Podcast
Questions and Answers
What type of joint is the elbow joint?
What type of joint is the elbow joint?
- Pivot Joint (correct)
- Ball-and-Socket Joint
- Gliding Joint
- Hinge Joint
Which muscle is responsible for flexion of the elbow joint?
Which muscle is responsible for flexion of the elbow joint?
- Brachialis
- Triceps
- Biceps Brachii (correct)
- Anconeus
What is the function of the Medial Collateral Ligament in the elbow complex?
What is the function of the Medial Collateral Ligament in the elbow complex?
- To stabilize the joint and prevent excessive motion (correct)
- To flex the elbow joint
- To rotate the radius around the ulna
- To connect the humerus to the ulna
What is the axis of rotation in flexion and extension of the elbow joint?
What is the axis of rotation in flexion and extension of the elbow joint?
What is the limitation for flexion of the elbow joint?
What is the limitation for flexion of the elbow joint?
What is the characteristic of an open kinematic chain?
What is the characteristic of an open kinematic chain?
What is the movement of the head of the radius and ulna in pronation and supination?
What is the movement of the head of the radius and ulna in pronation and supination?
What is the primary function of the elbow joint?
What is the primary function of the elbow joint?
Which muscle is responsible for supination?
Which muscle is responsible for supination?
What type of joint is the elbow?
What type of joint is the elbow?
What is the joint formed by the circular head of the radius in pronation and supination?
What is the joint formed by the circular head of the radius in pronation and supination?
What is the movement of the radius in pronation and supination?
What is the movement of the radius in pronation and supination?
How many degrees of freedom does the elbow joint have?
How many degrees of freedom does the elbow joint have?
What is the function of the proximal radioulnar joint?
What is the function of the proximal radioulnar joint?
What type of joint is the humeroradial joint?
What type of joint is the humeroradial joint?
What is the function of the annular ligament in the humeroradial joint?
What is the function of the annular ligament in the humeroradial joint?
What is unique about the humeroulnar joint?
What is unique about the humeroulnar joint?
Which of the following is NOT part of the elbow complex?
Which of the following is NOT part of the elbow complex?
How many bones form the elbow joint?
How many bones form the elbow joint?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
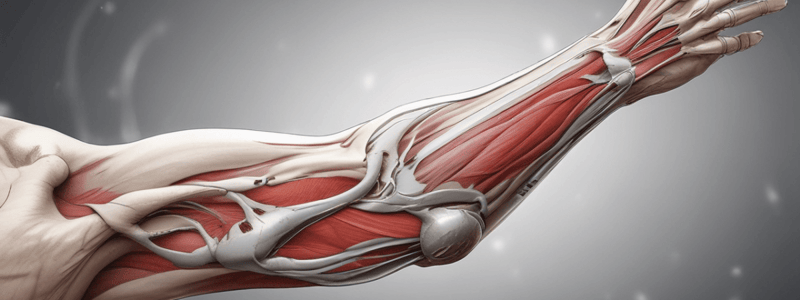
Elbow Biomechanics
- The elbow joint provides stability for the wrist and hand, allowing for shortening and lengthening of the arm for hand positioning.
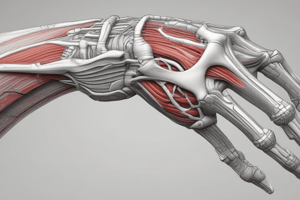
Elbow Complex: Structure
- The elbow complex is a uniaxial, diarthrodial (synovial hinge) joint with 1 degree of freedom of motion in the sagittal plane.
- The joint consists of three bones: humerus, radius, and ulna.
Articulations of the Elbow
- The elbow complex has three articulations:
- Humeroulnar joint (modified hinge joint with 1 degree of freedom: flexion/extension)
- Humeroradial joint (behaves like a pivot joint, with radial head pivoting around the humerus capitulum)
- Proximal radio-ulnar joint (pivot joint involved in pronation and supination of the forearm)
Muscles of the Elbow Complex
- Anterior muscles: Biceps Brachii, Brachioradialis, Brachialis (flexors)
- Posterior muscles: Triceps, Anconeus (extensors)
Ligaments of the Elbow Complex
- Medial collateral ligament
- Lateral collateral ligament
Flexion-Extension: Osteokinematics
- The axis of flexion and extension is not purely transversal due to the longer medial trochlea.
- Limitations for flexion: muscle mass, coronoid and radial head contact, and triceps.
- Limitations for extension: olecranon contact, tension of flexors, and anterior capsule tension.
Open and Closed Kinematics Chains
- Open kinematics chain: distal segment (ulna and radius) moves freely on the proximal segment (humerus), with concave on convex movement.
- Closed kinematics chain: distal segment is fixed, and the proximal segment performs the movement, with convex on concave movement in the opposite direction.
Arthrokinematics of Pronation and Supination
- Rotational movements occur when the distal end of the radius moves over the distal end of the ulna by rotating the radius in the pivot joint.
- Muscles involved: supination (supinator, biceps brachii), pronation (pronator teres, pronator quadratus).
- Osteokinematics: simultaneous movement of the head of the radius and ulna changes the position of the hand.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.