Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the syncytiotrophoblast during early pregnancy?
What is the primary function of the syncytiotrophoblast during early pregnancy?
- To transport nutrients directly to the embryo
- To protect the embryo from maternal immune response
- To erode the endometrium and establish a pathway for the blastocyst (correct)
- To produce progesterone for endometrial maintenance
What does the corpus luteum primarily produce to support early pregnancy?
What does the corpus luteum primarily produce to support early pregnancy?
- Interleukins
- Progesterone (correct)
- Estrogen
- Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG)
Which type of trophoblast is primarily responsible for invasive behavior during implantation?
Which type of trophoblast is primarily responsible for invasive behavior during implantation?
- Syncytiotrophoblast (correct)
- Decidual cells
- Endometrial stroma
- Cytotrophoblast
What is the role of the lacunae formed by the syncytiotrophoblast?
What is the role of the lacunae formed by the syncytiotrophoblast?
Which factor is produced early in pregnancy that can be found in maternal blood by day 8?
Which factor is produced early in pregnancy that can be found in maternal blood by day 8?
What is the purpose of the decidual reaction in the endometrium?
What is the purpose of the decidual reaction in the endometrium?
Which of the following describes the main role of interleukins produced by decidual cells?
Which of the following describes the main role of interleukins produced by decidual cells?
What might a woman mistake for her menstrual period during early pregnancy due to the embryonic process?
What might a woman mistake for her menstrual period during early pregnancy due to the embryonic process?
What is one of the outcomes of fertilization?
What is one of the outcomes of fertilization?
What role does the zona pellucida play during fertilization?
What role does the zona pellucida play during fertilization?
What is the primary effect of cleavage on the zygote?
What is the primary effect of cleavage on the zygote?
How long does it typically take for cleavage to begin after fertilization?
How long does it typically take for cleavage to begin after fertilization?
What are inner blastomeres?
What are inner blastomeres?
What is accomplished during the process of compaction?
What is accomplished during the process of compaction?
What is produced after cleavage leads to 16 blastomeres?
What is produced after cleavage leads to 16 blastomeres?
What is a consequence of the breakdown of protoamines in the male nucleus?
What is a consequence of the breakdown of protoamines in the male nucleus?
What is the main role of the decidual reaction in early pregnancy?
What is the main role of the decidual reaction in early pregnancy?
Which of the following structures is external to the embryo during early implantation?
Which of the following structures is external to the embryo during early implantation?
What is the primary factor that differentiates the epiblast from the hypoblast?
What is the primary factor that differentiates the epiblast from the hypoblast?
What does an ectopic pregnancy typically lead to?
What does an ectopic pregnancy typically lead to?
Which type of decidua lines the amniotic sac?
Which type of decidua lines the amniotic sac?
Which of the following is NOT a common risk factor for ectopic pregnancy?
Which of the following is NOT a common risk factor for ectopic pregnancy?
What characterizes the normal site of implantation in the uterus?
What characterizes the normal site of implantation in the uterus?
What is the embryonic shield primarily composed of?
What is the embryonic shield primarily composed of?
What is the primary function of hyaluronidase released by the acrosome during fertilisation?
What is the primary function of hyaluronidase released by the acrosome during fertilisation?
Where does the optimal environment for the sperm and oocyte meeting occur?
Where does the optimal environment for the sperm and oocyte meeting occur?
What prevents polyspermy after fertilisation?
What prevents polyspermy after fertilisation?
What role do zonal proteins like ZP3 play in the fertilisation process?
What role do zonal proteins like ZP3 play in the fertilisation process?
Which phase of fertilisation involves the attachment of one spermatozoon to the oocyte?
Which phase of fertilisation involves the attachment of one spermatozoon to the oocyte?
What occurs during Phase 2 of fertilisation after spermatozoa penetrate the zona pellucida?
What occurs during Phase 2 of fertilisation after spermatozoa penetrate the zona pellucida?
Which structures of the spermatozoon enter the cytoplasm of the egg during fertilisation?
Which structures of the spermatozoon enter the cytoplasm of the egg during fertilisation?
What is the size relationship between the egg and the sperm cell?
What is the size relationship between the egg and the sperm cell?
What is the main function of the parietal endoderm?
What is the main function of the parietal endoderm?
Where is the amniotic cavity formed?
Where is the amniotic cavity formed?
What is the relationship between the epiblast and the yolk sac?
What is the relationship between the epiblast and the yolk sac?
What forms the outer wall of the blastocyst?
What forms the outer wall of the blastocyst?
What happens to the yolk sac by the 13th day of development?
What happens to the yolk sac by the 13th day of development?
