Podcast
Questions and Answers
During male sexual differentiation, what is the role of Sertoli cells?
During male sexual differentiation, what is the role of Sertoli cells?
- To secrete anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH), causing the regression of the paramesonephric ducts. (correct)
- To secrete testosterone, promoting the development of male secondary sexual characteristics.
- To differentiate into Leydig cells.
- To penetrate the medulla and condense into seminiferous cords.
What is the consequence of the failure of the sinovaginal bulbs to develop?
What is the consequence of the failure of the sinovaginal bulbs to develop?
- Double uterus
- Imperforate hymen
- Bicornuate uterus
- Absence of the vagina (correct)
In male external genitalia development, what is the origin and the ultimate structure formed from the labioscrotal swellings?
In male external genitalia development, what is the origin and the ultimate structure formed from the labioscrotal swellings?
- Originate from the urethral folds and fuse to form the scrotum.
- Originate from the paramesonephric duct and develop into the prostate gland.
- Originate from the mesonephric duct and fuse to form the bulbourethral glands.
- Originate as paired structures that grow towards each other and fuse to form the scrotum. (correct)
Which event is dependent on the secretion of androgens by the fetal testes?
Which event is dependent on the secretion of androgens by the fetal testes?
Which structure in the female reproductive system is derived from the unfused cranial part of the paramesonephric duct?
Which structure in the female reproductive system is derived from the unfused cranial part of the paramesonephric duct?
How does the determination of genetic sex occur during embryonic development?
How does the determination of genetic sex occur during embryonic development?
What is the significance of the tunica albuginea in the developing ovary?
What is the significance of the tunica albuginea in the developing ovary?
Which developmental event leads to the formation of the rectouterine pouch and vesicouterine pouch?
Which developmental event leads to the formation of the rectouterine pouch and vesicouterine pouch?
What developmental process is disrupted in an individual with complete androgen insensitivity syndrome (AIS) and a 46,XY karyotype?
What developmental process is disrupted in an individual with complete androgen insensitivity syndrome (AIS) and a 46,XY karyotype?
How does the caudal end of the paramesonephric duct contribute to the development of the female reproductive tract?
How does the caudal end of the paramesonephric duct contribute to the development of the female reproductive tract?
Which of the following is the most accurate description of the role of the mesonephric duct in female development?
Which of the following is the most accurate description of the role of the mesonephric duct in female development?
A newborn male presents with an underdeveloped penis and the urethral orifice on the ventral surface near the junction of the penis and scrotum. Which developmental anomaly is most likely present?
A newborn male presents with an underdeveloped penis and the urethral orifice on the ventral surface near the junction of the penis and scrotum. Which developmental anomaly is most likely present?
Which of the following statements best describes the etiology of congenital ovarian hypoplasia syndrome?
Which of the following statements best describes the etiology of congenital ovarian hypoplasia syndrome?
What is the embryonic origin of the prostatic utricle in males?
What is the embryonic origin of the prostatic utricle in males?
Which statement accurately describes the initial stage of gonadal development?
Which statement accurately describes the initial stage of gonadal development?
Failure of the processus vaginalis to close in males can directly lead to which condition?
Failure of the processus vaginalis to close in males can directly lead to which condition?
What is the mechanism by which the indifferent gonad differentiates into a testis in males?
What is the mechanism by which the indifferent gonad differentiates into a testis in males?
What structures are formed by the sinovaginal bulbs?
What structures are formed by the sinovaginal bulbs?
Which abnormal condition results from incomplete separation of the cloaca?
Which abnormal condition results from incomplete separation of the cloaca?
Which structure gives rise to a sinus tubercle?
Which structure gives rise to a sinus tubercle?
What process stimulates the development of the uterine tube, uterus, and the superior part of the vagina?
What process stimulates the development of the uterine tube, uterus, and the superior part of the vagina?
Which statement is accurate regarding the development of female external genitalia?
Which statement is accurate regarding the development of female external genitalia?
Which condition is most commonly the cause of Hypospadias?
Which condition is most commonly the cause of Hypospadias?
What is the location of the urethra in Epispadias?
What is the location of the urethra in Epispadias?
The gubernaculum guides the descent of the gonad. What is that descent towards?
The gubernaculum guides the descent of the gonad. What is that descent towards?
