Podcast
Questions and Answers
The uterine mucosa is in what phase during attachment and implantation?
The uterine mucosa is in what phase during attachment and implantation?
- Secretory phase (correct)
- Proliferative phase
- Menstrual phase
- Gravid phase
The blastocyst attaches to the spongy layer of the endometrium before invading the compact layer.
The blastocyst attaches to the spongy layer of the endometrium before invading the compact layer.
False (B)
The transformation of the endometrial stroma in response to the implanting embryo is called the what?
The transformation of the endometrial stroma in response to the implanting embryo is called the what?
decidual reaction
During implantation, trophoblast cells attach to the uterine epithelium via ______.
During implantation, trophoblast cells attach to the uterine epithelium via ______.
Which of the following is/are the layers of the embryonic disc formed during the second week of development?
Which of the following is/are the layers of the embryonic disc formed during the second week of development?
The syncytiotrophoblast consists of cells with individual plasma membranes.
The syncytiotrophoblast consists of cells with individual plasma membranes.
Name the vacuoles that form in the syncytiotrophoblast during the second week of development.
Name the vacuoles that form in the syncytiotrophoblast during the second week of development.
The cells that line the innermost trophoblast cells (cytotrophoblasts) to encase the blastocyst cavity and form the primitive yolk sac are called ______ cells.
The cells that line the innermost trophoblast cells (cytotrophoblasts) to encase the blastocyst cavity and form the primitive yolk sac are called ______ cells.
Match each extraembryonic mesoderm layer to its adjacent structure:
Match each extraembryonic mesoderm layer to its adjacent structure:
What is the function of hCG produced by the syncytiotrophoblast?
What is the function of hCG produced by the syncytiotrophoblast?
Gastrulation is the process of forming two germ layers from the embryonic disk.
Gastrulation is the process of forming two germ layers from the embryonic disk.
What is the name of the surface indentation, or groove, that forms on the epiblast during gastrulation?
What is the name of the surface indentation, or groove, that forms on the epiblast during gastrulation?
Epiblast cell movement is controlled by what factor secreted by primitive streak cells?
Epiblast cell movement is controlled by what factor secreted by primitive streak cells?
During gastrulation, invaginating epiblast cells that migrate laterally and toward the cephalic/cranial end become what?
During gastrulation, invaginating epiblast cells that migrate laterally and toward the cephalic/cranial end become what?
The oropharyngeal and cloacal membranes contain intervening mesoderm cells.
The oropharyngeal and cloacal membranes contain intervening mesoderm cells.
What structure is formed by the epiblast cells that migrate cranially along the midline at the primitive node?
What structure is formed by the epiblast cells that migrate cranially along the midline at the primitive node?
The ______ is a rod-shaped midline structure derived from the endoderm/hypoblast.
The ______ is a rod-shaped midline structure derived from the endoderm/hypoblast.
Which layer give rise to the extraembryonic mesoderm?
Which layer give rise to the extraembryonic mesoderm?
The primitive streak increases in relative size throughout the fourth week of development.
The primitive streak increases in relative size throughout the fourth week of development.
What is the name for the process where the neural plate forms the neural tube?
What is the name for the process where the neural plate forms the neural tube?
Fusion of the neural folds to form the neural tube begins near the middle of the embryo, specifically at the level of the ______ somite.
Fusion of the neural folds to form the neural tube begins near the middle of the embryo, specifically at the level of the ______ somite.
What cell type migrates from the ectoderm after neural folds fuse?
What cell type migrates from the ectoderm after neural folds fuse?
The notochord induces the ectoderm to form the neural crest.
The notochord induces the ectoderm to form the neural crest.
Name the part of the somite that forms the vertebrae, ribs, and associated tendons.
Name the part of the somite that forms the vertebrae, ribs, and associated tendons.
What component do Wnt & Shh induce the development of?
What component do Wnt & Shh induce the development of?
Which of the following components derives from the intermediate mesoderm?
Which of the following components derives from the intermediate mesoderm?
The visceral layer of the lateral plate mesoderm contributes to the formation of the dermis of skin.
The visceral layer of the lateral plate mesoderm contributes to the formation of the dermis of skin.
What is the name of the process by which the mesoderm gives rise to the vascular system?
