Podcast
Questions and Answers
What structure does the notochord and prenotochordal cells extend cranially to?
What structure does the notochord and prenotochordal cells extend cranially to?
- Primitive pit
- Amniotic cavity
- Oropharyngeal membrane (correct)
- Cloacal membrane
Which axis is formed at the cranial end of the endoderm?
Which axis is formed at the cranial end of the endoderm?
- Cranio-caudal axis
- Anterior-posterior axis (correct)
- Left-right axis
- Dorso-ventral axis
What is the role of FGF8 during the development of mesoderm?
What is the role of FGF8 during the development of mesoderm?
- It influences ventralization crucial for kidney formation. (correct)
- It contributes to the formation of the notochord.
- It assists in bone development.
- It initiates formation of the cloacal membrane.
What connects the amniotic and yolk sac cavities temporarily?
What connects the amniotic and yolk sac cavities temporarily?
When does the allantoenteric diverticulum appear during embryonic development?
When does the allantoenteric diverticulum appear during embryonic development?
What structure is formed by the cranially migrating epiblast cells?
What structure is formed by the cranially migrating epiblast cells?
Which of the following describes the developmental process occurring at the cranial region of the streak?
Which of the following describes the developmental process occurring at the cranial region of the streak?
At what stage do the definitive endoderm and mesoderm begin to form?
At what stage do the definitive endoderm and mesoderm begin to form?
Which plate is associated with the induction of the forebrain?
Which plate is associated with the induction of the forebrain?
What is the result of the first cells moving inward from the epiblast?
What is the result of the first cells moving inward from the epiblast?
How do epiblast cells move during the second week of development?
How do epiblast cells move during the second week of development?
What anatomical structure is formed as a consequence of epiblast migration at the end of the second week?
What anatomical structure is formed as a consequence of epiblast migration at the end of the second week?
What role does the hypoblast play during the migration of epiblast cells?
What role does the hypoblast play during the migration of epiblast cells?
What is the primary event of gastrulation occurring during the 3rd week of development?
What is the primary event of gastrulation occurring during the 3rd week of development?
Which factor is primarily responsible for controlling cell specification into mesoderm during the 3rd week?
Which factor is primarily responsible for controlling cell specification into mesoderm during the 3rd week?
During gastrulation, what happens to the hypoblast cells?
During gastrulation, what happens to the hypoblast cells?
What structure is formed at the cephalic end of the epiblast during the development of the primitive streak?
What structure is formed at the cephalic end of the epiblast during the development of the primitive streak?
What embryonic structure is responsible for the establishment of body axes during the 3rd week?
What embryonic structure is responsible for the establishment of body axes during the 3rd week?
What type of cell movement occurs when cells migrate inward toward the primitive streak?
What type of cell movement occurs when cells migrate inward toward the primitive streak?
Which germ layer is formed from the cells that remain in the epiblast after invagination?
Which germ layer is formed from the cells that remain in the epiblast after invagination?
Which gene expression is regulated by FGF8 to control mesoderm specification?
Which gene expression is regulated by FGF8 to control mesoderm specification?
Which germ layer is responsible for forming the skin and muscle tissue in an embryo?
Which germ layer is responsible for forming the skin and muscle tissue in an embryo?
What process leads to the formation of the neural tube from the neural plate?
What process leads to the formation of the neural tube from the neural plate?
During neurulation, what structure forms at the midline where the neural folds approach each other?
During neurulation, what structure forms at the midline where the neural folds approach each other?
Which factor is NOT mentioned as involved in the upregulation of the neural plate?
Which factor is NOT mentioned as involved in the upregulation of the neural plate?
On which day does the anterior cranial neuropore typically close during embryonic development?
On which day does the anterior cranial neuropore typically close during embryonic development?
Which of the following is an organ derived from the endoderm germ layer?
Which of the following is an organ derived from the endoderm germ layer?
What is the primary shape of an 18-day presomite embryo?
What is the primary shape of an 18-day presomite embryo?
What occurs as the lateral edges of the neural plate elevate during neurulation?
What occurs as the lateral edges of the neural plate elevate during neurulation?
Which mesoderm migrates at the lateral edges of the node during gastrulation?
Which mesoderm migrates at the lateral edges of the node during gastrulation?
During which developmental stage does the growth and elongation of the embryonic disc primarily occur?
During which developmental stage does the growth and elongation of the embryonic disc primarily occur?
What role does the primitive streak play during embryonic development?
What role does the primitive streak play during embryonic development?
Which germ layer differentiates into structures in contact with the outside world?
