Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following is the oldest African hominin fossil?
Which of the following is the oldest African hominin fossil?
- Orrorin tugenensis
- Australopithecus africanus
- Australopithecus afarensis
- Sahelanthropus tchadensis (correct)
The foramen magnum being centrally located is a characteristic of which group?
The foramen magnum being centrally located is a characteristic of which group?
- Hominin (correct)
- Paranthropoid
- Hominoid
- Australopithecine
Orrorin tugenensis has been dated to approximately how many years ago?
Orrorin tugenensis has been dated to approximately how many years ago?
- 7 million years ago
- 6 million years ago (correct)
- 3.2 million years ago
- 4.4 million years ago
Which feature is characteristic of Orrorin tugenensis?
Which feature is characteristic of Orrorin tugenensis?
What is a notable characteristic of the teeth of Orrorin tugenensis?
What is a notable characteristic of the teeth of Orrorin tugenensis?
Which of the following hominins is considered a possible common ancestor?
Which of the following hominins is considered a possible common ancestor?
Ardipithecus ramidus possessed which of the following characteristics?
Ardipithecus ramidus possessed which of the following characteristics?
Which of these traits is associated with Ardipithecus ramidus?
Which of these traits is associated with Ardipithecus ramidus?
Australopithecines are associated with which geographical location?
Australopithecines are associated with which geographical location?
Which dentition characteristic is associated with early hominins?
Which dentition characteristic is associated with early hominins?
What is a characteristic molar feature of early hominins?
What is a characteristic molar feature of early hominins?
Savannah or Aridity is a hypothesis explaining what aspect of hominin evolution?
Savannah or Aridity is a hypothesis explaining what aspect of hominin evolution?
Where was Australopithecus anamensis discovered?
Where was Australopithecus anamensis discovered?
Which part of the body of Australopithecus anamensis is described as human-like?
Which part of the body of Australopithecus anamensis is described as human-like?
To which species might Australopithecus anamensis be ancestral?
To which species might Australopithecus anamensis be ancestral?
What evidence is associated with Australopithecus afarensis?
What evidence is associated with Australopithecus afarensis?
In what country was 'Lucy' discovered?
In what country was 'Lucy' discovered?
What percentage of the skeleton of 'Lucy' was discovered?
What percentage of the skeleton of 'Lucy' was discovered?
Which of the following describes the locomotion of Australopithecus afarensis ('Lucy')?
Which of the following describes the locomotion of Australopithecus afarensis ('Lucy')?
In what part of Africa was Australopithecus africanus discovered?
In what part of Africa was Australopithecus africanus discovered?
What is the name of the Australopithecus africanus fossil discovered in 1924?
What is the name of the Australopithecus africanus fossil discovered in 1924?
Which feature of Australopithecus africanus is more human-like?
Which feature of Australopithecus africanus is more human-like?
Some Australopithecus species are considered able to use tools because of their:
Some Australopithecus species are considered able to use tools because of their:
Australopithecus bahrelghazali was discovered in what country?
Australopithecus bahrelghazali was discovered in what country?
In which country was Australopithecus garhi discovered?
In which country was Australopithecus garhi discovered?
Which of the following is a characteristic of Australopithecus sediba?
Which of the following is a characteristic of Australopithecus sediba?
Where was Australopithecus sediba discovered?
Where was Australopithecus sediba discovered?
The Paranthropoids lived in which area?
The Paranthropoids lived in which area?
Which physical feature characterizes Paranthropoids?
Which physical feature characterizes Paranthropoids?
What is notable about the jaw and dentition of Paranthropus aethiopicus?
What is notable about the jaw and dentition of Paranthropus aethiopicus?
What is a characteristic of Paranthropus aethiopicus?
What is a characteristic of Paranthropus aethiopicus?
What is the likely diet of Paranthropus robustus?
What is the likely diet of Paranthropus robustus?
In what country was Paranthropus boisei partially discovered?
In what country was Paranthropus boisei partially discovered?
Who discovered 'Zinjanthropus'?