Which structure is primarily responsible for enclosing the amniotic cavity?
Which structure is primarily responsible for enclosing the amniotic cavity?
Why is the yolk sac not useful for nutrient provision in humans?
Why is the yolk sac not useful for nutrient provision in humans?
What structure connects the yolk sac and the amniotic sac to the mesoderm?
What structure connects the yolk sac and the amniotic sac to the mesoderm?
What is the primary function of the primitive blood vessels formed in the extraembryonic mesoderm?
What is the primary function of the primitive blood vessels formed in the extraembryonic mesoderm?
What occurs as the cytotrophoblast extends into the syncytiotrophoblast?
What occurs as the cytotrophoblast extends into the syncytiotrophoblast?
Which statement about spontaneous abortion (SA) is correct?
Which statement about spontaneous abortion (SA) is correct?
What complication might arise if red blood cells from the embryo enter the mother's circulation?
What complication might arise if red blood cells from the embryo enter the mother's circulation?
What is a possible consequence of something from the mother's blood reaching the fetus?
What is a possible consequence of something from the mother's blood reaching the fetus?
What is the most common timing for spontaneous abortion?
What is the most common timing for spontaneous abortion?
What is the role of the tertiary villus in early pregnancy?
What is the role of the tertiary villus in early pregnancy?
What might cause a higher incidence of spontaneous abortion in certain fetuses?
What might cause a higher incidence of spontaneous abortion in certain fetuses?
Flashcards
Where does fertilization occur?
Where does fertilization occur?
Fertilization happens in the ampullary region of the Fallopian tube. This is the widest part of the tube, with folds that slow down the egg, creating an optimal environment for the sperm to meet it.
Why is Hyaluronidase important?
Why is Hyaluronidase important?
Hyaluronidase is an enzyme released by the sperm's acrosome. It breaks down the sticky matrix (hyaluronic acid) of the corona radiata, allowing the sperm to swim freely towards the zona pellucida.
What is zona pellucida?
What is zona pellucida?
Zona pellucida is a thick, glycoprotein layer surrounding the egg. It acts as a protective barrier and plays a role in species-specific fertilization.
What is the role of ZP3 proteins?
What is the role of ZP3 proteins?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What happens in the perivitelline space?
What happens in the perivitelline space?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why does only one sperm fertilize the egg?
Why does only one sperm fertilize the egg?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What happens after the sperm fuses with the egg?
What happens after the sperm fuses with the egg?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the purpose of the acrosome?
What is the purpose of the acrosome?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Male pronucleus formation
Male pronucleus formation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Zygote formation
Zygote formation
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is accomplished by fertilization?
What is accomplished by fertilization?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Zona pellucida function
Zona pellucida function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cleavage
Cleavage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Morula
Morula
Signup and view all the flashcards
Compaction
Compaction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Outer vs. Inner blastomeres
Outer vs. Inner blastomeres
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Syncytiotrophoblast?
What is the Syncytiotrophoblast?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are lacunae?
What are lacunae?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Immunotolerance?
What is Immunotolerance?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Decidual Reaction?
What is the Decidual Reaction?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does hCG do?
What does hCG do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Corpus Luteum?
What is the Corpus Luteum?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Progesterone?
What is Progesterone?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why are Interleukins and growth factors important in implantation?
Why are Interleukins and growth factors important in implantation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decidua
Decidua
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decidua basalis
Decidua basalis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decidua capsularis
Decidua capsularis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decidua parietalis
Decidua parietalis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic Pregnancy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Embryonic Shield
Embryonic Shield
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epiblast
Epiblast
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypoblast
Hypoblast
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amniotic cavity
Amniotic cavity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Yolk sac
Yolk sac
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parital endoderm
Parital endoderm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Extraembryonic mesoderm
Extraembryonic mesoderm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chorion
Chorion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Extraembryonic coelom
Extraembryonic coelom
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the amniotic cavity?
What is the amniotic cavity?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are primary villi?
What are primary villi?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are secondary villi?
What are secondary villi?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are tertiary villi?
What are tertiary villi?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of the uteroplacental circulation?
What is the role of the uteroplacental circulation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the possible risks of the uteroplacental circulation?
What are the possible risks of the uteroplacental circulation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is spontaneous abortion (SA) or miscarriage?
What is spontaneous abortion (SA) or miscarriage?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the possible causes of spontaneous abortion after the 10th week?