What leads to the development of Patent processus vaginalis:
What leads to the development of Patent processus vaginalis:
The development of the penis includes the formation of a urethral groove. How does that formation occur?
The development of the penis includes the formation of a urethral groove. How does that formation occur?
If you observe that the testes are not located within the scrotum, but are found along its typical path of descent, how would you classify that developmental anomaly?
If you observe that the testes are not located within the scrotum, but are found along its typical path of descent, how would you classify that developmental anomaly?
A 5-year-old male patient is diagnosed with the presence of fluid accumulation around spermatic cord. What developmental anomaly is most likely to cause this symptom?
A 5-year-old male patient is diagnosed with the presence of fluid accumulation around spermatic cord. What developmental anomaly is most likely to cause this symptom?
Which cells completely invest the germ cells and are essential for germ cell development:
Which cells completely invest the germ cells and are essential for germ cell development:
Which of the following abnormalities of embryonic/fetal organ development can lead to infertility in a male?
Which of the following abnormalities of embryonic/fetal organ development can lead to infertility in a male?
Ovaries and testies are formed due to the developmentof which part of the indifferent gonad?
Ovaries and testies are formed due to the developmentof which part of the indifferent gonad?
What is the origin of the cells that completely invest the germ cells and are essential for their development?
What is the origin of the cells that completely invest the germ cells and are essential for their development?
How does the paramesonephric duct contribute to the formation of the female reproductive tract?
How does the paramesonephric duct contribute to the formation of the female reproductive tract?
What is the initial signal that triggers the differentiation of the indifferent gonad into a testis?
What is the initial signal that triggers the differentiation of the indifferent gonad into a testis?
In males, what is the fate of the mesonephric duct under the influence of testosterone?
In males, what is the fate of the mesonephric duct under the influence of testosterone?
A newborn female is diagnosed with an imperforate hymen. Which of the following developmental processes was disrupted?
A newborn female is diagnosed with an imperforate hymen. Which of the following developmental processes was disrupted?
What is the probable outcome if the labioscrotal swellings fail to fuse in a male embryo?
What is the probable outcome if the labioscrotal swellings fail to fuse in a male embryo?
What stimulates the development of the uterine tube, uterus, and superior part of the vagina?
What stimulates the development of the uterine tube, uterus, and superior part of the vagina?
What is the role of the uterovaginal primordium in the development of the female reproductive system?
What is the role of the uterovaginal primordium in the development of the female reproductive system?
A male infant is born with cryptorchidism. Which developmental process has been disrupted?
A male infant is born with cryptorchidism. Which developmental process has been disrupted?
What is the origin of the seminal vesicles in males?
What is the origin of the seminal vesicles in males?
A female patient is diagnosed with a bicornuate uterus. What embryological event most likely failed to occur properly?
A female patient is diagnosed with a bicornuate uterus. What embryological event most likely failed to occur properly?
The prostatic utricle is a remnant of which structure?
The prostatic utricle is a remnant of which structure?
A patient is diagnosed with a hydrocele of the spermatic cord. What developmental abnormality is most likely associated with this condition?
A patient is diagnosed with a hydrocele of the spermatic cord. What developmental abnormality is most likely associated with this condition?
A newborn male is diagnosed with hypospadias. Which of the following processes was most likely disrupted during development?
A newborn male is diagnosed with hypospadias. Which of the following processes was most likely disrupted during development?
What developmental defect results from the incomplete division of the cloaca?
What developmental defect results from the incomplete division of the cloaca?
What structures are formed by the proliferation of the sinovaginal bulbs?
What structures are formed by the proliferation of the sinovaginal bulbs?
In females, what is the remnant of the cranial end of the paramesonephric duct that does not contribute to the infundibulum of the uterine tube?
In females, what is the remnant of the cranial end of the paramesonephric duct that does not contribute to the infundibulum of the uterine tube?
How is the determination of genetic sex achieved during embryonic development?
How is the determination of genetic sex achieved during embryonic development?
What is the fate of the mesonephric duct in females?
What is the fate of the mesonephric duct in females?
What causes the development of the indifferent gonad into an ovary?
What causes the development of the indifferent gonad into an ovary?
If the processus vaginalis remains patent, which of the following conditions can occur?
If the processus vaginalis remains patent, which of the following conditions can occur?
Which structure is connected to the ovary after it separates from the regressing mesonephros?
Which structure is connected to the ovary after it separates from the regressing mesonephros?