Who discovered 'Zinjanthropus'?
Which genus is characterized by an increased brain size?
Which genus is characterized by an increased brain size?
Which of the following is a characteristic of Homo habilis?
Which of the following is a characteristic of Homo habilis?
Which of the following describes the diet of Homo habilis?
Which of the following describes the diet of Homo habilis?
What characteristic is associated with _Homo rudolfensis?
What characteristic is associated with _Homo rudolfensis?
What feature of the spinal column is associated with Bipedalism?
What feature of the spinal column is associated with Bipedalism?
Which evolutionary pressure is most directly associated with the development of bipedalism among early hominins?
Which evolutionary pressure is most directly associated with the development of bipedalism among early hominins?
Which change in dentition is associated with the dietary shift observed in early hominin evolution?
Which change in dentition is associated with the dietary shift observed in early hominin evolution?
How did the formation of the Great Rift Valley influence hominin evolution?
How did the formation of the Great Rift Valley influence hominin evolution?
What is the relationship between brain size and bipedalism in hominin evolution?
What is the relationship between brain size and bipedalism in hominin evolution?
Which of the following is a reason for the evolution of bipedalism related to thermoregulation?
Which of the following is a reason for the evolution of bipedalism related to thermoregulation?
How are the morphological changes in the face, teeth, and jaws of Homo species related to dietary adaptations?
How are the morphological changes in the face, teeth, and jaws of Homo species related to dietary adaptations?
How might increased infant dependency have influenced social structures among early hominins?
How might increased infant dependency have influenced social structures among early hominins?
What is the significance of the S-shaped spinal column in hominin evolution?
What is the significance of the S-shaped spinal column in hominin evolution?
How does the discovery of tools relate temporally to the development of bipedalism in hominin evolution?
How does the discovery of tools relate temporally to the development of bipedalism in hominin evolution?
What does the presence of a central foramen magnum in Sahelanthropus tchadensis suggest about its locomotion?
What does the presence of a central foramen magnum in Sahelanthropus tchadensis suggest about its locomotion?
What is the significance of the 'Turnover Pulse' hypothesis in understanding hominin evolution?
What is the significance of the 'Turnover Pulse' hypothesis in understanding hominin evolution?
Which of the following represents a trend in cranial capacity within the genus Homo?
Which of the following represents a trend in cranial capacity within the genus Homo?
Why is the discovery of relatively complete skeletons, such as those of Australopithecus sediba, particularly valuable to paleoanthropologists?
Why is the discovery of relatively complete skeletons, such as those of Australopithecus sediba, particularly valuable to paleoanthropologists?
How might forests giving way to grasslands and savannahs have influenced hominin evolution?
How might forests giving way to grasslands and savannahs have influenced hominin evolution?
Which of the following features is similar between Australopithecus afarensis and Australopithecus anamensis?
Which of the following features is similar between Australopithecus afarensis and Australopithecus anamensis?
Which dietary adaptation is most strongly associated with the evolution of Paranthropoids?
Which dietary adaptation is most strongly associated with the evolution of Paranthropoids?
What advantage did thermoregulation provide for bipedal hominins?
What advantage did thermoregulation provide for bipedal hominins?
What can the study of dentition tell us about the evolution of species?
What can the study of dentition tell us about the evolution of species?
Which of the following is most likely a reason that infant dependency increased for early hominins? Think about social living as well as the evolutionary advantages that may come out of immature infants.
Which of the following is most likely a reason that infant dependency increased for early hominins? Think about social living as well as the evolutionary advantages that may come out of immature infants.
How does an s-curved spinal column improve balance for hominins?
How does an s-curved spinal column improve balance for hominins?
Which species is believed to have possible tool use at approximately 2.5mya?
Which species is believed to have possible tool use at approximately 2.5mya?
Why is bipedal movement believed to be correlated with savannahs and grasslands?
Why is bipedal movement believed to be correlated with savannahs and grasslands?
How do smaller faces improve diet for early hominins?
