Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following cellular processes is LEAST involved in the transformation of a zygote into a morula?
Which of the following cellular processes is LEAST involved in the transformation of a zygote into a morula?
- DNA Replication
- Cell Differentiation (correct)
- Mitosis
- Cell Adhesion
A researcher is investigating the effects of a novel drug on early embryonic development. They observe that the drug prevents the formation of the blastocoel. Which of the following developmental processes is MOST likely being directly inhibited by this drug?
A researcher is investigating the effects of a novel drug on early embryonic development. They observe that the drug prevents the formation of the blastocoel. Which of the following developmental processes is MOST likely being directly inhibited by this drug?
- Gastrulation
- Fertilization
- Blastulation (correct)
- Cleavage
Which of the following statements correctly describes the temporal sequence of events in early embryonic development?
Which of the following statements correctly describes the temporal sequence of events in early embryonic development?
- Fertilization → Blastulation → Cleavage → Gastrulation
- Fertilization → Cleavage → Blastulation → Gastrulation (correct)
- Fertilization → Gastrulation → Cleavage → Blastulation
- Cleavage → Fertilization → Blastulation → Gastrulation
During gastrulation, cells migrate to form three primary germ layers. If a disruption occurred preventing the formation of the mesoderm, which of the following structures would be MOST affected?
During gastrulation, cells migrate to form three primary germ layers. If a disruption occurred preventing the formation of the mesoderm, which of the following structures would be MOST affected?
Which of the following BEST describes the role of uterine secretions during the early stages of embryonic development?
Which of the following BEST describes the role of uterine secretions during the early stages of embryonic development?
After fertilization, the zygote undergoes rapid mitotic cell division. What would be the MOST likely consequence if cleavage occurred without a corresponding increase in overall cytoplasmic volume?
After fertilization, the zygote undergoes rapid mitotic cell division. What would be the MOST likely consequence if cleavage occurred without a corresponding increase in overall cytoplasmic volume?
If a drug known to inhibit the production of prostaglandins is administered to a pregnant woman near full term, which process would be MOST likely affected?
If a drug known to inhibit the production of prostaglandins is administered to a pregnant woman near full term, which process would be MOST likely affected?
Which physiological change is a component of the initiation of labor?
Which physiological change is a component of the initiation of labor?
If a fetus is determined to have testes, and thus is an XY fetus, by which week of development would the sex-determining pathways be activated?
If a fetus is determined to have testes, and thus is an XY fetus, by which week of development would the sex-determining pathways be activated?
Which of the following BEST describes the developmental stage when the embryo first enters the uterus?
Which of the following BEST describes the developmental stage when the embryo first enters the uterus?
Which function is NOT performed by the ectoderm?
Which function is NOT performed by the ectoderm?
Sperm must make their way where for fertilization to be possible?
Sperm must make their way where for fertilization to be possible?
Approximately how many hours after fertilization does the morula form?
Approximately how many hours after fertilization does the morula form?
Approximately how many days after fertilization does the blastula form?
Approximately how many days after fertilization does the blastula form?
Implantation occurs how many days after fertilization?
Implantation occurs how many days after fertilization?
What is the first thing the embryo undergoes?
What is the first thing the embryo undergoes?
Up to how many weeks does the embryo exist as the developmental stage from the start of cleavage?
Up to how many weeks does the embryo exist as the developmental stage from the start of cleavage?
During which trimester does the circulatory and respiratory systems mature in preparation for air breathing?
During which trimester does the circulatory and respiratory systems mature in preparation for air breathing?
During which trimester are footprints and fingerprints formed?
During which trimester are footprints and fingerprints formed?
By which week are all organ systems formed?
By which week are all organ systems formed?
The embryo becomes a fetus by which week?
The embryo becomes a fetus by which week?
The scientific name for embryonic development is embryogenesis. What does embryogenesis entail?
The scientific name for embryonic development is embryogenesis. What does embryogenesis entail?
What is the first cell of a new individual called?
What is the first cell of a new individual called?
Where does fertilization occur?
Where does fertilization occur?