How do the primitive sex cords in the developing testis contribute to the formation of the seminiferous tubules?
How do the primitive sex cords in the developing testis contribute to the formation of the seminiferous tubules?
Which best describes the origin of Leydig cells?
Which best describes the origin of Leydig cells?
Which hormone is produced by Leydig cells and influences the differentiation of the mesonephric ducts?
Which hormone is produced by Leydig cells and influences the differentiation of the mesonephric ducts?
Which cells secrete anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) in the developing male embryo?
Which cells secrete anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) in the developing male embryo?
A patient is diagnosed with uterus didelphys. What embryological defect is most likely the cause?
A patient is diagnosed with uterus didelphys. What embryological defect is most likely the cause?
What developmental process leads to the formation of the rectouterine pouch and vesicouterine pouch in females?
What developmental process leads to the formation of the rectouterine pouch and vesicouterine pouch in females?
Which of the following structures contributes to the formation of the spongy urethra?
Which of the following structures contributes to the formation of the spongy urethra?
Which of the following layers of the abdominal wall does NOT contribute to the layers of the testis and spermatic cord?
Which of the following layers of the abdominal wall does NOT contribute to the layers of the testis and spermatic cord?
What is the cause of congenital ovarian hypoplasia syndrome?
What is the cause of congenital ovarian hypoplasia syndrome?
What determines if primordial follice increase in size and break up to cell clusters?
What determines if primordial follice increase in size and break up to cell clusters?
What would result in meconium in urine of males?
What would result in meconium in urine of males?
The decent of genitals occurs due to the guidance of what?
The decent of genitals occurs due to the guidance of what?
Flashcards
Sex differentiation
Sex differentiation
The process by which indifferent gonads differentiate into male or female gonads, influenced by the presence or absence of the Y chromosome.
Paramesonephric ducts
Paramesonephric ducts
Pair of ducts that develop lateral to the mesonephric ducts and are crucial for the development of the female reproductive system, including the uterus and uterine tubes.
Cloaca
Cloaca
The embryonic cavity that divides into the urogenital sinus and the rectum, playing a key role in the development of the urinary and digestive systems.
Perineal development
Perineal development
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intersex states
Intersex states
Signup and view all the flashcards
Primordial germ cells
Primordial germ cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Somatic support cells
Somatic support cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Paramesonephric ducts ends
Paramesonephric ducts ends
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cortex of the indifferent gonad
Cortex of the indifferent gonad
Signup and view all the flashcards
Medulla of the indifferent gonad
Medulla of the indifferent gonad
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gonadal cords
Gonadal cords
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sex cords
Sex cords
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sertoli cells
Sertoli cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Leydig cells
Leydig cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cortex of the developing ovary
Cortex of the developing ovary
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tunica albuginea
Tunica albuginea
Signup and view all the flashcards
Paramesonephric ducts
Paramesonephric ducts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Uterovaginal primordium
Uterovaginal primordium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sinus tubercle
Sinus tubercle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vaginal plate
Vaginal plate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Male Duct
Male Duct
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epididymis
Epididymis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Double uterus
Double uterus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bicornuate uterus with a rudimentary horn
Bicornuate uterus with a rudimentary horn
Signup and view all the flashcards
Unicornuate uterus
Unicornuate uterus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Absence of the vagina
Absence of the vagina
Signup and view all the flashcards
Imperforate hymen
Imperforate hymen
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gartner Duct
Gartner Duct
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prostatic utricle
Prostatic utricle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypospadias
Hypospadias
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epispadias
Epispadias
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urorectal fistula
Urorectal fistula
Signup and view all the flashcards
Processus vaginalis
Processus vaginalis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cryptochidism
Cryptochidism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Turner Syndrome
Turner Syndrome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reproductive system
Reproductive system
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thickened Mesothelium
Thickened Mesothelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Müllerian Ducts
Müllerian Ducts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Genetic sex determinant.
Genetic sex determinant.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gubernaculum
Gubernaculum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Patent processus vaginalis
Patent processus vaginalis
Signup and view all the flashcards
46,XX With excessive androgens
46,XX With excessive androgens
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- The lecture covers the embryology of the cloaca, uterus, and external genitalia in both males and females.
- Learning objectives include detailing sex differentiation, gonadal development, paramesonephric duct development, cloaca development into the urogenital sinus and rectum, perineal development, and common intersex states.