What are the possible causes of spontaneous abortion after the 10th week?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Fertilization Process
- Egg cell is significantly larger than a sperm cell (10 million times the volume)
- Fertilization takes place in the ampullary region of the Fallopian tube
- The folds in the Fallopian tube slow down the oocyte, creating an optimal environment
- Many changes are needed for fertilization
Phase 1 of Fertilization
- Spermatozoa swim through the granulosa cells of the corona radiata
- Hyaluronidase is released from the acrosome, breaking down the hyaluronic acid
- Spermatozoa swim rapidly toward the zona pellucida
- Tubal enzymes may aid the process
Phase 2 of Fertilization
- Spermatozoa reach the zona pellucida and attach to it
- Spermatozoa bind to species-specific zonal proteins (mainly ZP3)
- Enzymes (like acrosin) are released from the acrosome, digesting the zona pellucida membrane
- Sperm head fuses with the zona pellucida
- Sperm enters the perivitelline space between the zona pellucida and the plasma membrane
- Only one sperm will attach to the oocyte's plasma membrane
Phase 3 of Fertilization
- One sperm attaches to the oocyte's microvilli
- Sperm's plasma membrane fuses with the oocyte's membrane
- Sperm head, midpiece, and tail enter the oocyte's cytoplasm (mitochondria remain outside)
- Juno receptors from the oocyte membrane are ejected to prevent polyspermy (multiple sperm fertilizing an egg)
- Paternal mitochondria are eliminated
Phase 4 of Fertilization
- Prevention of polyspermy:
- Fast block: membrane depolarization in a few seconds, preventing further sperm entry
- Permanent block: Changes in calcium concentration trigger cortical granules to release their contents into the perivitelline space, causing the zona pellucida to swell and harden
Phase 5 of Fertilization
- Oocyte completes meiosis II and releases a second polar body
- Two pronuclei (oocyte's and sperm's) form, fuse
- Fertilized egg (zygote) ready for cleavage
Importance of Calcium
- Calcium changes induce meiosis resumption, pronucleus formation and polyspermy prevention
Cleavage
- Series of cell divisions increasing the cell number, without the zygote increasing in size
- Occurs around 30 hours after fertilization
- Resulting cells are called blastomeres
- Blastomeres compact to form a morula, then a blastocyst (within 3 days)
Blastocyst Formation
- Inner cell mass (embryoblast): forms the embryo
- Trophoblast: forms the placenta
- Blastocoele: fluid-filled cavity within the blastocyst
- Zona pellucida sheds allowing blastocyst to hatch
Early Communication with Mother
- Trophoblast produces the Early pregnancy factor to prevent maternal immune attack
Blastocyst Polarity
- Embryonic (inner cell mass) pole and abembryonic (opposite) pole
- Trophoblast on embryo side is polar trophoblast; other side is mural trophoblast
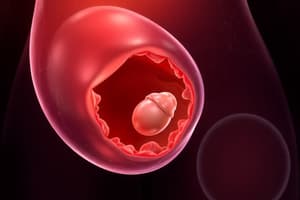
Implantation
- Blastocyst attaches firmly to the endometrium
- Three stages:
- Apposition: blastocyst approaches the endometrium
- Adhesion: close contact with adhesion molecules
- Invasion: blastocyst penetrates the endometrium
- Implantation window: occurs 6 days after the LH surge
- Cytokines aid implantation readiness: LIF
- Immunotolerance regulation of the embryo as a semi-allograft
Trophoblast
- Syncytiotrophoblast: invasive, erodes endometrium for implantation
- Cytotrophoblast: provides nourishment for embryo: cells fuse to form the primary, secondary and tertiary villi
Chorionic Cavity
- Cavity outside of the embryo formed from the extaembryonic mesoderm and cytotrophoblast
- The yolk sac and body stalk form, connecting the embryo with the developing placenta
Uterine Mucosa
- Provides the suitable environment for implantation before the fertilized egg's arrival.
- Endometrium prepared for implantation at the end of menstrual cycle.
Ectopic Pregnancy
- Implantation occurs outside the uterine cavity, most often in the fallopian tubes (and potentially other locations)
- May cause hemorrhage.
Early Pregnancy
- Corpus luteum produces progesterone to maintain endometrial function
- Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG) maintains the corpus luteum and detectable in maternal blood by day 8 and urine by day 10.
- Immune response regulated by maternal immune system.
- Blood vessels formation inside the chorion for improved nutrient absorption
Second Week (of Development)
- Inner cell mass forms the epiblast and hypoblast
- Amniotic cavity and yolk sac formation
- Beginning of primary, secondary, and tertiary villi formation in the chorion
- Early circulatory systems begin developing to supply oxygen and nutrients.
Important Notes:
- The process described is for human fertilization.
- The provided information summarizes the initial steps of prenatal development.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.