Podcast
Questions and Answers
What occurs in an ectopic pregnancy?
What occurs in an ectopic pregnancy?
- The fertilized egg implants in the uterus.
- The fertilized egg is absorbed by surrounding tissues.
- The fertilized egg grows outside the uterus. (correct)
- The fertilized egg stops developing immediately.
Which location is the most common site for ectopic pregnancies?
Which location is the most common site for ectopic pregnancies?
- The cervix
- An ovary
- A fallopian tube (correct)
- The abdominal cavity
What is a significant risk associated with interstitial ectopic pregnancies?
What is a significant risk associated with interstitial ectopic pregnancies?
- Increased chance of live birth
- Absence of pregnancy symptoms
- Rupture leading to severe bleeding (correct)
- Low levels of hCG production
Which symptom is NOT typically associated with ectopic pregnancy?
Which symptom is NOT typically associated with ectopic pregnancy?
Why is a cervical ectopic pregnancy particularly dangerous?
Why is a cervical ectopic pregnancy particularly dangerous?
What hormone is detected in pregnancy tests that also indicates an ectopic pregnancy?
What hormone is detected in pregnancy tests that also indicates an ectopic pregnancy?
What is a rare site for ectopic pregnancy implantation?
What is a rare site for ectopic pregnancy implantation?
Which of the following best describes the condition of the tissue in the ovaries during an ectopic pregnancy?
Which of the following best describes the condition of the tissue in the ovaries during an ectopic pregnancy?
What is the primary reason an ultrasound may show an empty uterine cavity despite a positive pregnancy test?
What is the primary reason an ultrasound may show an empty uterine cavity despite a positive pregnancy test?
What is the significance of using ultrasound in the evaluation of a suspected ectopic pregnancy?
What is the significance of using ultrasound in the evaluation of a suspected ectopic pregnancy?
What is the role of methotrexate in the management of an ectopic pregnancy?
What is the role of methotrexate in the management of an ectopic pregnancy?
Why might a surgical approach be required in the management of an ectopic pregnancy?
Why might a surgical approach be required in the management of an ectopic pregnancy?
What is a potential risk for the fetus in an ectopic pregnancy?
What is a potential risk for the fetus in an ectopic pregnancy?
What complication can arise from a ruptured ectopic pregnancy?
What complication can arise from a ruptured ectopic pregnancy?
Which of the following is a known risk factor for developing an ectopic pregnancy?
Which of the following is a known risk factor for developing an ectopic pregnancy?
What may necessitate the complete removal of a fallopian tube in the case of an ectopic pregnancy?
What may necessitate the complete removal of a fallopian tube in the case of an ectopic pregnancy?
What is the most critical action required upon diagnosis of an ectopic pregnancy?
What is the most critical action required upon diagnosis of an ectopic pregnancy?
How can previous pelvic or abdominal surgery contribute to the risk of ectopic pregnancy?
How can previous pelvic or abdominal surgery contribute to the risk of ectopic pregnancy?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
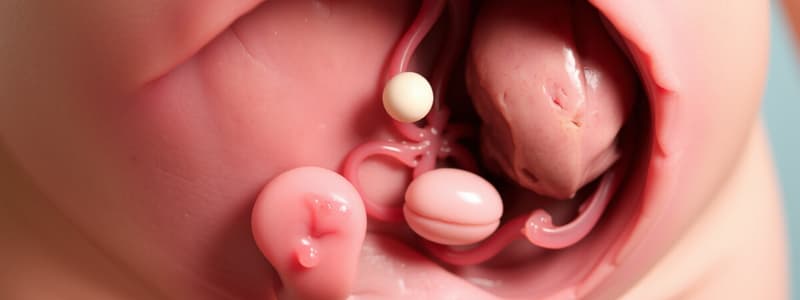
Ectopic Pregnancy Overview
- An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, most commonly in a fallopian tube.
- This condition results in a non-viable pregnancy and poses significant risks to the pregnant individual, necessitating termination.
Diagnosis
- The fertilized egg fails to migrate properly to the uterus, leading to abnormal implantation.
- Locations other than the uterine lining where implantation can occur include:
- Ovary: Cannot sustain a pregnancy due to insufficient tissue support.
- Abdomen: Extremely rare and highly dangerous with no conducive environment for fetal development.
- Interstitial: Relevant to a section of the fallopian tube that penetrates the uterus, posing severe bleeding risks if ruptured.
- Fallopian Tube (Tubal Ectopic): Most common site for ectopic pregnancies, leading to rupture as it cannot expand like the uterus.
- Cervix: Can cause significant bleeding as it is not designed for fetal implantation.
Signs and Symptoms
- Positive pregnancy test indicating rising hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) levels, despite abnormal implantation.
- Abdominal pain resulting from tissue damage or stretching around the implantation site.
- Bleeding due to damaged surrounding tissues from abnormal implantation.
- Ultrasound may reveal an empty uterine cavity despite positive pregnancy test results.
Lab Evaluation
- Ultrasound serves as the critical tool for determining the pregnancy's location and confirming an ectopic pregnancy requiring immediate medical intervention.
Management
- Early termination of the ectopic pregnancy prevents life-threatening ruptures and internal bleeding.
- Medication: Methotrexate is utilized to terminate the pregnancy by stopping cell division without surgery in early cases.
- Surgical Options:
- Laparoscopy: Incision in the affected tube to remove the ectopic pregnancy while preserving surrounding organs.
- Removal of Affected Tube: Necessary if the fallopian tube is severely damaged to prevent future complications.
Timing and Birth Considerations
- Termination of an ectopic pregnancy is essential; continued growth increases rupture risks leading to fatal hemorrhage.
- Types of birth (vaginal vs. C-section) are not applicable since the pregnancy is terminated.
Risks to the Fetus
- A developing fetus outside the uterus will not survive due to lack of essential support and environment.
Risks to the Pregnant Individual
- A ruptured ectopic pregnancy can cause severe internal hemorrhage, necessitating surgical intervention to prevent further complications.
- Removal of the ruptured organ (e.g., fallopian tube) can still allow future pregnancies through the other functional tube.
Risk Factors for Ectopic Pregnancy
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): Scarring may obstruct normal zygote passage, increasing ectopic risk.
- Previous Ectopic Pregnancy: Past incidents may lead to higher recurrence probability due to potential anatomical damage.
- Pelvic or Abdominal Surgery: Surgical procedures may leave scarring obstructing zygote movement.
- Endometriosis: The presence of endometrial tissue outside the uterus can distort reproductive anatomy, raising ectopic implantation chances.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.