Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the role of the acrosomal reaction in fertilization?
What is the role of the acrosomal reaction in fertilization?
- To help the spermatozoon penetrate the oocyte's plasma membrane (correct)
- To stimulate the release of hormones from the pituitary gland
- To facilitate the fusion of sperm and oocyte plasma membranes
- To prevent additional sperm from fertilizing the oocyte (correct)
At what stage does the primary oocyte resume meiosis I?
At what stage does the primary oocyte resume meiosis I?
- At ovulation (correct)
- At the morula stage
- During cleavage
- After fertilization
What process follows the fusion of male and female haploid pronuclei?
What process follows the fusion of male and female haploid pronuclei?
- Mitosis (correct)
- Cleavage
- Initiation of Meiosis I
- Spermatogenesis
Which of the following stages occurs first during the cleavage process?
Which of the following stages occurs first during the cleavage process?
What differentiates the inner and outer cells following cleavage?
What differentiates the inner and outer cells following cleavage?
What initiates the transformation of spermatids into spermatozoa?
What initiates the transformation of spermatids into spermatozoa?
How often do cells divide during the cleavage phase post-fertilization?
How often do cells divide during the cleavage phase post-fertilization?
Which cell type gives rise to pyramidal neurons and astrocytes?
Which cell type gives rise to pyramidal neurons and astrocytes?
What is the primary process that leads to the formation of different cell types during embryogenesis?
What is the primary process that leads to the formation of different cell types during embryogenesis?
Which of the following best describes the embryonic period of development?
Which of the following best describes the embryonic period of development?
What initiates the process of fertilization?
What initiates the process of fertilization?
What is the role of proteins and peptides produced during cell differentiation?
What is the role of proteins and peptides produced during cell differentiation?
Which statement about fertilization is correct?
Which statement about fertilization is correct?
What determines the genetic expression in a cell during differentiation?
What determines the genetic expression in a cell during differentiation?
Which of the following best describes the role of channels and pumps in cells?
Which of the following best describes the role of channels and pumps in cells?
During which period do organs grow and begin to function?
During which period do organs grow and begin to function?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Embryogenesis Overview
- Embryogenesis involves forming body structures and organs through organogenesis.
- Cell division (proliferation) and cell differentiation (specialization) are critical processes in embryogenesis.
- A wide variety of cell types and extracellular products are created during this stage.
Cell Specialization
- Selective gene expression dictates cell differentiation by producing specific proteins and suppressing others.
- A cell's genetic expression is influenced by its genetic history (commitment lineage) and its current cellular environment (intercellular communications).
Role of Proteins and Peptides
- Different proteins and peptides determine cell specialization and functions:
- Structural components (e.g., cytoskeleton, extracellular structures)
- Enzymes regulating cell metabolism
- Secretory products (e.g., hormones, digestive enzymes)
- Channels and pumps for molecular transport
- Receptors for cellular communication
Periods of Development
- Embryonic Period: Lasts from fertilization to the early stages of organ development (approximately 30 days in dogs, cats, sheep, and pigs; nearly 60 days in horses, cattle, and humans).
- Fetal Period: Occurs from the end of the embryonic phase to parturition, during which organs grow and start functioning.
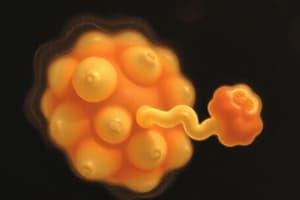
Fertilization Process
- Fertilization is the fusion of a haploid oocyte and a haploid spermatozoon, resulting in a diploid zygote, a pluripotent cell.
- Occurs in the uterine tube near the ovary; required species recognition prevents fusion with foreign sperm.
- Sperm attaches to a glycoprotein on the zona pellucida of the oocyte, triggering the acrosomal reaction.
- Enzymatic degradation of the zona pellucida allows sperm penetration and completion of oocyte meiosis.
- Male and female pronuclei unite, lose nuclear membranes, and mitosis initiates 12 hours post-fusion.
Oocyte Development
- Oocytes, surrounded by zona pellucida and corona radiata, mature selectively in response to FSH from the pituitary.
- Germ cells (oogonia) produce primary oocytes via mitosis during embryonic development.
- Primary oocytes initiate Meiosis I and remain arrested until ovulation.
- Secondary oocytes complete Meiosis II upon fertilization; if unfertilized, they degenerate.
Spermatozoa Development
- Spermatozoa are produced in large quantities (hundreds of millions per ejaculation).
- Movement occurs via contractions in the female genital tract.
- Spermatogonia become primary spermatocytes through repeated mitosis after puberty.
- Primary spermatocytes undergo Meiosis I, resulting in secondary spermatocytes, which complete Meiosis II to form spermatids.
- Spermatids mature into spermatozoa (spermiogenesis) and undergo capacitation to enable oocyte interaction.
Cleavage Stage
- Cleavage begins as the zygote undergoes mitotic divisions, producing smaller cells called blastomeres.
- The process progresses from zygote to morula and ends at the blastocyst stage.
- The first cleavage division happens 1 to 5 days post-ovulation, dividing every 12 hours.
- The initial eight blastomeres in mammals are undifferentiated with identical potential before differentiating into inner and outer cells.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.