Podcast
Questions and Answers
Hormones released directly into the extracellular fluid are characteristic of which type of gland?
Hormones released directly into the extracellular fluid are characteristic of which type of gland?
- Exocrine
- Holocrine
- Apocrine
- Endocrine (correct)
What is the primary function of hormones?
What is the primary function of hormones?
- To digest food
- To transport oxygen
- To act as chemical messengers (correct)
- To fight infections
Which of the following glands is located in the Sella Turcica of the sphenoid bone?
Which of the following glands is located in the Sella Turcica of the sphenoid bone?
- Pineal gland
- Pituitary gland (correct)
- Thyroid gland
- Adrenal gland
Which hormone directly stimulates the thyroid gland?
Which hormone directly stimulates the thyroid gland?
Which hormone stimulates sperm production in males?
Which hormone stimulates sperm production in males?
Which hormone primarily targets the adrenal cortex?
Which hormone primarily targets the adrenal cortex?
Which of the following non-tropic hormones leads to milk production?
Which of the following non-tropic hormones leads to milk production?
What is the primary effect of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)?
What is the primary effect of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)?
Which hormone is secreted by the pineal gland?
Which hormone is secreted by the pineal gland?
What effect does calcitonin have on calcium levels in the blood?
What effect does calcitonin have on calcium levels in the blood?
Which hormone increases blood calcium levels?
Which hormone increases blood calcium levels?
The thymus gland is MOST closely associated with which bodily system?
The thymus gland is MOST closely associated with which bodily system?
Epinephrine is secreted by which part of the adrenal gland?
Epinephrine is secreted by which part of the adrenal gland?
Which hormone increases sodium absorption in the kidneys?
Which hormone increases sodium absorption in the kidneys?
Which hormone is secreted by the pancreas in response to decreased blood glucose levels?
Which hormone is secreted by the pancreas in response to decreased blood glucose levels?
Which hormones regulate the menstrual cycle?
Which hormones regulate the menstrual cycle?
Which hormone promotes the development of male reproductive organs?
Which hormone promotes the development of male reproductive organs?
What is a key characteristic of endocrine glands compared to exocrine glands?
What is a key characteristic of endocrine glands compared to exocrine glands?
Damage to the anterior pituitary could directly impair the function of which of the following?
Damage to the anterior pituitary could directly impair the function of which of the following?
Which of the following hormones is NOT produced by the anterior pituitary gland?
Which of the following hormones is NOT produced by the anterior pituitary gland?
What is the relationship between GnRH and FSH?
What is the relationship between GnRH and FSH?
If a patient presents with hypercalcemia (elevated blood calcium levels), which of the following hormonal imbalances is LEAST likely to be the cause?
If a patient presents with hypercalcemia (elevated blood calcium levels), which of the following hormonal imbalances is LEAST likely to be the cause?
A researcher is investigating a new hormone that increases the rate of protein synthesis, conserves glucose, and stimulates body growth. This hormone is MOST likely:
A researcher is investigating a new hormone that increases the rate of protein synthesis, conserves glucose, and stimulates body growth. This hormone is MOST likely:
Which of the following hormones is NOT directly involved in stress response?
Which of the following hormones is NOT directly involved in stress response?
A patient is experiencing difficulty with milk ejection during breastfeeding. Which hormone is MOST likely deficient?
A patient is experiencing difficulty with milk ejection during breastfeeding. Which hormone is MOST likely deficient?
If the zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex were damaged, the production of which hormone would be MOST directly affected?
If the zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex were damaged, the production of which hormone would be MOST directly affected?
A deficiency in the production of mineralocorticoids by the adrenal cortex would MOST likely result in which of the following?
A deficiency in the production of mineralocorticoids by the adrenal cortex would MOST likely result in which of the following?
Which pancreatic hormone facilitates the conversion of glucose into glycogen?
Which pancreatic hormone facilitates the conversion of glucose into glycogen?
A patient presents with an enlarged thyroid gland (goiter) and elevated levels of T3 and T4. However, their TSH levels are very low. What is the MOST likely explanation?
A patient presents with an enlarged thyroid gland (goiter) and elevated levels of T3 and T4. However, their TSH levels are very low. What is the MOST likely explanation?