What is the name of the process by which the mesoderm gives rise to the vascular system?
The ______ will be the major embryonic hematopoietic organ, where most hematopoiesis occurs by 5-6 weeks.
The ______ will be the major embryonic hematopoietic organ, where most hematopoiesis occurs by 5-6 weeks.
Match the germ layer with its primary derivatives:
Match the germ layer with its primary derivatives:
During what week does the oropharyngeal membrane typically break down?
During what week does the oropharyngeal membrane typically break down?
Gestational age begins at fertilization.
Gestational age begins at fertilization.
What is the term for the measure of embryo size used due to its limited variability in the first trimester?
What is the term for the measure of embryo size used due to its limited variability in the first trimester?
By 24 days, it is possible to visualize the first two ______ arches.
By 24 days, it is possible to visualize the first two ______ arches.
Mesonephric ridges, interim regions for the kidneys, are found during which week?
Mesonephric ridges, interim regions for the kidneys, are found during which week?
Physiologic herniation, when the intestines enter the umbilical cord, occurs during the fifth week.
Physiologic herniation, when the intestines enter the umbilical cord, occurs during the fifth week.
During which week, what are the primordia of digits (fingers) called?
During which week, what are the primordia of digits (fingers) called?
By the end of the eighth week, eyelids ______ and close and will begin to unite by epithelial fusion.
By the end of the eighth week, eyelids ______ and close and will begin to unite by epithelial fusion.
Which of the following is a characteristic feature of the embryo towards the end of the fourth week?
Which of the following is a characteristic feature of the embryo towards the end of the fourth week?
What is the approximate time frame for fertilization to occur?
What is the approximate time frame for fertilization to occur?
At the time of attachment and implantation, the uterine mucosa is in the proliferative phase.
At the time of attachment and implantation, the uterine mucosa is in the proliferative phase.
What is the first layer of the endometrium to which the blastocyst attaches during implantation?
What is the first layer of the endometrium to which the blastocyst attaches during implantation?
The trophoblast cells attach to the uterine epithelium via ______.
The trophoblast cells attach to the uterine epithelium via ______.
What transformation does the endometrial stroma undergo in response to the implanting embryo?
What transformation does the endometrial stroma undergo in response to the implanting embryo?
The epiblast is adjacent to the blastocyst cavity.
The epiblast is adjacent to the blastocyst cavity.
The embryoblast forms two layers of cells, what are they called?
The embryoblast forms two layers of cells, what are they called?
The space within the extraembryonic mesoderm that separates it into somatic and splanchnic layers is called the ______ cavity.
The space within the extraembryonic mesoderm that separates it into somatic and splanchnic layers is called the ______ cavity.
Match the trophoblast layer with its correct description:
Match the trophoblast layer with its correct description:
What is the main function of the syncytiotrophoblast?
What is the main function of the syncytiotrophoblast?
The somatic mesoderm is adjacent to the yolk sac.
The somatic mesoderm is adjacent to the yolk sac.
During week 3, what structure forms that initiates gastrulation?
During week 3, what structure forms that initiates gastrulation?
Epiblast cell movement during gastrulation is controlled by fibroblast growth factor 8 or ______.
Epiblast cell movement during gastrulation is controlled by fibroblast growth factor 8 or ______.
What structure is formed by epiblast cells that invaginate at the primitive node and migrate cranially?
What structure is formed by epiblast cells that invaginate at the primitive node and migrate cranially?
The cloacal membrane breaks down in the fourth week of development.
The cloacal membrane breaks down in the fourth week of development.
What process describes how the neural plate forms the neural tube?
What process describes how the neural plate forms the neural tube?
Neural crest cells migrate from the ectoderm epithelium into the ______ underneath.
Neural crest cells migrate from the ectoderm epithelium into the ______ underneath.
Match each mesoderm type with its corresponding description:
Match each mesoderm type with its corresponding description:
What process gives rise to the vascular system?
What process gives rise to the vascular system?
The liver is the primary hematopoietic organ throughout fetal development.
The liver is the primary hematopoietic organ throughout fetal development.
Around what day does the heart begin to beat?
Around what day does the heart begin to beat?
The cells in the cardiogenic area, which is a horseshoe shaped region where the heart will form, will become ______.