How do smaller faces improve diet for early hominins?
Where are Paranthropoids likely to be discovered?
Where are Paranthropoids likely to be discovered?
What is the approximate brain size for Homo habilis?
What is the approximate brain size for Homo habilis?
Which is not a location for Genus Homo discovery?
Which is not a location for Genus Homo discovery?
What traits of the Au. africanus species is most human-like?
What traits of the Au. africanus species is most human-like?
Which is a characteristic of hominin evolution?
Which is a characteristic of hominin evolution?
What does Homo habilis have in common with the Australopithecus?
What does Homo habilis have in common with the Australopithecus?
Which of the following is the best explanation for the robust cranial and dental features found in Paranthropus species?
Which of the following is the best explanation for the robust cranial and dental features found in Paranthropus species?
Which of the following hominin species is most likely to possess a combination of traits from both Australopithecus and Homo?
Which of the following hominin species is most likely to possess a combination of traits from both Australopithecus and Homo?
In the context of hominin evolution, what does 'adaptive radiation' refer to?
In the context of hominin evolution, what does 'adaptive radiation' refer to?
What is one of the major evolutionary differences between Genus Homo and prior hominins?
What is one of the major evolutionary differences between Genus Homo and prior hominins?
What is the significance of the location, Olduvai Gorge, in regards to paleoanthropology?
What is the significance of the location, Olduvai Gorge, in regards to paleoanthropology?
Which of the following hominin species is often referred to as 'Handy Man'?
Which of the following hominin species is often referred to as 'Handy Man'?
What is the Variable Selection hypothesis in regards to hominin evolution?
What is the Variable Selection hypothesis in regards to hominin evolution?
Which environment change made the Savannah or Aridity hypothesis for hominin evolution?
Which environment change made the Savannah or Aridity hypothesis for hominin evolution?
Flashcards
Sahelanthropus tchadensis
Sahelanthropus tchadensis
The oldest African hominin fossil, dating back to ~7 mya in Chad. Characterized by a small brain, elongated skull, sloping face, and prominent brow ridges.
Orrorin tugenensis
Orrorin tugenensis
An early hominin species found in Kenya, dating back to approximately 6 million years ago. Displays a chimpanzee-sized body with small teeth, thick enamel, and overall human-like characteristics.
Ardipithecus ramidus
Ardipithecus ramidus
An early hominin species from ~4.4mya in Ethiopia, considered a possible hominin common ancestor. Features include hominoid dentition, adaptations for bipedalism and arboreal life, and a central foramen magnum.
Great Rift Valley
Great Rift Valley
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hominin Dentition
Hominin Dentition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hominin Diversity
Hominin Diversity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Australopithecus anamensis
Australopithecus anamensis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Australopithecus afarensis
Australopithecus afarensis
Signup and view all the flashcards
"Lucy"
"Lucy"
Signup and view all the flashcards
Australopithecus africanus
Australopithecus africanus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Au. bahrelghazali
Au. bahrelghazali
Signup and view all the flashcards
Au. garhi
Au. garhi
Signup and view all the flashcards
Australopithicus sediba
Australopithicus sediba
Signup and view all the flashcards
Paranthropoids
Paranthropoids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Paranthropus aethiopicus
Paranthropus aethiopicus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Paranthropus robustus
Paranthropus robustus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Paranthropus boisei
Paranthropus boisei
Signup and view all the flashcards
Genus Homo
Genus Homo
Signup and view all the flashcards
Homo habilis
Homo habilis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Homo rudolfensis
Homo rudolfensis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bipedalism Trends
Bipedalism Trends
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reasons for Bipedalism?
Reasons for Bipedalism?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Enlarging the brain
Enlarging the brain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reducing the face
Reducing the face
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trends of Hominin evolution
Trends of Hominin evolution
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hominin
Hominin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Transition to Hominins
- Lectures covered occurred on February 28 and March 3, 2025, as part of ANTH 1210 A01.
Oldest African Hominin Fossils
- Sahelanthropus tchadensis is dated to around 7 million years ago in Chad.
