Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following conditions are primarily involved in COPD?
Which of the following conditions are primarily involved in COPD?
- Asthma and pneumonia
- Interstitial lung disease and pulmonary fibrosis
- Tuberculosis and cystic fibrosis
- Emphysema and chronic bronchitis (correct)
What is the primary initial treatment goal for mild to moderate COPD exacerbation?
What is the primary initial treatment goal for mild to moderate COPD exacerbation?
- Administering antibiotics to combat infection
- Reducing bronchospasm and clearing sputum (correct)
- Providing mechanical ventilation
- Increasing oxygen levels to maximum
Why must caution be taken when administering oxygen to patients with long-standing COPD?
Why must caution be taken when administering oxygen to patients with long-standing COPD?
- They require high levels of oxygen for survival
- They become insensitive to carbon dioxide levels
- They have a hypercapnic respiratory drive
- They may lose their hypoxic respiratory drive (correct)
What is considered an adequate SaO2 level for monitoring patients with COPD?
What is considered an adequate SaO2 level for monitoring patients with COPD?
What types of medications are typically used to manage COPD?
What types of medications are typically used to manage COPD?
What is the primary goal of prehospital care for patients experiencing respiratory distress?
What is the primary goal of prehospital care for patients experiencing respiratory distress?
In which situation is the use of oxygen considered carefully stratified rather than applied indiscriminately?
In which situation is the use of oxygen considered carefully stratified rather than applied indiscriminately?
What method might some patients utilize for long-term oxygen therapy when nasal cannulas are irritating?
What method might some patients utilize for long-term oxygen therapy when nasal cannulas are irritating?
What has advanced life support (ALS) interventions shown to do in relation to patients with respiratory distress?
What has advanced life support (ALS) interventions shown to do in relation to patients with respiratory distress?
What is a notable characteristic of bronchial constriction associated with asthma?
What is a notable characteristic of bronchial constriction associated with asthma?
Why might ongoing research change the guidelines for oxygen delivery in prehospital care?
Why might ongoing research change the guidelines for oxygen delivery in prehospital care?
What is one risk associated with the use of oxygen in prehospital settings?
What is one risk associated with the use of oxygen in prehospital settings?
What is a common demographic affected by acute respiratory distress?
What is a common demographic affected by acute respiratory distress?
What is the primary focus in the management of asthma?
What is the primary focus in the management of asthma?
Which class of medication is considered the first line for treating asthma exacerbations?
Which class of medication is considered the first line for treating asthma exacerbations?
What potential side effects can occur with the stimulation of beta1 receptors in asthma medications?
What potential side effects can occur with the stimulation of beta1 receptors in asthma medications?
Which of the following statements regarding albuterol and levalbuterol is correct?
Which of the following statements regarding albuterol and levalbuterol is correct?
What defines the third-generation asthma medications?
What defines the third-generation asthma medications?
What should be done if inhaled bronchodilators are ineffective for a patient experiencing an asthma attack?
What should be done if inhaled bronchodilators are ineffective for a patient experiencing an asthma attack?
Which of the following is an example of an intrinsic trigger for asthma attacks?
Which of the following is an example of an intrinsic trigger for asthma attacks?
What effect does stimulation of the alpha receptors have in a patient with asthma?
What effect does stimulation of the alpha receptors have in a patient with asthma?
What is the primary effect of bronchospasm on the respiratory system?
What is the primary effect of bronchospasm on the respiratory system?
Which of the following best describes selective bronchodilators?
Which of the following best describes selective bronchodilators?
What is a potential side effect of excessive doses of beta2 agonists?
What is a potential side effect of excessive doses of beta2 agonists?
What condition should paramedics be cautious about when administering beta2 agonists?
What condition should paramedics be cautious about when administering beta2 agonists?
Which bronchodilator is classified as a nonselective agent?
Which bronchodilator is classified as a nonselective agent?
What is the primary mechanism of action of beta2 agonists?
What is the primary mechanism of action of beta2 agonists?
How does mucosal edema impact airway function?
How does mucosal edema impact airway function?
Acute asthma attacks can affect which demographic?
Acute asthma attacks can affect which demographic?
What is the primary action of ipratropium bromide in patients with COPD?
What is the primary action of ipratropium bromide in patients with COPD?
Which medication is commonly combined with ipratropium bromide for enhanced therapeutic effects?
Which medication is commonly combined with ipratropium bromide for enhanced therapeutic effects?
In patients experiencing an asthma exacerbation, when should corticosteroids be administered?
In patients experiencing an asthma exacerbation, when should corticosteroids be administered?
What is NOT a characteristic of a patient having an asthma attack?
What is NOT a characteristic of a patient having an asthma attack?
Which corticosteroids are mentioned as commonly used for managing moderate or severe asthma symptoms?
Which corticosteroids are mentioned as commonly used for managing moderate or severe asthma symptoms?
What is a limitation of bronchodilators like albuterol in asthma and COPD treatment?