The cells in the cardiogenic area, which is a horseshoe shaped region where the heart will form, will become ______.
From which germ layer is the epithelial lining of the gastrointestinal tract derived?
From which germ layer is the epithelial lining of the gastrointestinal tract derived?
During embryonic folding, the flat trilaminar disc converts into a cuboidal shape.
During embryonic folding, the flat trilaminar disc converts into a cuboidal shape.
During embryonic folding, which two areas move ventrally?
During embryonic folding, which two areas move ventrally?
The oropharyngeal membrane ruptures during the ______ week of development.
The oropharyngeal membrane ruptures during the ______ week of development.
What is the method of choice to estimate embryonic age in the first trimester?
What is the method of choice to estimate embryonic age in the first trimester?
During the fourth week the heart starts to loop.
During the fourth week the heart starts to loop.
What is the lateral ectodermal depression formed on each side as the second pharyngeal arch overgrows the third and fourth arches?
What is the lateral ectodermal depression formed on each side as the second pharyngeal arch overgrows the third and fourth arches?
During the sixth week ______ enter the umbilical cord, which is called physiological herniation.
During the sixth week ______ enter the umbilical cord, which is called physiological herniation.
What structures are clearly visible at the beginning of the eighth week?
What structures are clearly visible at the beginning of the eighth week?
At the end of eight weeks, the auricles of the external ears begin to change shape.
At the end of eight weeks, the auricles of the external ears begin to change shape.
Before gastrulation, the embryoblast organizes into two layers. What are these two layers?
Before gastrulation, the embryoblast organizes into two layers. What are these two layers?
After migrating through the primitive streak, some epiblast cells displace the hypoblast cells to become embryonic ______.
After migrating through the primitive streak, some epiblast cells displace the hypoblast cells to become embryonic ______.
Match the structure listed with its embryonic origin:
Match the structure listed with its embryonic origin:
Flashcards
Oocyte
Oocyte
The female reproductive cell; arrested in meiosis.
Morula
Morula
A solid ball of 16 cells formed ~3 days after fertilization.
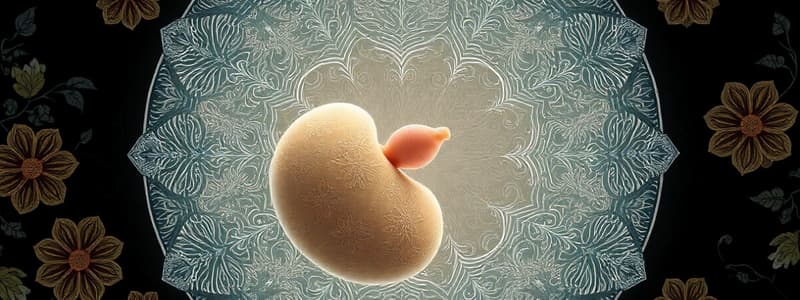
Blastocyst
Blastocyst
A structure ~4-5 days post-fertilization with an inner cell mass.
