
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mechanism pattern 3
Mechanism pattern 3
Signup and view all the flashcards
Markovnikov's Rule
Markovnikov's Rule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Carbocation Stability
Carbocation Stability
Signup and view all the flashcards
Carbocation Rearrangement
Carbocation Rearrangement
Signup and view all the flashcards
1,2-shift
1,2-shift
Signup and view all the flashcards
Electrophilic Addition
Electrophilic Addition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hydration of an alkene
Hydration of an alkene
Signup and view all the flashcards
Regioselective
Regioselective
Signup and view all the flashcards
Types of Carbocation Reactions
Types of Carbocation Reactions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nucleophile Addition
Nucleophile Addition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proton Loss
Proton Loss
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stereoselective Reaction
Stereoselective Reaction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anti Stereoselectivity
Anti Stereoselectivity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lindlar Catalyst
Lindlar Catalyst
Signup and view all the flashcards
Syn Stereoselective
Syn Stereoselective
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is 1-Butyne synthesized?
How is 1-Butyne synthesized?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is 1-Butene synthesized?
How is 1-Butene synthesized?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is 1-Butanol synthesized?
How is 1-Butanol synthesized?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is 2-Butanol synthesized?
How is 2-Butanol synthesized?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is 3-Hexyne synthesized?
How is 3-Hexyne synthesized?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is cis-3-Hexene synthesized?
How is cis-3-Hexene synthesized?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trans-Diaxial Addition
Trans-Diaxial Addition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trans-Diequatorial Conformation
Trans-Diequatorial Conformation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anti Addition
Anti Addition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Syn Addition
Syn Addition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Catalytic Reduction
Catalytic Reduction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Heat of Hydrogenation
Heat of Hydrogenation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stability of Alkenes
Stability of Alkenes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trans Isomers
Trans Isomers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Introduction to Organic Chemistry - Chapter 5
- Chapter 5 focuses on Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes.
Reactions of Alkenes
- Hydrohalogenation (Hydrochlorination, Hydrobromination, Hydroiodination): A double bond reacts with HX (where X = Cl, Br, or I) causing the pi bond to break and sigma bonds form.
- Hydration: A double bond reacts with H₂O (water) forming a sigma bond to the oxygen.
- Halogenation: Double bond reacts with X₂ (Cl₂ or Br₂) forming sigma bonds to the X atoms.
- Hydroboration: A double bond reacts with BH₃, a boron-containing compound.
Energy Diagrams
- Energy Diagram: A graph depicting energy changes during a chemical reaction. Energy is plotted on the y-axis, and reaction progress is plotted on the x-axis.
- Figure 5.1: A one-step exothermic reaction of C with A-B to form C-A and B.
- Transition state: An unstable species of maximum energy formed during a reaction.
- Activation energy (Ea): The difference in energy between the reactants and the transition state.
- Heat of Reaction (ΔH): The difference in energy between reactants and products.
- Exothermic reaction: A reaction releases heat
- Endothermic reaction: A reaction absorbs heat
Energy Diagram (Continued)
- Reaction intermediate: An energy minimum between two transition steps in a complex reaction; usually highly reactive.
- Rate-determining step: The slowest step in a multistep reaction, which involves the highest activation energy.
Mechanism Patterns
- Pattern 1: Add a Proton: A proton is added across a carbon-carbon double bond, typically catalyzed by an acid.
- Pattern 2: Take a Proton Away: Reversing Pattern 1, a proton is removed from a molecule.
- Pattern 3: Reaction of an Electrophile and a Nucleophile: An electron-poor species (electrophile) and an electron-rich species (nucleophile) react to form a new covalent bond.
- Electrophile: An electron-poor species that can accept a pair of electrons to form a bond.
- Nucleophile: An electron-rich species that can donate a pair of electrons to form a bond.
- Pattern 4: Rearrangement of a Bond: Electrons of a sigma bond move to connect an adjacent atom. Commonly seen with carbocations
- Pattern 5: Break a Bond to Form a Stable Molecule/Ion: A bond breaks, and electrons move with a fragment to form a stable molecule. The fragment removed is called the leaving group.
Electrophilic Additions to Alkenes
- Addition of Hydrogen Halides (HCl, HBr, HI): Alkenes react with hydrogen halides to yield alkyl halides.
- Addition of Water (H₂O/H₂SO₄): Alkenes react with water under acid conditions to produce alcohols (hydration).
- Addition of Halogens (Cl₂, Br₂): Alkenes react with halogens to produce vicinal dihalides.
Addition of Hydrogen Halides
-
Regioselective: A reaction that forms one product from a pair of possible regioisomers
-
Markovnikov's rule: In the addition of HX to a double bond, the hydrogen adds to the carbon with more hydrogens already attached.
Regioselectivity
- Markovnikov's rule examples: Illustrates cases for how products vary based on the substituent placement.
Carbocation
- Figure 5.3: The structure and orbital interactions of a tert-butyl carbocation
- Carbocation: Species containing a positively charged carbon bonded to three other atoms.
- Stability (3° > 2° > 1°): Carbocation stability increases with the number of alkyl groups attached to the positively charged carbon.
- Inductive Effect: The polarization of electron density in a covalent bond due to a nearby electronegative atom.
Carbocation Rearrangements
- Rearrangement: A reaction that changes the connectivity of atoms in a molecule.
- 1,2-shift: A rearrangement where an alkyl group moves from one atom to an adjacent atom in a molecule.
- Carbocation Intermediate: Intermediate stage in a reaction where a positively charged carbon is formed.
- Mechanism for acid-catalyzed hydration reactions
Addition of H₂O to an Alkene
- Hydration: Addition of water to an alkene, usually catalyzed by acid.
- Markovnikov's rule in Hydration: Addition follows Markovnikov's rule for hydration
Reduction of Alkenes
- Catalytic Reduction (Hydrogenation): Alkenes react with Hydrogen (H₂) in the presence of metal catalysts (Pd, Pt, Ni) to give alkanes
- Syn Stereoselectivity: Addition of hydrogen to the same face of the double bond.
- Lindlar Catalyst: Special catalyst to reduce alkynes to alkenes, with syn steroselectivity.
Heats of Hydrogenation
- Heat of hydrogenation: The energy released when a double bond is saturated.
Reactions of Alkynes
- Acidity of Terminal Alkynes: Terminal alkynes are weak acids compared to alkanes & alkenes
Alkylation of Terminal Alkynes
- Acetylide anion: A nucleophile and base that alkylates terminal alkynes.
- Alkylation reaction: Adding an alkyl group to the terminal alkyne.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.