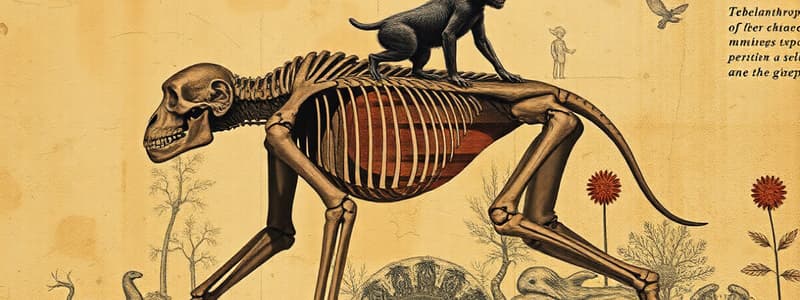
- It is considered a hominoid due to a small brain, elongated skull, sloping face, and prominent brow ridges.
- It is considered a hominin because the foramen magnum is centrally located.
- Orrorin tugenensis is dated to around 6 million years ago in Kenya.
- It was about Chimpanzee sized with small teeth with thick enamel and overall human-like features.
- It was bipedal and partially arboreal.
- The neck length between human and Orrorin femora are similar and the proximal end of the Orrorin femur fits into the hip socket to allow movement (Clark et al 2020).
- Ardipithecus ramidus is dated to around 4.4 million years ago in Ethiopia.
- It is considered a possible hominin common ancestor.
- It had hominoid dentition and other hominin body characteristics like a big toe and rigid foot, a central foramen magnum, and it was bipedal/arboreal.
First Hominins: Great Rift Valley
- First hominins in the Great Rift Valley are dated from 4 to 1 million years ago.
- These include Australopithecines (Australopithecus) and Paranthropoids (Paranthropus).
- Their features included:
- Small canines
- Flat and thickly enameled molars
- Fully bipedal; Partially arboreal
Hominin Diversity
- Hominin diversity can be seen as adaptive radiation to a dynamic environment.
- Forests were giving way to grasslands and savannahs.
- Hypotheses for hominin evolution include the Savannah or Aridity hypothesis, the Turnover Pulse, and Variable Selection.
Australopithecus anamensis
- Australopithecus anamensis dates to around 4.2 million years ago in Kenya.
- It was a small bipedal hominin with a human-like lower body.
- It was also partially arboreal.
- Its teeth were similar to Au. afarensis and it is thought to be ancestral to Au. afarensis.
- They had a small brain and a protruding face
Australopithecus afarensis
- Australopithecus afarensis dates to 4-3 million years ago and fossils have been found in Laetoli, Tanzania and Hadar, Ethiopia
- Laetoli is dated to around 3.6 million years ago.
- A large number of individuals have been recovered (n=24+).
- There is clear evidence of bipedalism in Australopithecus afarensis as well.
- "Lucy" is an Australopithecus afarensis skeleton from Hadar, Ethiopia, dating to 3.2mya that is 40% complete.
- As a species, They were completely bipedal but also occasionally arboreal and retained an ape-like skull, jaw and dentition
Australopithecus africanus
- Australopithecus africanus dates to around 3-2 million years ago in South Africa.
- The Taung Child was discovered was discovered in 1924 and is around 3.5 million years old.
- Australopithecus africanus had a rounder cranium, larger brain, smaller teeth, and an S-shaped lumbar curve.
- The bone morphology of the hand suggests it may have been a possible tool maker.
Australopithecus sp.
- Au. bahrelghazali dates to around 3 million years ago in Chad.
- It may be the same species as Au. afarensis.
- Au. garhi dates to around 2.5 million years ago in Ethiopia and is possibly the first species to have used tools.
Australopithicus sediba
- Australopithicus sediba was recently discovered in 1999 in Malapa Cave, South Africa dating to ~2mya.
- Fairly complete skeletons of juvenile and adult individuals were found.