L-selectin
L-selectin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decidual Reaction
Decidual Reaction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epiblast and Hypoblast
Epiblast and Hypoblast
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypoblast cells
Hypoblast cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chorion
Chorion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lacunae
Lacunae
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chorionic Cavity
Chorionic Cavity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Invagination
Invagination
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibroblast growth factor 8 (FGF8)
Fibroblast growth factor 8 (FGF8)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oropharyngeal and cloacal membranes
Oropharyngeal and cloacal membranes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Forebrain
Forebrain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Notochordal Plate
Notochordal Plate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Primitive Streak
Primitive Streak
Signup and view all the flashcards
Notochord, paraxial mesoderm, intermediate mesoderm, lateral plate mesoderm, extraembryonic mesoderm
Notochord, paraxial mesoderm, intermediate mesoderm, lateral plate mesoderm, extraembryonic mesoderm
Signup and view all the flashcards
The cardiogenic area
The cardiogenic area
Signup and view all the flashcards
End of fourth week
End of fourth week
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bilaminar to trilaminar
Bilaminar to trilaminar
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neural Plate
Neural Plate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Elevate
Elevate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Midline
Midline
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neural Crest Cells
Neural Crest Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ectoderm
Ectoderm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mesoderm
Mesoderm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neuromeres
Neuromeres
Signup and view all the flashcards
42-44 Pairs
42-44 Pairs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Shh and Noggin
Shh and Noggin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sclerotome
Sclerotome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intermediate Mesoderm
Intermediate Mesoderm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Visceral Layer of Lateral Plate Mesoderm
Visceral Layer of Lateral Plate Mesoderm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vasculogenesis in extraembryonic and intraembryonic mesoderm
Vasculogenesis in extraembryonic and intraembryonic mesoderm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Liver
Liver
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myoblasts and Blood Islands
Myoblasts and Blood Islands
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cranial-Caudal embryo folding
Cranial-Caudal embryo folding
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oropharyngeal membrane
Oropharyngeal membrane
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mesoderm produces:
Mesoderm produces:
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endoderm produces:
Endoderm produces:
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rapid Growth of the embryo
Rapid Growth of the embryo
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ventrally
Ventrally
Signup and view all the flashcards
Crown-Rump Length (CRL)
Crown-Rump Length (CRL)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gestational Age
Gestational Age
Signup and view all the flashcards
Embryonic age
Embryonic age
Signup and view all the flashcards
Week 4
Week 4
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mesonephric ridges
Mesonephric ridges
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sixth Week
Sixth Week
Signup and view all the flashcards
Eighth Week
Eighth Week
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Embryological Development Week 1
- Ovulation occurs at time T = 0
- Fertilization occurs at approximately T ≈ 12-24 hours
- The 2-cell stage occurs at T ≈ 30 hours, involving the first cell division
- The 4-cell stage occurs at T ≈ 40 hours, involving the second cell division
- The morula (16-cell stage) forms at approximately T ≈ 3 days
- The blastocyst emerges in its early stage at approximately T ≈ 4-5 days
- At the time of attachment and implantation, the uterine mucosa is in the secretory phase
- The endometrium consists of three layers: compact, spongy, and basal
- The blastocyst first attaches to the compact layer and then invades the spongy layer
- Trophoblast cells attach to the uterine epithelium via L-selectin
- Integrin-laminin binding promotes stronger attachment
- Trophoblast cells invade the uterine epithelium via integrin-fibronectin binding which promotes migration
- By 10-12 days post-fertilization, the embryo is fully embedded in the endometrium, with maternal endometrial epithelium cells covering it
- The endometrial stroma undergoes the decidual reaction in response to the implanting embryo
- Stromal cells accumulate glycogen and lipids, swell, and become decidual cells, providing nutrition to the early embryo via the trophoblast
- Maternal leukocytes infiltrate endometrial stroma and secrete interleukin-2 to prevent maternal recognition of the implanting embryo as foreign
Embryological Development Week 2
- Marked by the "week of twos" which consists of 2 layers of the embryonic disk: Epiblast and Hypoblast
- Further development leads to the formation of 2 trophoblast layers: Cytotrophoblast and Syncytiotrophoblast
- Also leads to the 2 extraembryonic membrane layers: extraembryonic somatic mesoderm and extraembryonic splanchnic mesoderm
- The embryoblast (inner cell mass) forms two layers of cells which creates the bilaminar disk
- Hypoblast (yellow) is adjacent to the epiblast and blastocyst cavity
- Epiblast (blue) is adjacent to the hypoblast and cytotrophoblast (innermost trophoblast cells)
- Amnioblast (blue) forms from the epiblast cells
- Amnioblast cells are adjacent to the cytotrophoblast cells
- A small cavity appears between the epiblast cells and amnioblast cells
- This small cavity becomes the amniotic cavity
- Hypoblast cells line the innermost trophoblast cells (cytotrophoblasts) to encase the blastocyst cavity and form the primitive yolk sac
- The trophoblast forms two layers consisting of Cytotrophoblast (mitotic mononucleated cells) and Syncytiotrophoblast (cells without individual plasma membranes)
- Trophoblast cells will contribute to the chorion that surrounds the embryo and is a fetal component of the placenta
- Syncytiotrophoblast is highly invasive and Penetrates into maternal stroma and engulfs decidual cells and also invades maternal capillaries (sinusoids)
- Lacunae (vacuoles) form in syncytiotrophoblast
- This enables the Lacunae to form intercommunicating network (lacunar stage)
- Maternal blood enters lacunae network to form the uteroplacental circulation
- Syncytiotrophoblast produces hCG to maintain corpus luteum activity (estrogen & progesterone)
- Extraembryonic mesoderm forms between the primitive yolk sac and the cytotrophoblast
- A space (chorionic cavity) forms within the extraembryonic mesoderm separating the extraembryonic mesoderm into two layers consistisng of Splanchnic mesoderm (adjacent to the yolk sac) and Somatic mesoderm (adjacent to cytotrophoblast & amnioblast).
