Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following is NOT a symptom of a cholesteatoma?
Which of the following is NOT a symptom of a cholesteatoma?
- Impaired hearing (correct)
- Vertigo
- Malodorous otorrhea
- Tinnitus
Which of these conditions can be associated with auricular disorders?
Which of these conditions can be associated with auricular disorders?
- Addison's disease
- Cartilage calcification
- Hansen's nodules
- All of the above (correct)
What is the most common type of cholesteatoma?
What is the most common type of cholesteatoma?
- Idiopathic
- Inflammatory
- Acquired (correct)
- Congenital
Which of the following diagnostic tools is NOT used to diagnose a cholesteatoma?
Which of the following diagnostic tools is NOT used to diagnose a cholesteatoma?
What is a potential complication of auricular disorders?
What is a potential complication of auricular disorders?
What might indicate a possible cause of malignant otitis externa?
What might indicate a possible cause of malignant otitis externa?
Which of the following is NOT a factor associated with gradual hearing loss?
Which of the following is NOT a factor associated with gradual hearing loss?
Which of these patient groups is at a higher risk of developing malignant otitis externa?
Which of these patient groups is at a higher risk of developing malignant otitis externa?
What is the definitive treatment for a cholesteatoma?
What is the definitive treatment for a cholesteatoma?
What is the typical treatment for mild infections related to auricular disorders?
What is the typical treatment for mild infections related to auricular disorders?
Which of the following is a possible cause of fluctuating hearing loss?
Which of the following is a possible cause of fluctuating hearing loss?
Which of the following is NOT a contraindication to the use of cerumenolytic agents?
Which of the following is NOT a contraindication to the use of cerumenolytic agents?
Which of these items can contribute to cerumen impaction?
Which of these items can contribute to cerumen impaction?
What is a potential symptom of cerumen impaction?
What is a potential symptom of cerumen impaction?
What is the most common cause of acquired cholesteatoma?
What is the most common cause of acquired cholesteatoma?
What should be done before attempting to remove cerumen from the ear?
What should be done before attempting to remove cerumen from the ear?
What is the immediate action indicated for patients experiencing sudden hearing loss?
What is the immediate action indicated for patients experiencing sudden hearing loss?
Which of the following symptoms is NOT typically associated with impaired hearing?
Which of the following symptoms is NOT typically associated with impaired hearing?
What diagnostic test is NOT included in the evaluation of impaired hearing?
What diagnostic test is NOT included in the evaluation of impaired hearing?
What is a common management approach for patients with cerumen impaction?
What is a common management approach for patients with cerumen impaction?
Which condition is NOT indicated for otolaryngology referral?
Which condition is NOT indicated for otolaryngology referral?
What is the primary symptom associated with acute otitis media (AOM)?
What is the primary symptom associated with acute otitis media (AOM)?
Which management option is recommended for treating pain associated with ear conditions?
Which management option is recommended for treating pain associated with ear conditions?
What type of otitis media features accumulation of serous fluid without acute inflammation?
What type of otitis media features accumulation of serous fluid without acute inflammation?
Which diagnostic test is used to assess middle ear function?
Which diagnostic test is used to assess middle ear function?
Which medication is considered a first-line treatment for acute otitis media (AOM)?
Which medication is considered a first-line treatment for acute otitis media (AOM)?
What is the main reason for immediate referral in cases of acute otitis media?
What is the main reason for immediate referral in cases of acute otitis media?
What common symptom is associated with tympanic membrane perforation?
What common symptom is associated with tympanic membrane perforation?
Which of the following describes the condition of tympanic membrane perforation?
Which of the following describes the condition of tympanic membrane perforation?
What diagnostic tool is primarily used to assess tympanic membrane perforation?
What diagnostic tool is primarily used to assess tympanic membrane perforation?
What should patients do to protect their tympanic membrane until healing occurs?
What should patients do to protect their tympanic membrane until healing occurs?
In which scenario would an antibiotic treatment be necessary?
In which scenario would an antibiotic treatment be necessary?
Which of the following does NOT contribute to impacted cerumen?
Which of the following does NOT contribute to impacted cerumen?
What is the recommended treatment for acute otitis media in young children?
What is the recommended treatment for acute otitis media in young children?
Which question is important to assess before removing impacted cerumen?
Which question is important to assess before removing impacted cerumen?
What common symptom might indicate a need for an otoscopic exam in a child?
What common symptom might indicate a need for an otoscopic exam in a child?