Indifferent Gonads
- Reproductive system development is integrated with primitive urinary organs in males and females.
- By the 6th week, the gonadal ridge develops.
- Primordial germ cells migrate from the yolk sac via the dorsal mesentery.
- These populate the mesenchyme of the posterior body wall.
- A thickened area of mesothelium develops on the medial side of the mesonephros.
- Coelomic epithelium forms somatic support cells and interstitial stromal cells, which are essential for germ cell development.
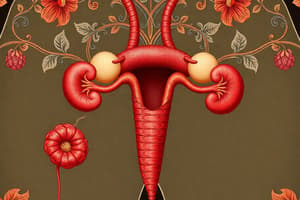
Paramesonephric Ducts
- A new pair of ducts, the paramesonephric or Müllerian ducts, form lateral to the mesonephric ducts in both male and female embryos.
- The caudal ends adhere, connect with the pelvic urethra, and cross ventral/anterior to the mesonephric ducts.
- The cranial ends form funnel-shaped openings into the peritoneal cavity.
- Germ cells and somatic support cells are present in presumptive gonads.
- Mesonephric and paramesonephric ducts are present.
- Genetic sex depends on whether the sperm carries an X or a Y chromosome.
- In XX embryos, the cortex differentiates into an ovary and the medulla regresses.
- In XY embryos, the medulla differentiates into a testis and the cortex regresses.
Male Sex Differentiation
- Sperm carries a Y chromosome, leading to an XY genetic makeup in the developing embryo.
- The presence of the SRY gene produces a protein (testis-determining factor).
- Gonadal cords differentiate into seminiferous cords.
- Sertoli cells secrete antimullerian hormone, leading to paramesonephric duct degeneration.
- Mesenchyme between cords differentiates into Lyding cells, which secrete testosterone.
- Testosterone is converted to dihydrotestosterone.
- Development includes testicular differentiation, mesonephric duct differentiation to the epididymis and vas deferens, prostate differentiation, and external genitalia differentiation into a penis and scrotum.
Development of the Testis
- The Y-chromosome's sex-determining gene produces a protein.
- This protein promotes the development of a testis.
- Primitive sex cords proliferate and penetrate the medulla, forming seminiferous tubules.
- Leydig cells secrete testosterone>>mesonephric ducts for differentiation.
- Sertoli cells regress AMH>>paramesonephric ducts.
Female Sex Differentiation
- Sperm carries an X chromosome, leading to an XX genetic make-up in the developing embryo.
- The absence of the SRY gene results in no Sertoli cells or testosterone production.
- Consequently, the paramesonephric ducts differentiate and develop, while the mesonephric ducts degenerate.
Development of the Ovary
- Cortical cords extend from the developing ovary's surface epithelium into the mesenchyme.
- These increase in size, breaking into cell clusters (primordial follicles).
- After birth, flattening of the surface epithelium to a single layer of cells occurs.
- The surface epithelium is separated from the follicles by the tunica albuginea, a thin fibrous capsule.
- The ovary is suspended by the mesovarium.
Duct Differentiation
- Mesonephric (Wolffian) ducts and paramesonephric (Müllerian) ducts develop parallel to each other.
- Paramesonephric ducts are funnel-shaped and open into the peritoneal cavity.
- Paramesonephric ducts cross ventrally to the mesonephric ducts and form a Y-shaped uterovaginal primordium.
- The uterovaginal primordium projects into the dorsal wall of the urogenital sinus, forming the sinus tubercle.
Female Reproductive Organs
- The paramesonephric ducts develop due to the absence of AMH.
- Oestrogens stimulate the development of the uterine tube, uterus, and superior part of the vagina.
- Uterine tubes develop from unfused cranial parts of the paramesonephric ducts.
- The uterovaginal primordium gives rise to the uterus and the superior part of the vagina.
- Mesonephric ducts fuse to form the uterovaginal primordium.
- The uterovaginal primordium projects into the dorsal wall of the urogenital sinus to give the sinus tubercle.
- Sinus tubercle induces the development of sinovaginal bulbs, forming the vaginal plate.
- The vaginal plate forms the vagina, with central cells breaking down to form the lumen, separated from the urogenital sinus by the hymen.
- Broad ligament fusion forms a peritoneal fold on either side.
- Forms the rectouterine and vesicouterine pouches.