What is a limitation of bronchodilators like albuterol in asthma and COPD treatment?
What role does the peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR) serve in the management of asthma exacerbations?
What role does the peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR) serve in the management of asthma exacerbations?
How does ipratropium compare to adrenergic agents like albuterol in terms of action site?
How does ipratropium compare to adrenergic agents like albuterol in terms of action site?
Under what condition should corticosteroids be considered for asthma treatment?
Under what condition should corticosteroids be considered for asthma treatment?
What is the current recommendation regarding the use of aminophylline in acute asthma exacerbations?
What is the current recommendation regarding the use of aminophylline in acute asthma exacerbations?
In which situation is magnesium sulfate considered beneficial for asthma patients?
In which situation is magnesium sulfate considered beneficial for asthma patients?
What caution should be taken when using epinephrine for asthma treatment?
What caution should be taken when using epinephrine for asthma treatment?
What side effect might result from the administration of epinephrine?
What side effect might result from the administration of epinephrine?
What is a characteristic of the effects of epinephrine in asthma management?
What is a characteristic of the effects of epinephrine in asthma management?
What should be considered regarding corticosteroid treatment in asthma management?
What should be considered regarding corticosteroid treatment in asthma management?
When is epinephrine still indicated for asthma patients?
When is epinephrine still indicated for asthma patients?
Flashcards
What is respiratory distress?
What is respiratory distress?
A common occurrence in the field, affecting people of all ages and backgrounds.
What is oxygen?
What is oxygen?
The most frequently used medication for prehospital treatment.
Why has oxygen use become controversial?
Why has oxygen use become controversial?
The use of oxygen in prehospital care has become more selective and individualized.
What is Asthma?
What is Asthma?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is COPD?
What is COPD?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are bronchodilators?
What are bronchodilators?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a transtracheal catheter?
What is a transtracheal catheter?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is titrated oxygen therapy?
What is titrated oxygen therapy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mucosal Edema
Mucosal Edema
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bronchospasm
Bronchospasm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bronchodilator
Bronchodilator
Signup and view all the flashcards
Selective Bronchodilators
Selective Bronchodilators
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nonselective Bronchodilators
Nonselective Bronchodilators
Signup and view all the flashcards
Beta2 Agonists
Beta2 Agonists
Signup and view all the flashcards
Racemic Epinephrine
Racemic Epinephrine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acute Asthma Attack
Acute Asthma Attack
Signup and view all the flashcards
Asthma Triggers
Asthma Triggers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Asthma Management: Prevention
Asthma Management: Prevention
Signup and view all the flashcards
Asthma Management: Acute Attack
Asthma Management: Acute Attack
Signup and view all the flashcards
Asthma Treatment: First Line
Asthma Treatment: First Line
Signup and view all the flashcards
Albuterol: Beta2 Agonist
Albuterol: Beta2 Agonist
Signup and view all the flashcards
Levalbuterol: Purified Albuterol
Levalbuterol: Purified Albuterol
Signup and view all the flashcards
Asthma Medications: Evolution
Asthma Medications: Evolution
Signup and view all the flashcards
Third Generation Asthma Medications
Third Generation Asthma Medications
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is emphysema?
What is emphysema?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is chronic bronchitis?
What is chronic bronchitis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is hypoxic respiratory drive?
What is hypoxic respiratory drive?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How much oxygen should COPD patients receive?
How much oxygen should COPD patients receive?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Ipratropium bromide (Atrovent) used for?
What is Ipratropium bromide (Atrovent) used for?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What type of medication is Ipratropium bromide?
What type of medication is Ipratropium bromide?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does Ipratropium bromide compare to albuterol in severe bronchospasm?
How does Ipratropium bromide compare to albuterol in severe bronchospasm?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the different sites of action for albuterol and ipratropium bromide?
What are the different sites of action for albuterol and ipratropium bromide?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do albuterol and ipratropium bromide differ in their effectiveness in asthma and COPD?
How do albuterol and ipratropium bromide differ in their effectiveness in asthma and COPD?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Combivent and how does it work?
What is Combivent and how does it work?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of corticosteroids in acute asthma and COPD exacerbations?
What is the role of corticosteroids in acute asthma and COPD exacerbations?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are two commonly used corticosteroids for moderate to severe asthma and COPD?
What are two commonly used corticosteroids for moderate to severe asthma and COPD?
Signup and view all the flashcards
When are corticosteroids used in acute asthma exacerbations?
When are corticosteroids used in acute asthma exacerbations?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the current role of aminophylline and methylxanthines in asthma management?
What is the current role of aminophylline and methylxanthines in asthma management?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does magnesium sulfate work in asthma management?
How does magnesium sulfate work in asthma management?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the considerations regarding epinephrine use in adult asthma?
What are the considerations regarding epinephrine use in adult asthma?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the disadvantages of using epinephrine in adults with asthma?
What are the disadvantages of using epinephrine in adults with asthma?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why is epinephrine not the first-line treatment for adult asthma?
