Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following best describes the relationship between the lithosphere and the asthenosphere?
Which of the following best describes the relationship between the lithosphere and the asthenosphere?
- The lithosphere is a rigid layer that sits above the asthenosphere. (correct)
- The asthenosphere is a rigid layer located above the lithosphere.
- The asthenosphere is broken into plates, while the lithosphere is a continuous layer.
- The lithosphere and asthenosphere are the same layer, just with different names.
What is the primary driving force behind the movement of the Earth's tectonic plates?
What is the primary driving force behind the movement of the Earth's tectonic plates?
- The rotation of the Earth.
- Tidal forces from the sun.
- The gravitational pull of the moon.
- Convection currents in the lower mantle. (correct)
Which type of plate boundary is characterized by plates moving towards each other, often resulting in subduction zones and mountain formation?
Which type of plate boundary is characterized by plates moving towards each other, often resulting in subduction zones and mountain formation?
- Convergent (correct)
- Divergent
- Conservative
- Transform
At which type of plate boundary would you expect to find mid-ocean ridges?
At which type of plate boundary would you expect to find mid-ocean ridges?
Which of Earth's layers is best described as 'squishy, semi-solid'?
Which of Earth's layers is best described as 'squishy, semi-solid'?
What causes the molten material in Earth's interior to rise and fall?
What causes the molten material in Earth's interior to rise and fall?
Which layer of the Earth is composed of solid iron and nickel?
Which layer of the Earth is composed of solid iron and nickel?
What is a common event or feature associated with transform plate boundaries?
What is a common event or feature associated with transform plate boundaries?
How does the density of continental crust generally compare to the density of oceanic crust?
How does the density of continental crust generally compare to the density of oceanic crust?
Which of the following describes how the temperature and pressure change as you move from the crust towards the inner core?
Which of the following describes how the temperature and pressure change as you move from the crust towards the inner core?
Flashcards
Crust
Crust
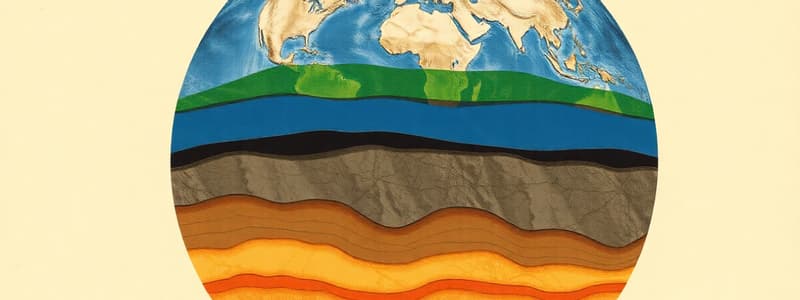
The outermost solid layer of the Earth, divided into continental (thick, less dense, granite) and oceanic (thin, more dense, basalt) types.
Lithosphere
Lithosphere
The rigid outermost layer of the Earth, made up of the crust and the uppermost part of the mantle, broken into tectonic plates.
Asthenosphere
Asthenosphere
A semi-solid, squishy layer within the mantle that slowly flows due to convection currents.
Lower Mantle
Lower Mantle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Outer Core
Outer Core
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inner Core
Inner Core
Signup and view all the flashcards
Convergent Boundary
Convergent Boundary
Signup and view all the flashcards
Divergent Boundary
Divergent Boundary
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transform Boundary
Transform Boundary
Signup and view all the flashcards
Plate Tectonic Theory
Plate Tectonic Theory
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Pressure, density, and temperature increase with depth in Earth's interior
Crust
- Continental crust is thick, less dense, and made of granite rock
- Oceanic crust is thin, more dense, and made of basalt rock
- The crust has the least density
Lithosphere
- The rigid layer under the crust, broken into plates
- Sits above the asthenosphere
Asthenosphere
- Squishy, semi-solid layer flowing due to convection currents within the lower mantle
Lower Mantle
- Hotter than the crust and asthenosphere
- More pressure than layers above
- Contains moving convection currents
Outer Core
- Experiences great heat and pressure
- Composed of liquid nickel and iron
Inner Core
- Experiencing the greatest heat, pressure, and density
- Composed of solid iron and nickel
Boundary Types
- Convergent boundaries occur when two plates move towards each other (colliding)
- Convergent events include earthquakes, subduction, deep ocean trenches, land mountains, and volcanoes
- Divergent boundaries occur when two plates move away from each other (dividing)
- Divergent events include earthquakes, new rock, mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and new bodies of water
- Transform boundaries occur when two plates move along one another (sliding)
- Transform event examples include earthquakes
Plate Tectonic Theory
- Earth's lithosphere is broken into large plates
- Plates slowly interact with each other along plate boundaries
Earth’s Interior Effect On Exterior
- Heat from the inner and outer core warms molten material
- As molten material heats, it becomes less dense and rises
- Less dense molten material rises into upper mantle, causes asthenosphere to flow
- As molten material moves along the asthenosphere, it begins to cool
- Cooler, denser material sinks back towards the inner/outer core
- Constant rising and falling of molten material moves the cracked plates
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.