What is a possible complication that should be assessed in patients with trauma-related ear symptoms?
What is a possible complication that should be assessed in patients with trauma-related ear symptoms?
What are the primary symptoms of Meniere Disease?
What are the primary symptoms of Meniere Disease?
Which management options are indicated for tinnitus?
Which management options are indicated for tinnitus?
In the early phase of Meniere Disease, how long do episodes of vertigo typically last?
In the early phase of Meniere Disease, how long do episodes of vertigo typically last?
What is the main characteristic of acute otitis externa?
What is the main characteristic of acute otitis externa?
Which statement about chronic otitis externa is true?
Which statement about chronic otitis externa is true?
What is a common symptom of otitis externa?
What is a common symptom of otitis externa?
What is one of the goals of therapy for Meniere Disease?
What is one of the goals of therapy for Meniere Disease?
How is tinnitus primarily perceived?
How is tinnitus primarily perceived?
Which of these symptoms is NOT characteristically associated with Meniere Disease?
Which of these symptoms is NOT characteristically associated with Meniere Disease?
What is a distinguishing characteristic of acute otitis externa?
What is a distinguishing characteristic of acute otitis externa?
Which of the following is a common management approach for tinnitus?
Which of the following is a common management approach for tinnitus?
Which of the following is NOT a management option for otitis externa?
Which of the following is NOT a management option for otitis externa?
Which of these statements accurately describes chronic otitis externa?
Which of these statements accurately describes chronic otitis externa?
What is a common symptom associated with otitis externa?
What is a common symptom associated with otitis externa?
Which of the following conditions is NOT typically associated with ear disorders?
Which of the following conditions is NOT typically associated with ear disorders?
Which of these is a primary reason for referring a patient with Meniere Disease to an otolaryngologist?
Which of these is a primary reason for referring a patient with Meniere Disease to an otolaryngologist?
What is the recommended treatment for mild ear infections caused by auricular disorders?
What is the recommended treatment for mild ear infections caused by auricular disorders?
Which of the following is NOT a possible cause of tinnitus?
Which of the following is NOT a possible cause of tinnitus?
Which of the following is NOT a common cause of cerumen impaction?
Which of the following is NOT a common cause of cerumen impaction?
What is the primary symptom associated with cerumen impaction?
What is the primary symptom associated with cerumen impaction?
What is the most appropriate course of action for a patient with suspected malignant otitis externa?
What is the most appropriate course of action for a patient with suspected malignant otitis externa?
Which of the following patients is MOST likely to experience malignant otitis externa?
Which of the following patients is MOST likely to experience malignant otitis externa?
Prior to attempting to remove cerumen from the ear, what information is essential to gather from the patient?
Prior to attempting to remove cerumen from the ear, what information is essential to gather from the patient?
Which of the following clinical features is NOT typical of acute otitis media (AOM)?
Which of the following clinical features is NOT typical of acute otitis media (AOM)?
Which diagnostic tool is primarily used to assess the function of the middle ear?
Which diagnostic tool is primarily used to assess the function of the middle ear?
Which of the following conditions is NOT typically associated with a tympanic membrane perforation?
Which of the following conditions is NOT typically associated with a tympanic membrane perforation?
Which diagnostic test is recommended for assessing the potential cause of ear inflammation and fluid accumulation?
Which diagnostic test is recommended for assessing the potential cause of ear inflammation and fluid accumulation?
What is the preferred first-line medication for managing acute otitis media (AOM) in most cases?
What is the preferred first-line medication for managing acute otitis media (AOM) in most cases?
What is the most prevalent symptom that may initially indicate a cholesteatoma?
What is the most prevalent symptom that may initially indicate a cholesteatoma?
Which of the following factors is NOT associated with gradual hearing loss?
Which of the following factors is NOT associated with gradual hearing loss?
In the context of cholesteatoma treatment, what does the term "definitive treatment" refer to?
In the context of cholesteatoma treatment, what does the term "definitive treatment" refer to?
Which condition is often a contributing factor to the development of acquired cholesteatoma?
Which condition is often a contributing factor to the development of acquired cholesteatoma?
What diagnostic tools are primarily employed to evaluate a cholesteatoma?
What diagnostic tools are primarily employed to evaluate a cholesteatoma?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the relationship between hearing loss and age?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the relationship between hearing loss and age?
What is the most likely cause of fluctuating hearing loss?
What is the most likely cause of fluctuating hearing loss?