Why is epinephrine not the first-line treatment for adult asthma?
Signup and view all the flashcards
When is epinephrine still indicated in asthma management?
When is epinephrine still indicated in asthma management?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why is epinephrine not considered a sustainable treatment for recurring asthma attacks?
Why is epinephrine not considered a sustainable treatment for recurring asthma attacks?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Drugs Used to Treat Respiratory Emergencies
- Respiratory distress is a common presentation in prehospital settings, affecting people of all ages and ethnicities.
- While underlying conditions vary, reversible bronchial constriction (bronchospasm) is a frequent cause, excluding acute pulmonary edema.
- Advanced life support (ALS) interventions, including respiratory medications, significantly reduce mortality in patients with respiratory distress.
Oxygen
- Oxygen is the most commonly used medication in prehospital settings.
- Like any drug, oxygen has associated benefits and risks.
- Routine oxygen use is often applied indiscriminately, but now more carefully titrated to prescribed oxygen saturation ranges in situations such as neonatal resuscitation, COPD exacerbations, and acute coronary syndrome.
- EMS providers should anticipate guideline updates and paradigm shifts in oxygen delivery approaches.
- Some patients require continuous home oxygen, often via transtracheal catheters (inserted surgically).
- Nasal cannulas are another long-term oxygen therapy option, addressing chronic lung disease, but can be irritating to the nose.
Bronchodilators
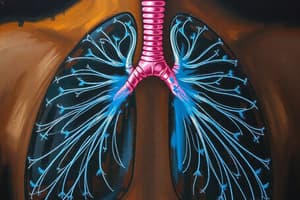
- Patients with asthma and COPD often experience respiratory distress due to airway narrowing.
- Bronchospasm (smooth muscle spasm) and mucosal edema reduce airway diameter.
- Increased secretions contribute to patient distress.
- Bronchodilators (medications widening the airways) are categorized as selective or nonselective.
- Selective agents target primarily bronchial smooth muscle, minimizing side effects.
- Beta2 agonists (sympathomimetics) relax bronchial smooth muscle without causing tachycardia or hypertension.
- Common examples include albuterol, terbutaline, formoterol, and pirbuterol.
- Nonselective agents act on alpha, beta1, and beta2 adrenergic receptors.
- Alpha receptor stimulation constricts peripheral blood vessels, raising blood pressure.
- Beta1 receptor stimulation increases heart rate and contractility.
- Beta2 receptor stimulation causes bronchodilation.
- Racemic epinephrine is a nonselective bronchodilator.
Management of Asthma
- Asthma management prioritizes avoiding triggers and alleviating their effects.
- When EMS is called, the focus shifts to reversing acute bronchospasm.
- Initial treatment for asthma and COPD exacerbations typically involves inhaled beta2-specific drugs.
- If inhaled bronchodilators fail, intravenous medications are used.
- Albuterol (Proventil, Ventolin) is a common inhaled bronchodilator primarily targeting beta2 receptors.
- Newer, "purified" versions like levalbuterol (Xopenex) are developed to minimize side-effects.
- First-generation drugs have significant beta1 effects alongside beta2 effects, while later generations target beta2 receptors more effectively.
- Ipratropium bromide (Atrovent) is an anticholinergic and is not an adrenergic; useful in severe exacerbations or patients with a limited response to albuterol.
- It is useful in more severe cases. Adrenergic agents like albuterol target the central bronchial tree, whereas ipratropium works better in the peripheral airways.
Management of COPD Exacerbations
- In severe COPD exacerbations, immediate oxygenation and ventilation are prioritized.
- Oxygen should be administered cautiously to patients with hypoxic respiratory drive (requiring a mild degree of hypoxia for breathing).
- Pulse oximetry (SaO2 level in the low 90s) is considered adequate for COPD patients.
- Bronchodilators and steroids are used to manage COPD similarly to asthma.
Second-Line Therapies for Acute Asthma Exacerbation
- Consider corticosteroids for prolonged transport times, addressing underlying inflammatory processes.
- Common corticosteroids include methylprednisolone and dexamethasone.
- PEFR (peak expiratory flow rate) is a vital objective measure for guiding treatment decisions and assessing therapy response.
- PEFR less than 50% of predicted value or improvement less than 10% after bronchodilators suggest a need for corticosteroids.
- Aminophylline/methylxanthines were once common but are less frequently used now.
- Magnesium sulfate might be effective in some patients who don't respond to beta2 agonists.
- Epinephrine, while effective, also has short-lived effects and can provoke unwanted alpha and beta1 effects.
Dexamethasone and Methylprednisolone
- Dexamethasone and methylprednisolone are corticosteroids used to manage inflammation in various medical conditions (e.g. asthma, COPD, or airway edema).
- They reduce inflammation, offering benefits in a variety of situations.
- Possible side effects (e.g., depression, euphoria, dizziness) and potential contraindications (e.g., fungal infections or pre-existing renal conditions) should be considered during administration.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.