- These individuals had a mix of Australopithecine and Homo traits.
- Physical features included small cranial capacity, dentition, and long arms. The chest was more Australopithecine-like.
- They had more regular, human-like bipedal locomotion.
Paranthropoids
- Paranthropoids were present in South Africa and East Africa from ~2.7m - 1mya.
- They had a body size similar to a robust Au. africanus.
- They are characterized by their thick jaws, larger molars, massive muscle attachments and well developed sagittal crests.
Paranthropus aethiopicus
- Paranthropus aethiopicus lived in southern Ethiopia and northern Kenya, & Tanzania 2.7 – 2.3mya.
- It was contemporary with A. afarensis.
- Paranthropus aethiopicus had very robust jaws and dentition, broad/dish shaped faces, and large sagittal crests for muscle attachments.
Paranthropus robustus
- Paranthropus robustus was found in Kromdraai Cave, South Africa and dates to 2m - 1mya.
- This is the type specimen for Parathropus.
- It had a robust jaw and teeth and likely had a vegetarian diet.
Paranthropus boisei
- Paranthropus boisei was found in Kenya, Malawi, and the Olduvai Gorge in Tanzania and dates to 2.4 – 1.4mya.
- 'Zinjanthropus' was discovered by Mary Leakey in 1959, which is the type specimen for P. boisei.
- This was the first evidence of early hominins present in East Africa.
- Paranthropus boisei can be characterized as a hyper-robust Parathropus sp. and they possibly used tools.
Genus Homo
- Genus Homo was present in western Kenya and Tanzania, Ethiopia and South Africa.
- Members of this genus have an increased brain size, flatter face, and a similar body to Au.
- Homo habilis lived around (~2.3-1.4mya).
- H. rudolfensis lived around (~1.9-1.8mya).
- Genus Homo was contemporary with P. boisei and possibly H. erectus.
Homo habilis 'Handy Man'
- Homo habilis had a larger brain with a brain size of 630-640cc.
- Homo habilis had reduced molars and premolars with thick enamel and were likely omnivorous.
- These individuals had hand bones capable of a precision grip and a body similar to australopithecines
- They were however still partially arboreal.
- Homo habilis fossils have been found in the same layers as butchered bone and the first stone tools, however, it is unconfirmed whether they actually made and used them.
Homo rudolfensis
- Homo rudolfensis had a brain size of ~775cc.
- Additional physical features includes a longer face and larger molars/premolars.
- They had a body similar to australopithecines and were still partially arboreal.
Hominin Trends: Bipedalism
- Bipedalism trends can be seen across hominins and include the following:
- Spinal column centered on foramen magnum
- Spinal column S-curved to act as a spring
- Pelvis became more bowl-shaped
- Legs angled inward at the knee
- Arch in the foot
Why Bipedalism?
- Bipedalism may have evolved due to adaptation to life in savannahs, advantageous in tall grass for better vision. This is related to Savannah or aridity hypothesis for hominin diversity and evolution in general.
- Bipedalism may have evolved for energy conservation, because it is easier to walk on two legs than four.
- Bipedalism may have evolved for thermoregulation for better dispersion of body heat, which can have a cooling effect, for example, the Bergmann & Allen Rules.
- Bipedalism may have evolved for adaptation, allowing free hands while body moves, facilitating efficient foraging, and tool manufacture and use.
- Bipedal walking may have occurred ~ 1mya prior to tools in archaeological record.
Enlarging the Brain
- Brain development occurred after bipedalism, starting 2 mya.
- It was selected for tool making, and group living etc.
Reducing the Face, Teeth, and Jaws
- Reducing face, teeth, and jaws happened simultaneously with increased brain size.
- Homo species have narrower faces and smaller teeth
Other Trends in Hominin Evolution
- Hairlessness and sweatiness also contributed to changes (Shook et al 2023).
- Increased dependency of infants resulted in an evolutionary advantage for physiologically immature infants.
- Social living improved survivability of young.
- A larger brain was advantageous, but made birthing more dangerous.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.