Which of the following is the definition of implantation?
Which of the following is the definition of implantation?
At the end of the first trimester in the fetus, which of the following is NOT true?
At the end of the first trimester in the fetus, which of the following is NOT true?
At the end of the second trimester in the fetus, which of the following is NOT true?
At the end of the second trimester in the fetus, which of the following is NOT true?
During which stage of pregnancy does the baby have fat under its skin and smooth wrinkles?
During which stage of pregnancy does the baby have fat under its skin and smooth wrinkles?
The initiation of labor includes all of the following EXCEPT:
The initiation of labor includes all of the following EXCEPT:
Before the gonads form, what determines the gender?
Before the gonads form, what determines the gender?
What stage of pregnancy is the 'beginning of human development'?
What stage of pregnancy is the 'beginning of human development'?
Labor during Childbirth is defined as which of the following?
Labor during Childbirth is defined as which of the following?
Which of the following is true about the viability of the egg, post ovulation?
Which of the following is true about the viability of the egg, post ovulation?
Which of the following is true about the viability of the sperm, post ejaculation?
Which of the following is true about the viability of the sperm, post ejaculation?
What is the chronological ordering of the stages of pregnancy and development?
What is the chronological ordering of the stages of pregnancy and development?
Which of the following is the definition of Cleavage?
Which of the following is the definition of Cleavage?
When is the fetal stage?
When is the fetal stage?
Flashcards
Embryonic Development
Embryonic Development
The process where an embryo is formed and develops, starting with the fertilization of an egg (zygote) and involving rapid cell divisions.
Embryogenesis
Embryogenesis
The scientific term for embryonic development.
Fertilization
Fertilization
The fusion of sperm and egg to form a zygote, initiating the development of a new individual.
Cleavage (Embryonic Development)
Cleavage (Embryonic Development)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fetal Differentiation
Fetal Differentiation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovulation
Ovulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Zygote
Zygote
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fallopian Tubes
Fallopian Tubes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Morula
Morula
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blastula
Blastula
Signup and view all the flashcards
Implantation
Implantation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Embryo (Stage)
Embryo (Stage)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gastrulation
Gastrulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ectoderm
Ectoderm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endoderm
Endoderm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mesoderm
Mesoderm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Differentiation (Embryo)
Differentiation (Embryo)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fetus (2 Months)
Fetus (2 Months)
Signup and view all the flashcards
2 Months Fetus
2 Months Fetus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fetus (4 Months)
Fetus (4 Months)
Signup and view all the flashcards
7 Months Fetus
7 Months Fetus
Signup and view all the flashcards
9 Months Fetus
9 Months Fetus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Childbirth (Labor)
Childbirth (Labor)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Initiation of labor
Initiation of labor
Signup and view all the flashcards
First 3 months
First 3 months
Signup and view all the flashcards
Second 3 months
Second 3 months
Signup and view all the flashcards
Third 3 months
Third 3 months
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Embryonic development is when the embryo forms and develops.
- It starts with the fertilization of an egg, which then becomes a zygote.
- The zygote then undergoes rapid cell division.
- The scientific name for embryonic development is embryogenesis.
- Stages of pregnancy and development include: fertilization, embryonic development (cleavage), fetal development (differentiation), growth and development, and childbirth.
Fertilization
- Fertilization is the first stage of pregnancy and development.
- Fertilization is when the sperm and egg join to form a zygote.
- The zygote is the first cell of a new individual.
- Fertilization occurs in the Fallopian tubes.
- The zygote begins rapid mitotic cell division.
- Beginning of human development.
- The egg is viable for 12 to 24 hours after ovulation.
- Sperm are viable for 12 to 48 hours after ejaculation.
- Sperm cells must travel to the uterine tube for fertilization to be possible.
- Only thirty hours after conception, the zygote is no larger than the head of a pin.
- The zygote is still rapidly dividing.
- The zygote floats down from the fallopian tube towards the uterus.
Cleavage
- Cleavage is mitotic division of the cells in the early embryo.