- Paraurethral glands develop from urethral outgrowths, while greater vestibular glands develop from urogenital sinus outgrowths.
Male Ducts
- Testosterone stimulates the mesonephric duct's development and differentiation.
- Mesonephric tubules become the efferent ductules.
- Mesonephric duct's proximal part becomes the epididymis.
- Mesonephric duct becomes the vas deferens
- Lateral mesonephric duct outgrowths become the seminal vesicles at the caudal end.
- Prostate develops from the mesenchyme.
Abnormalities of the Uterus
- Double uterus (uterus didelphys) results from the failure of fusion of the inferior paramesonephric ducts, potentially with a double or single vagina.
- The uterus appears normal externally but is divided internally by a thin septum.
- Bicornuate uterus occurs when duplication involves only the superior part of the body.
- Bicornuate uterus with a rudimentary horn has a retarded paramesonephric duct that doesn't fuse with the second duct.
- Unicornuate uterus occurs when one paramesonephric duct fails to develop.
- A twin pregnancy in a bicornuate uterus can result in one fetus in each horn.
Abnormalities of the Vagina
- Absence of the Vagina- Failure of the sinovaginal bulbs to develop and form the vaginal plate.
- Rudimentary second Vagina.
- Partial Septate vagina.
- Atresia- Failure of canalization of the vaginal plate.
- Failure of the inferior end of the vaginal plate to perforate results in an imperforate hymen.
Remains of Embryonic Genital Ducts
- Some duct parts remain vestigial and can cause pathological issues.
- Examples in females include the epoophoron persisting in the mesovarium, Gartner duct cysts along the uterus, and a hydatid.
- The hydatid is (of Morgagni).
- Males- the cranial end of the mesonephric duct may persist as an appendix of the epididymis.
- The prostatic utricle persists.
- The prostatic utricle is the small sac-like structure.
- The prostatic utricle arises from the Paramesonephric duct.
External Genitalia - Males
- Masculinization of the indifferent external genitalia is induced by testosterone.
- The primordial phallus enlarges to form the penis.
- A urethral plate forms on the ventral side.
- The urethral plate becomes the urethral groove.
- The urethral folds fuse along the ventral surface of the penis to form the spongy urethra.
- The two labioscrotal swellings grow toward each other and fuse to form the scrotum.
External Genitalia - Females
- The primordial phallus gradually becomes the clitoris.
- Urethral folds do not fuse, except to form the frenulum.
- The unfused parts of the urogenital folds form the labia minora.
- The labioscrotal enlarges, forming labia majora.
Hypospadias
- A common defect is Hypospadias
- Results from inadequate androgen production or receptor sites for hormones.
- The penis is underdeveloped and curved.
- The external urethral orifice exists on the surface.
- Glans penis (glandular hypospadias)
- Body of the penis (penile hypospadias).
- Junction of the penis and scrotum (penoscrotal hypospadias)
- Scrotum (perineal hypospadias)
Epispadias
- The Urethra opens on the dorsal surface.
- Associated with the exstrophy of the urinary bladder.
- The urinary bladder opens broadly onto the abdominal wall.
- Results of ectodermal-mesenchymal interactions in the tubercle.
Urorectal Fistula
- The incomplete separation of the cloaca due to the septum.
- Meconium in urine (males)
- Meconium in vestibule (females).
Descent of the Gonads
- The gonads descend the gubernaculum towards the labioscrotal swellings.
- Males process vaginalis protrudes into the labioscrotal swellings.
- Processus vaginalis pushes through the abdominal wall.
- The female descends the gonad far as the pelvic cavity.
- During which the ovarian ligament remains as part of the gubernaculums and attaches to the ovary and uterus
- The round ligament is between the uterus and the labia.
- The testis acquires layers from the abdominal wall (skin, superficial fascia, external oblique and internal oblique).
- During which the processus extends out of the swelling that project in the scrotum and acquires layers of the testis (Skin, Colles Fascia and Dartos muscle , External cremasteric fascia-spermatic, internal spermatic).
Other abnormalities
- Cryptorchidism occurs where tests are hidden near the inguinal canal.
- Congenital ovarian hypoplasia syndrome or Tuerner's syndrome results in the absence of Oocytes
- Some male cells have both, ovum and tests leading to ovotestis
- 46, XX chromosomes have excessive production of hormones which can lead to abnormalities.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.