Which hormone is synthesized from cholesterol?
Which hormone is synthesized from cholesterol?
Which process would be directly inhibited by a drug that blocks the action of GnRH?
Which process would be directly inhibited by a drug that blocks the action of GnRH?
A researcher discovers a novel hormone that stimulates the activity of osteoblasts. Which gland is MOST likely responsible for secreting this hormone?
A researcher discovers a novel hormone that stimulates the activity of osteoblasts. Which gland is MOST likely responsible for secreting this hormone?
You are studying a cell sample and observe numerous large cells with abundant colloid-filled follicles. This sample is MOST likely from which gland?
You are studying a cell sample and observe numerous large cells with abundant colloid-filled follicles. This sample is MOST likely from which gland?
Predict the consequences of a mutation causing malfunctioning chromaffin cells:
Predict the consequences of a mutation causing malfunctioning chromaffin cells:
Which of the following describes a hormone that does NOT directly affect its target tissue, but instead stimulates another gland to release its own hormone?
Which of the following describes a hormone that does NOT directly affect its target tissue, but instead stimulates another gland to release its own hormone?
A patient undergoes a procedure that damages a portion of their hypothalamus. Post-surgery, the patient experiences extreme dehydration despite adequate fluid intake. Which hormone is MOST likely affected?
A patient undergoes a procedure that damages a portion of their hypothalamus. Post-surgery, the patient experiences extreme dehydration despite adequate fluid intake. Which hormone is MOST likely affected?
A new drug selectively inhibits the conversion of T4 to T3 in peripheral tissues. Predict the MOST likely outcome:
A new drug selectively inhibits the conversion of T4 to T3 in peripheral tissues. Predict the MOST likely outcome:
A researcher isolates a hormone that is found to be bound to a transport protein in the bloodstream. Which type of hormone is this MOST likely to be?
A researcher isolates a hormone that is found to be bound to a transport protein in the bloodstream. Which type of hormone is this MOST likely to be?
Flashcards
Hormones
Hormones
Chemical messengers that are released directly into extracellular fluid.
Exocrine Gland
Exocrine Gland
A gland that secrets hormones into extracellular fluid via ducts.
Pituitary Gland
Pituitary Gland
Located in the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone, the gland has two lobes.
TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone)
TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone)
Signup and view all the flashcards
FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone)
FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone)
Signup and view all the flashcards
LH (Luteinizing Hormone)
LH (Luteinizing Hormone)
Signup and view all the flashcards
ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic Hormone)
ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic Hormone)
Signup and view all the flashcards
GH (Growth Hormone)
GH (Growth Hormone)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prolactin
Prolactin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxytocin
Oxytocin
Signup and view all the flashcards
ADH (Anti-Diuretic Hormone)
ADH (Anti-Diuretic Hormone)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pineal Gland
Pineal Gland
Signup and view all the flashcards
T3 and T4
T3 and T4
Signup and view all the flashcards
Calcitonin
Calcitonin
Signup and view all the flashcards
PTH (Parathyroid Hormone)
PTH (Parathyroid Hormone)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thymus
Thymus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Aldosterone
Aldosterone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cortisol
Cortisol
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gonadocorticoids
Gonadocorticoids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adrenal Medulla Hormones
Adrenal Medulla Hormones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Insulin
Insulin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glucagon
Glucagon
Signup and view all the flashcards
LH and FSH
LH and FSH
Signup and view all the flashcards
Estrogens and Progesterone
Estrogens and Progesterone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Testosterone
Testosterone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Hormones
- Chemical messengers that function mostly endocrine, but some are mixed.
- Released directly into extracellular fluid.
- Exocrine glands secrete into ducts.