Which of the following conditions is NOT typically associated with sudden hearing loss?
Which of the following conditions is NOT typically associated with sudden hearing loss?
Which of these is NOT a symptom commonly associated with sudden hearing loss?
Which of these is NOT a symptom commonly associated with sudden hearing loss?
Which diagnostic test is specifically designed to assess middle ear function?
Which diagnostic test is specifically designed to assess middle ear function?
What is the primary characteristic of acute otitis externa?
What is the primary characteristic of acute otitis externa?
What is the recommended treatment for impacted cerumen?
What is the recommended treatment for impacted cerumen?
Which diagnostic test is NOT typically used to evaluate impaired hearing?
Which diagnostic test is NOT typically used to evaluate impaired hearing?
Which of the following is NOT a possible cause of intermittent hearing loss?
Which of the following is NOT a possible cause of intermittent hearing loss?
Which of the following is NOT a condition that would typically warrant a referral to an otolaryngologist?
Which of the following is NOT a condition that would typically warrant a referral to an otolaryngologist?
What are possible causes of intermittent hearing loss?
What are possible causes of intermittent hearing loss?
Flashcards
Auricular Disorders
Auricular Disorders
Conditions affecting the external ear, including benign and serious illnesses.
Malignant Otitis Externa
Malignant Otitis Externa
A serious ear infection that may follow other illnesses, particularly in immunosuppressed individuals.
Symptoms of Auricular Disorders
Symptoms of Auricular Disorders
Symptoms vary based on the cause and may include hearing loss, pain, and itching.
Cerumen Impaction
Cerumen Impaction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Management of Ear Infections
Management of Ear Infections
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cerumen Removal Techniques
Cerumen Removal Techniques
Signup and view all the flashcards
Warning signs for referral
Warning signs for referral
Signup and view all the flashcards
Risk factors for Malignant Otitis Externa
Risk factors for Malignant Otitis Externa
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sudden Hearing Loss
Sudden Hearing Loss
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rinne and Weber Test
Rinne and Weber Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Otolaryngology Referral
Otolaryngology Referral
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vestibular Neuritis
Vestibular Neuritis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tympanic Membrane Perforation
Tympanic Membrane Perforation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diagnosis of Tympanic Membrane Perforation
Diagnosis of Tympanic Membrane Perforation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Management of Tympanic Membrane Perforation
Management of Tympanic Membrane Perforation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Importance of Keeping Water Out
Importance of Keeping Water Out
Signup and view all the flashcards
Impacted Cerumen
Impacted Cerumen
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cerumen Removal Options
Cerumen Removal Options
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acute Otitis Media Diagnosis
Acute Otitis Media Diagnosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Symptom Assessment for Ear Problems
Symptom Assessment for Ear Problems
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acute Otitis Media (AOM)
Acute Otitis Media (AOM)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Otitis Media with Effusion (OME)
Otitis Media with Effusion (OME)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Middle Ear Effusion (MEE)
Middle Ear Effusion (MEE)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Management of AOM
Management of AOM
Signup and view all the flashcards
Symptoms of TM Perforation
Symptoms of TM Perforation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diagnostics for Otitis Media
Diagnostics for Otitis Media
Signup and view all the flashcards
Referral for Children with AOM
Referral for Children with AOM
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ear Irrigation
Ear Irrigation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cholesteatoma
Cholesteatoma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Symptoms of Cholesteatoma
Symptoms of Cholesteatoma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Impaired Hearing
Impaired Hearing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Causes of Hearing Loss
Causes of Hearing Loss
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fluctuating Hearing Loss
Fluctuating Hearing Loss
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diagnostics for Cholesteatoma
Diagnostics for Cholesteatoma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Meniere Disease
Meniere Disease
Signup and view all the flashcards
Symptoms of Meniere Disease
Symptoms of Meniere Disease
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acute Otitis Externa
Acute Otitis Externa
Signup and view all the flashcards
Symptoms of Acute Otitis Externa
Symptoms of Acute Otitis Externa
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chronic Otitis Externa
Chronic Otitis Externa
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tinnitus
Tinnitus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Management of Tinnitus
Management of Tinnitus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Treatment Goals for Meniere Disease