- About 96 hours after fertilization, the morula forms.
- The morula is a solid ball of 32 cells resembling a raspberry.
- Five days after fertilization, the blastula forms.
- The blastula is a ball of more than 64 cells surrounding a fluid-filled cavity (the blastocele).
- Blastula is produced by the repeated mitotic division of a zygote.
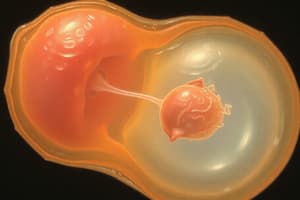
Implantation
- Implantation is the fastening of the embryo to the wall of the uterus.
- Implantation occurs seven days after fertilization.
- Implantation takes place in the uterus.
The Embryo
- The embryo is the developmental stage from the start of cleavage until the ninth week.
- The embryo first undergoes division without growth.
- The embryo enters the uterus at the 16-cell state.
- The embryo floats freely in the uterus temporarily.
- Uterine secretions are used for nourishment.
Differentiation and Gastrulation
- Gastrulation involves cell migrations to form the three primary cell layers.
- Ectoderm forms the outer layer and develops into skin, hair, sweat glands, epithelium, brain, and nervous system.
- Endoderm forms the inner layer and develops into digestive, respiratory systems, liver, pancreas, bladder, and endocrine glands like thyroid and parathyroid.
- Mesoderm forms the middle layer and develops into body muscles, cartilage, bone, blood, reproductive system organs, and kidneys.
- The embryo begins to form organs during the third week, about 20 days after fertilization, and reaches approximately 0.5 cm in size.
- It's difficult to determine if it's a human or another vertebrate at this stage but is tall and visible.
- After one month, the embryo is 0.6 cm long, with ears, nose, and eyes not visible yet
- Small arm and leg buds and backbone are seen, and the heart beats.
The Fetus
- During the second month, major organ systems form, and limb buds develop in the fetus, which is about 3 cm long.
- Limbs become distinct with fingers and toes forming, and eyes begin to separate.
- The embryo becomes a fetus by the seventh week.
- All organ systems are formed by the end of the eighth week.
- Activities of the fetus are growth and organ specialization.
- A stage of tremendous growth and change in appearance.
- Beginning the eighth week, the sexually neutral fetus activates gene pathways for sex determination, forming testes in XY fetuses and ovaries in XX fetuses.
- External genitalia develop.
- By four months, the fetus is 18 cm long with an enlarged head and human facial features.
- The fetus increases in size during this trimester, and bony parts of the skeleton begin to form.
- Fetal movements can be felt by the mother.
- During this trimester, the fetus increases in size
- Circulatory and respiratory systems mature in preparation for air breathing.
- Fetal growth during this time uses large parts of its mother's protein and calcium intake.
- Maternal antibodies pass to the fetus during the last month, conferring temporary immunity.
- Fat develops under the skin, smoothing out wrinkles.
- Nails on fingers and toes are completely formed.
- Baby is at term.
Childbirth (Partition)
- Labor is a series of events that expel the infant from the uterus.
- Initiation of labor includes: rise in estrogen levels, the beginning of uterine contractions, the placenta releasing prostaglandins, the pituitary releasing oxytocin, and the combination of these hormones produces contractions.
Developmental Aspects of the Reproductive System
- Gender is determined at fertilization.
- Males have XY sex chromosomes.
- Females have XX sex chromosomes.
- Gonads do not begin to form until the eighth week.
The First Trimester
- The first trimester is when the cell starts to divide.
- The zygote begins to develop.
- At the end of this trimester, the head is round, eyes are closed, taste buds are forming, internal organs move into the body cavity, and upper and lower limbs are formed.
The Second Trimester
- In the second trimester, the baby is becoming more developed.
- At the end of the trimester, the baby's eyes are open, the sex is determined, and the baby weighs 12.5 ounces with growing bones and muscles.
The Third Trimester
- In the third trimester, the baby is developing.
- Footprints and fingerprints are formed, eyelids open and close, brain development grows rapidly, and the baby is born.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.