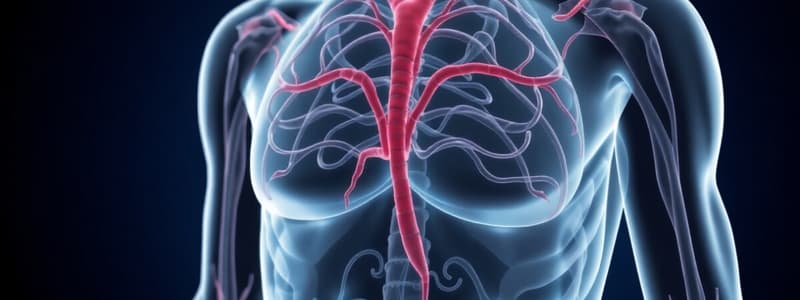
Glands
- Pituitary (anterior and posterior)
- Thyroid
- Parathyroid
- Thymus
- Pineal
- Adrenal
- Pancreas
- Gonads
Pituitary Gland
- Located in the Sella Turcica of the sphenoid bone.
- Contains 2 lobes: Anterior and Posterior.
- The anterior secretes more.
Anterior Pituitary
- Manufactures four tropic hormones that target glands to release other hormones
- TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) = targets the thyroid and stimulates secretion of thyroid hormones.
- FSH = stimulated by GnRH (Gonadotropin releasing hormone) and targets the gonads.
- FSH stimulates sperm production in males, and ovarian follicle maturation/estrogen production in females.
- LH = stimulated by GnRH and leads to testosterone production in males.
- LH = ovulation/estrogen + progesterone production in females.
- ACTH = CRH stimulates release (Corticotropin Releasing Hormone) and targets the adrenal cortex.
- CRH and GnRH are released by the hypothalamus and target the anterior pituitary.
Anterior Pituitary Non-Tropic hormones
- GH (Growth Hormone) and GHRH (growth hormone releasing hormone stimulates release).
- GH and GHRH target the liver, muscle, bone, and cartilage.
- They also stimulate body growth, protein synthesis, and conserve glucose.
- Prolactin = Decrease in Prolactin inhibition hormone stimulates release, which then leads to milk production.
Posterior Pituitary
- Oxytocin stimulates powerful uterine contractions during birth and also stimulates milk ejection.
- ADH targets kidneys and leads to water conservation (Anti-Diuretic Hormone).
- Both oxytocin and ADH are stimulated by impulses from the hypothalamus.
Pineal Gland
- Secretes melatonin, exhibiting a daily cycle.
Thyroid
- Produces Thyroglobulin which is known as T3 and TH Precursor.
- T3 and T4 are stimulated by TSH.
- T3 and T4 increase basal metabolic rate and regulates tissue growth and development.
- Calcitonin = causes deposit of calcium in bones.
- C-cells produce calcitonin.
- Thyroid globulin makes T3 and T4.
- T3 and T4 are released into extracellular fluid.
Parathyroid Gland
- PTH (Parathyroid hormone) = low levels of calcium in the blood stimulates release.
- PTH targets bones and kidneys, increasing blood calcium by stimulating osteoclasts and kidneys to reabsorb calcium.
Thymus
- Produces peptide hormones, which may play a role in T lymphocyte development.
- It helps in the immune system (white blood cells).
Adrenal Gland (medulla)
- Epinephrine and Norepinephrine are produced by chromaffin cells.
Adrenal Gland (cortex)
- Zona glomerulosa produces Mineral corticoids in the superficial layer.
- Zona fasciculata produces Glucocorticoids in the middle layer.
- Zona reticularis produces Gonadocorticoids in the deep layer.
- Aldosterone (mineralcorticoid) increases sodium absorption and H20 absorption (in the glomerusa layer of cortex).
- Aldosterone also increases K secretion.
- Cortisol (glucocorticoids) breaks down fat and protein, inhibits the immune response, and is secreted from the fasciculata of cortex.
- Gonadocorticoids are mostly converted to testosterone and estrogen in the reticularis layer of cortex.
- Epinephrine and Norepinephrine is essentially the "fight or flight" or response, they increase the heart rate in response to some stimuli.
Pancreas
- Insulin: an increase of glucose blood levels increases insulin release and transport of glucose.
- Glucose is then converted into glycogen, fat and protein.
- Glucagon: a decrease of glucose blood levels increases glucagon release and leads to the break down of glycogen and lactic acid into glucose.
Gonads
- Estrogen is stimulated by LH and FSH release, leading to female reproductive organ maturation.
- Estrogens and Progestrone regulate the menstrual cycle and breast development.
- Testosterone promotes male reproductive organ development, sperm production, and sex drive.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.