Treatment Goals for Meniere Disease
Signup and view all the flashcards
Benign Auricular Conditions
Benign Auricular Conditions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Serious Ear Conditions
Serious Ear Conditions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Symptoms of Cerumen Impaction
Symptoms of Cerumen Impaction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Management of Cerumen Impaction
Management of Cerumen Impaction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Malignant Otitis Externa Management
Malignant Otitis Externa Management
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diagnostic Tests for Auricular Disorders
Diagnostic Tests for Auricular Disorders
Signup and view all the flashcards
Referral for Severe Symptoms
Referral for Severe Symptoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Symptoms of Tympanic Membrane Perforation
Symptoms of Tympanic Membrane Perforation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Meniere Disease Symptoms
Meniere Disease Symptoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Symptoms of Tinnitus
Symptoms of Tinnitus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Management of Meniere Disease
Management of Meniere Disease
Signup and view all the flashcards
Presentation of Tinnitus
Presentation of Tinnitus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acute Otitis Externa Symptoms
Acute Otitis Externa Symptoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Meniere Disease Management
Meniere Disease Management
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vestibular Exercises
Vestibular Exercises
Signup and view all the flashcards
Causes of Tinnitus
Causes of Tinnitus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sudden Hearing Loss Referral
Sudden Hearing Loss Referral
Signup and view all the flashcards
Unilateral vs Bilateral Hearing Loss
Unilateral vs Bilateral Hearing Loss
Signup and view all the flashcards
Associated Symptoms of Hearing Loss
Associated Symptoms of Hearing Loss
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rinne and Weber Test Purpose
Rinne and Weber Test Purpose
Signup and view all the flashcards
Causes of Impaired Hearing
Causes of Impaired Hearing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vestibular Neuritis Symptoms
Vestibular Neuritis Symptoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Management of Vestibular Neuritis
Management of Vestibular Neuritis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Referral for Severe Hearing Loss
Referral for Severe Hearing Loss
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tympanic Membrane Management
Tympanic Membrane Management
Signup and view all the flashcards
Contraindications for Cerumenolytic Agents
Contraindications for Cerumenolytic Agents
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cholesteatoma Symptoms
Cholesteatoma Symptoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cholesteatoma Diagnostics
Cholesteatoma Diagnostics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cholesteatoma Management
Cholesteatoma Management
Signup and view all the flashcards
Impaired Hearing Definition
Impaired Hearing Definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sudden Hearing Loss Causes
Sudden Hearing Loss Causes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fluctuating Hearing Loss Causes
Fluctuating Hearing Loss Causes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Risk Factors for Gradual Hearing Loss
Risk Factors for Gradual Hearing Loss
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Ear Disorders
- Ear disorders encompass various conditions affecting the external, middle, and inner ear.
- Conditions affecting the external ear include benign conditions, those related to cultural practices (body piercing), and serious illnesses.
- Benign conditions may involve disease processes (Addison's disease, cartilage calcification, Hansen's nodules, keloids).
- Serious external ear illnesses requiring immediate referral include malignant otitis externa and basal cell cancer.
- Symptoms depend on the underlying cause of the disorder.
- Malignant otitis externa may result from infections or respiratory illnesses, often in immunocompromised or diabetic patients.
- Diagnostics vary depending on the disease process, including biopsy, rheumatoid arthritis panels, autoimmune profiles, and uric acid profiles.
- Management varies widely, from topical alcohol and antibiotic ointments for mild infections to hospitalization and intravenous antibiotics for severe cases.
Cerumen Impaction
- Cerumen impaction occurs when thickened earwax (cerumen) partially or completely occludes the external ear canal.
- Ear plugs, hearing aids, earbuds, and cotton-tipped swabs can contribute to impaction.
- Symptoms include unilateral or bilateral fullness, hearing loss, otalgia, itching, discomfort, tinnitus, cough, vertigo, and dizziness.
- Management involves evaluating for a history of ruptured eardrums (TM), tympanostomy tubes, or recent ear surgery.
- Removal may be with a cerumen spoon or curette.
- Cerumenolytic agents (mineral oil, liquid docusate sodium, hydrogen peroxide) can be inserted daily.
- Irrigation with water or normal saline using an ear syringe may be performed.
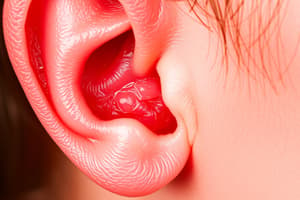
Cholesteatoma
- Cholesteatoma is an abnormal buildup of squamous epithelial cells usually within the middle ear, mastoid air spaces, or epitympanum.
- Cholesteatoma can be acquired, often associated with repeat infections or tinnitus, or congenital.