- Somatic mesoderm contributes to the fetal component of the placenta; it forms the chorion
Embryological Development Week 3
- Gastrulation begins with the formation of the Primitive streak
- Primitive streak is a linear indentation (groove) that forms on the surface of the epiblast
- The primitive node forms at the cephalic end of the primitive streak
- Epiblast cells at the primitive streak detach and migrate into the area between the epiblast and hypoblast
- This process is termed invagination
- There are now three embryonic layers of cells consisting of ectoderm, endoderm, and intraembryonic mesoderm
- Epiblast cell movement is controlled by Fibroblast growth factor 8 (FGF8) which is secreted by primitive streak cells
- FGF8 downregulates E-cadherin surface expression, reducing cell-cell contact strength and regulates Brachyury expression to induce invaginated cells to become embryonic mesoderm
- Some invaginating cells displace hypoblast cells and become embryonic endoderm
- Remaining epiblast cells become embryonic ectoderm
- Epiblast is the source of all germ layers
- The oropharyngeal and cloacal membranes are ectoderm cells adjacent to endoderm cells, without intervening mesoderm cells
- Oropharyngeal becomes the oral cavity, Cloacal becomes the anus & urethra
- Invaginated epiblast cells become mesoderm cells and spread/migrate laterally and toward the cephalic/cranial end
- The cephalic/cranial region expands the most in size
- The epiblast cells that invaginated (mesoderm cells) at the primitive node migrate cranially (cephalic end) along the midline and become the prechordal plate
- This is adjacent to the oropharyngeal membrane
- Prechordal plate forms the forebrain
- Some prenotochordal cells intercalate with hypoblast cells, while others migrate on top. Together, these two layers form the notochordal plate at the midline
- The cells of the notochordal plate detach from the endoderm/hypoblast, replicate, forming a separate entity, which defines the notochord
- The notochord is a rod-shaped midline structure
- The primitive streak is a linear indentation.
- Epiblast cells invaginate along the streak to form mesoderm
- Invaginated cells (mesoderm) form in cranial to caudal order consisting of notochord, paraxial mesoderm, intermediate mesoderm, lateral plate mesoderm, and extraembryonic mesoderm
- Epiblast cells that invaginate through the primitive streak near the primitive node become mesoderm, migrating to the area cranial to the oropharyngeal membrane (cardiogenic area)
- These cells form cardiogenic mesoderm
- The cardiogenic area is a horseshoe (crescent) shaped region where the heart will form
- The primitive streak diminishes in size and degenerates by the end of the fourth week
Embryological Development Weeks 2 - 3
- Bilaminar transforms to trilaminar
- The primitive streak (see Chapter 4) further transforms into mesoderm, embryonic ectoderm and extraembryonic mesoderm
- The amniotic ectoderm leads to the formation of ectoderm of the amnion
- The embryonic endoderm leads to the formation of the embryonic ectoderm
- The endoderm of the umbilical vesicle leads to the formation of extraembryonic mesoderm
Embryological Development Weeks 3 - 8
- Known as the Period of organogenesis
- Tissues and organs are generated from each of the three germ layers, which also generates main organ systems that develop concurrently
- The external body becomes recognizable
- The three germ layers consist of the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm
- During ectoderm development, notochord and prenotochord mesoderm induce overlying ectoderm to form the neural plate
- Neural plate cells will become neuroectoderm
- Neurulation describes how the neural plate forms the neural tube
- Lateral edges of the neural plate elevate to form neural fold and groove
- Neural folds move toward the midline
- Neural folds meet at the midline and fuse to form the neural tube
- After fusion, ectoderm cells cover the neural tube
- Fusion begins near the middle of the embryo (cervical level, 5th somite) and continues cranially and caudally
- Cranial (anterior) neuropore closes around day 25, caudal (posterior) closes around day 28
- As neural folds fuse, cells separate from the ectoderm epithelium and migrate into the mesoderm underneath the epithelium
- These are neural crest cells that differentiate into numerous cell types (nerve ganglia, melanocytes, glia, odontoblasts, etc.)