Which germ layer differentiates into structures in contact with the outside world?
What process continues in the caudal segments of the embryo while cranial structures develop?
What process continues in the caudal segments of the embryo while cranial structures develop?
What is the primary morphological change observed in the embryonic disc as development progresses?
What is the primary morphological change observed in the embryonic disc as development progresses?
Which type of mesoderm generally contributes to the formation of extraembryonic structures?
Which type of mesoderm generally contributes to the formation of extraembryonic structures?
Which stage in embryonic development is characterized by the formation of tissues and organs from germ layers?
Which stage in embryonic development is characterized by the formation of tissues and organs from germ layers?
Study Notes
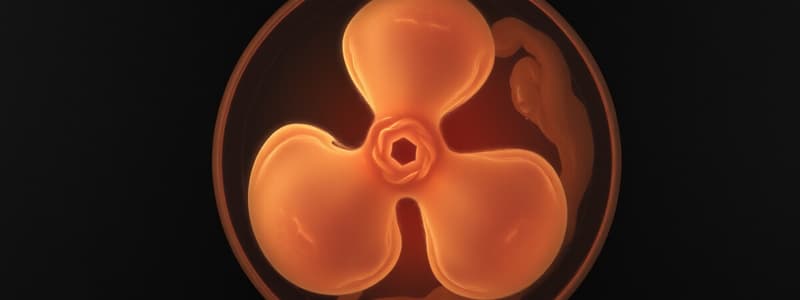
3rd Week of Development: Trilaminar Disc
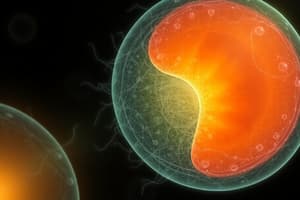
- Gastrulation marks the onset of the third week with the formation of the primitive streak on the epiblast surface, initiating major developmental processes.
- Invagination occurs as cells migrate inward towards the primitive streak, guided by Fibroblast Growth Factor 8 (FGF8), which regulates mesoderm specification by modulating BRACHYURY (T) expression.
- Cells that move inward replace the hypoblast to create definitive endoderm, while those remaining in the epiblast establish the ectoderm.
- The precordial plate is formed from epiblast cells that migrate cranially, leading to future forebrain development, and the oropharyngeal membrane, which will become the oral cavity.
- The notochord and prenotochordal cells extend from the oropharyngeal membrane to the primitive pit and are vital for axial skeleton development.
Establishment of Body Axes
- Body axes are established early, including anterior-posterior (AP), dorso-ventral (DV), and left-right (LR) axes.
- The anterior visceral endoderm (AVE) at the cranial end indicates future head region formation.
- The cloacal membrane develops at the caudal end of the embryonic disc, with the allantoenteric diverticulum appearing around day 16.
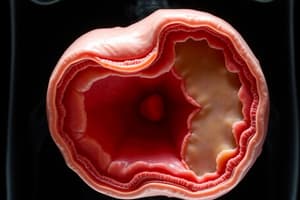
Growth of the Embryonic Disc
- Initially flat, the embryonic disc undergoes elongation, with continuous cell migration from the primitive streak directed toward the cephalic end.
- The primitive streak regresses and shrinks as cranial structures differentiate, persisting throughout the fourth week.
3rd to 8th Weeks: The Embryonic Period
Period of Organogenesis
- The period is characterized by the formation of organs and tissues from the three germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
- Ectoderm gives rise to structures interacting with the external environment, including the CNS, PNS, sensory epithelium, skin, hair, nails, and glands.
- Mesoderm forms supportive tissues such as muscle (myotome), cartilage (sclerotome), and skin (dermatome).
- Endoderm develops into internal organs including the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, kidneys, liver, and pancreas.
- Neural plate induction is driven by FGF upregulation and BMP4 inhibition.
Neurulation
- Neurulation involves the neural plate elongating, with lateral edges lifting to form neural folds, creating a neural groove.
- Neural folds fuse in the midline to form the neural tube, leading to the development of the spinal cord and brain.
- The anterior cranial neuropore closes by day 25 and the posterior caudal neuropore by day 28, completing neurulation.
- During this phase, the embryonic axis is defined, where the length is approximately 1.25 mm and width is about 0.68 mm at 18 days.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
This quiz covers the stages of the embryonic period from the 3rd to the 8th week of development, focusing specifically on the trilaminar germ disc, gastrulation, and the formation of key structures such as the notochord. Dive into the crucial concepts of organogenesis during this pivotal time in embryonic development.