- Symptoms include impaired hearing, malodorous otorrhea, tinnitus, and vertigo (symptoms may not occur immediately).
- Diagnosis involves otoscopic exam, audiogram, CT, and MRI scans.
- Management involves removal of debris, avoidance of water entering the ear canal, treatment with bacterial agents, and reducing inner ear inflammation, possible surgical intervention for definitive treatment.
Impaired Hearing
- Impaired hearing is a defect in detecting or processing sound waves.
- It can negatively affect communication and safety.
- Prevalence increases with age.
- Hearing loss may present as sudden, progressive, or fluctuating.
- It can be caused by a myriad of abnormalities.
- Diagnostics include Rinne and Weber tests, screening audiograms, tympanometric screenings, MRI, and CT scans.
- Factors associated with gradual hearing loss include cholesteatoma, chronic renal failure, chronic otitis media, diabetes hypothyroidism, noise, otosclerosis, presbycusis, retrocochlear neoplasm, autoimmune disorders, Meniere's disease, migraine headaches, multiple sclerosis, otitis media, perilymphatic fistula, sarcoidosis, and syphilis.
Inner Ear Disorders
- Inner ear disorders can involve Vestibular neuritis, Meniere's disease, and tinnitus.
- Vestibular neuritis causes acute unilateral labyrinthine dysfunction, characterized by severe vertigo, nausea, and vomiting, with symptoms lasting days to months. Symptoms worsen with head movement.
- Meniere's disease involves recurrent vertigo, hearing loss, tinnitus, and fullness in the ear. Symptoms are often intermittent.
- Tinnitus is the perception of a sound in the absence of an external source.
- Treatment for each condition varies and can include pharmacological therapies (anticholinergics, antihistamines, benzodiazepines, antiemetics) and vestibular exercises.
Otitis Externa
- Otitis externa, commonly known as swimmer's ear, is an inflammation of the external ear canal.
- It can involve acute or chronic forms.
- Acute otitis externa is characterized by pain, tenderness around the tragus and with ear movement, drainage, and hearing loss.
- Chronic otitis externa involves a dry ear canal without cerumen and often intense itching.
- Management focuses on clearing debris from the canal, managing pain with NSAIDs or opioids, topical anesthetics, and treating any infection or inflammation with antibiotics.
Otitis Media
- Otitis media is inflammation of the middle ear, often associated with fluid buildup in the middle ear cavity.
- It can be acute (rapid onset and short duration) or chronic (associated with persistent middle ear effusion).
- Symptoms can vary from mild to severe, encompassing otalgia (ear pain), fever, and worse symptoms that tend to worsen when lying down, and can include hearing loss.
- Diagnostics typically include otoscopic exam, tympanometry, acoustic reflectometry, Rinne and Weber tests, sinus X-ray and CT scans, CBC with diff, and tympanocentesis tests, as needed.
- Management may range from watchful waiting for some cases, to antibiotics for more severe cases, to otolaryngological referrals as appropriate.
Tympanic Membrane Perforation
- Tympanic membrane perforation is an opening in the eardrum, which separates the outer from the inner ear (separates the external ear from the middle ear).
- It can cause conductive hearing loss.
- Most cases heal spontaneously without intervention; however, some may require referral to an otolaryngologist for repair using a patch or graft.
- Diagnoses may include otoscopic exams, and audiograms may be taken to assess the integrity and degree of hearing loss.
- Management focuses on keeping water out of the ear until healed.
- Antibiotic use may be necessary if infection is present.
Case Study 1 (58-year-old male with impacted cerumen)
- Possible Causes for impacted cerumen:* Age, use of earbuds/cotton swabs, and frequent ear cleaning.
- Appropriate removal methods:* Irrigation, manual removal (with curette), cerumenolytic agents.
- Important Questions for the patient:* History of ruptured TM, tympanostomy tubes, recent ear surgery, and prior cerumen impaction.
Case Study 2 (2-year-old boy with ear pain and fevers):
- Likely diagnosis:* acute otitis media
- Appropriate examination/diagnostics:* Otoscopic exam, possibly a viral respiratory nasal swab and CBC/chemistry depending on the specific presentation.
- Treatment:* Analgesics and watchful waiting; in some cases, antibiotics may be used (especially if there is a severe presentation), and otolaryngology referral should be considered if symptoms continue or worsen.
- (Important Considerations):* Immediate referral to an otolaryngologist may be necessary if symptoms are very severe or concerning, even if the preliminary treatment approach is watchful waiting.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.