- Ectoderm produces the central and peripheral nervous system, sensory epithelium of the eye, ear, and nose, Epidermis including skin, hair, nails, Subcutaneous and mammary glands, Pituitary gland and Tooth enamel
- Near the Notochord (midline) the Mesoderm cells proliferate and form the paraxial mesoderm and adjacent to the paraxial mesoderm the intermediate mesoderm forms
- Mesoderm that is most lateral remains thin and forms the lateral plate mesoderm
Mesoderm Development
- The paraxial mesoderm organizes into segments that become neuromeres found cranially and somites
- Neuromeres will form mesenchyme in the head and Somites will form skeletal muscle and form the axial skeleton
- Paraxial mesoderm is initially unsegmented tissue, becoming segmented first in the cephalic regions then caudally
- Segmentation is formed by the 'segmentation clock' via a number of genes (retinoic acid, FGF8, Wnts) that are expressed in a cyclic manner
- By the end of the fifth week, 42-44 pairs of somites are present
- The somites consist of 4 occipital, 8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 8-10 coccygeal
- First occipital and last 5-7 coccygeal somites later disappear, giving a final count of approximately 35 pairs of somites
- The somite is at first a clump of cells then arranges into a donut shape creating a lumen
- Each somite is induced by surrounding tissues to form all 3 components consisting of Sclerotome, Dermatome and Myotome
- Sclerotome, myotome & dermatome formation is regulated by different molecular signals
- Shh and Noggin induce sclerotome being identified by PAX1 experession, Wnt & Shh induce dorsomedial myotome Myf5 and Wnt & BMP4 induce ventrolateral myotome myoD = NT-3 induces dermatome PAX3
- The medial and ventral cells of the somite become the sclerotome, which will form the vertebrae, ribs, and tendon
- The dorsal-medial cells and the ventral-lateral cells of the somite become muscle cell precursors (myotome)
- Ventral-lateral muscle precursors will form most of the body wall and limb musculature, dorsal-medial muscle precursors will form back and body wall muscles
- Intermediate mesoderm forms the urogenital structures (gonads and urinary system)
- The parietal layer will line the intraembryonic cavity and form the lateral body wall folds (along with the ectoderm), closing the ventral body wall to form the dermis of skin, bones & connective tissue of limbs
- Mesoderm produces axial and limb muscles along with the axial and limb skeleton, dermis of skin and the genitourinary system.
- Other systems produced by mesoderm include the heart, Hematopoietic system and the wall of the gastrointestinal system, parietal pleura and visceral peritoneum
Blood Vessel & Tube Development
- Mesoderm gives rise to the vascular system through vasculogenesis
- Blood islands appear in extraembryonic and intraembryonic mesoderm, via mesoderm cells induced to form hemangioblasts
- The hemangioblasts will form vessels and blood cells and later the liver will be the major embryonic hematopoietic organ
- Vessels also form via angiogenesis (sprouting from existing vessels)
- Within hematopoiesis, hemangioblasts give rise to hematopoietic stem cells and hematopoiesis begins within the mesoderm around the yolk sac in week 3
- Intraembryonic hematopoiesis begins in mesoderm associated with the dorsal aorta, in the aorta/genital ridge/mesonephros (AGM) region
- AGM cells migrate to the liver and by 5-6 weeks, the liver is the prominent site, followed by spleen and bone marrow to produce Hematopoiess
- The heart tube forms in the cardiogenic area
- The cardiovascular system is the first organ system to reach a functional state (starts to beat around day 21-22)
- Epiblast cells invaginate through the primitive streak near the primitive node becoming mesoderm and migrate to the area cranial to the oropharyngeal membrane (cardiogenic area) to form cardiogenic mesoderm
- The cardiogenic area (heart field) is a horseshoe (crescent) shaped region where the heart will form and is cranial to the oropharyngeal membrane and to the neural folds, lying in the splanchnic layer of lateral plate mesoderm
- There are distinct mesoderm populations forming a primary and a secondary heart field, enabling the heart formation
Cardiac Development
- Mesoderm cells migrate cranially from the primitive streak to form crescent-shaped PHF
- PHF cells area specified from lateral to medial into the atria, left ventricle, and right ventricle
- Pharyngeal mesoderm cells and neural crest cells (from cranial neural folds) form crescent-shaped SHF, which is medial to PHF
- SHF cells are specified to become the right ventricle,along with the outflow tract (conus cordis and truncus arteriosus)
- Myoblasts and blood islands form in Primary Heart Fields, where they form two endocardial tubes
- The embryo folds cranially-caudally and also laterally, merging the paired endocardial tubes (except at the caudalmost end)
- The central portion of the fused tubes expands and these tubes form the future ventricles and outflow tract
- Cranial – Caudal embryo folding changes the position of the developing heart dramatically
- The gastrointestinal tract experiences folding of the embryo to create a 'Purse string' ventral portion of the embryo to separate the endoderm of the gut from the yolk sac proper
- Endoderm develops to gastrointestinal tract and Lungs
- Endoderm produces epithelial lining of the gastrointestinal and respiratory tracts along with the urinary bladder and the tympanic cavity, as well as thyroid, parathyroid and liver
Folding & Development
- A flat trilaminar disc transforms into a cylindrical shaped embryo in conjunction with rapid growth
- The embryo experiences folding, specifically in the fourth week in which the Head and tail move ventrally and the lateral body walls move ventrally
- During 4th week, The Oropharyngeal membrane breaks down and in the 7th week the cloacal membrane also breaks down
- Crown-Rump Length (CRL) is the measurement of the embryo to determine size since Little variability in size occurs in the 1st trimester
- This serves as the optimal method to estimate age until end of 1st trimester Gestational age marks pregnancy from the first day of the LNMP (last normal menstrual period) where the embryonic age begins at fertilization and approximately 2 weeks after LNMP
Week 4 - 8 Development
- Major changes in body form occur during week 4, where at the beginning, the embryo is almost straight and has four to 12 somites
- By the end of this week, the embryo is slightly curved because of head and tail folds
- The neural tube is formed opposite the somites, but it is widely open at rostral and caudal neuropores
- On/Around day 24, the first two pharyngeal arches are visible as the first known arch (mandibular arch) and the second arch.
- During heart looping (cardiac loop) completion produces a large ventral prominence, and pumps blood
- Three pairs of pharyngeal arches are visible by day 26
- The Rostral neuropore closes and the Forebrain produces a prominent elevation of head
- Folding gives the embryo a C-shaped curvature
- Upper limb buds are recognizable by day 26 or 27 as small swellings on the ventrolateral body walls to form Otic pits and lens placodes that are visible on sides of head
- An additional Fourth pair of pharyngeal arches and lower limb buds are visible by end of fourth week, ultimately forming a long tail-like caudal eminence that is a characteristic feature
- On the fifth week, the second pharyngeal arch overgrows the third and fourth arches, forming a lateral ectodermal depression on each side called the cervical sinus
- Mesonephric ridges indicate site of mesonephric kidneys as temporary excretory organs
- Around the sixth week, embryos show reflex response to touch and the Upper limbs begin to show regional differentiation as the elbows and large handplates develop
- Primordia of digits (fingers) digital rays, begin to develop in the handplates, indicating formation of digits and major septa of the heart form
- Intestines enter umbilical cord also occurs around week 6
- During week eight (50-56d) the digits of the hand are separated but noticeably webbed and notches are now clearly visible between digital rays of feet
- The caudal eminence is still present but stubby
- At the end of the eight week, the embryo as distinct human characteristics
- All major systems are developed and the hhead is disproportionately large
- Eyelids are obvious and closing; by end of eighth week, they begin to unite by epithelial fusion
- The neck region is established with intestines still in the proximal portion of the umbilical cord
- Auricles of external ears begin to assume their final shape and external genitalia are present, yet not distinctive enough to permit accurate sexual identification
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.