Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the role of the hepatic portal vein in nutrient transport?
What is the role of the hepatic portal vein in nutrient transport?
- It carries nutrient-rich blood directly to the liver for regulation. (correct)
- It transports oxygenated blood to the intestines.
- It removes toxins from the large intestine.
- It helps absorb fatty acids into the bloodstream.
What role does saliva play during the mechanical digestion process?
What role does saliva play during the mechanical digestion process?
- It alters the pH level of the saliva.
- It provides the primary source of energy for digestion.
- It chemically breaks down food enzymes.
- It lubricates food, facilitating swallowing. (correct)
Which structure significantly increases the surface area for nutrient absorption in the intestine?
Which structure significantly increases the surface area for nutrient absorption in the intestine?
- Gastrovascular cavity
- Microvilli on epithelial cells (correct)
- Villi projecting into the intestinal lumen
- Chylomicrons in lymphatic vessels
Which enzymes and substances are primarily involved in fat digestion and absorption?
Which enzymes and substances are primarily involved in fat digestion and absorption?
Which statement correctly describes the absorption stage in the digestive process?
Which statement correctly describes the absorption stage in the digestive process?
Which type of molecule is NOT directly processed in the digestive system?
Which type of molecule is NOT directly processed in the digestive system?
How do specialized compartments prevent animals from digesting their own cells during digestion?
How do specialized compartments prevent animals from digesting their own cells during digestion?
How do teeth contribute to the mechanical digestion process?
How do teeth contribute to the mechanical digestion process?
What is a characteristic feature of the digestive system in sponges that differentiates them from more complex organisms?
What is a characteristic feature of the digestive system in sponges that differentiates them from more complex organisms?
What evolutionary adaptation in digestion allows some animals to utilize larger food sources?
What evolutionary adaptation in digestion allows some animals to utilize larger food sources?
What is a key function of bile in the digestive system?
What is a key function of bile in the digestive system?
Which element does NOT contribute to the neural regulation of digestive processes?
Which element does NOT contribute to the neural regulation of digestive processes?
What is the primary purpose of peristalsis in the digestive system?
What is the primary purpose of peristalsis in the digestive system?
What is the primary function of the alimentary canal compared to the gastrovascular cavity?
What is the primary function of the alimentary canal compared to the gastrovascular cavity?
Which statement best describes the sequence of digestion in the alimentary canal?
Which statement best describes the sequence of digestion in the alimentary canal?
How does the enteric nervous system influence digestion?
How does the enteric nervous system influence digestion?
In relation to energy storage in humans, which statement is accurate?
In relation to energy storage in humans, which statement is accurate?
What distinguishes a crop and gizzard from the typical stomach function in humans?
What distinguishes a crop and gizzard from the typical stomach function in humans?
Which evolutionary adaptation is most associated with the advancement of the alimentary canal?
Which evolutionary adaptation is most associated with the advancement of the alimentary canal?
What triggers the secretion of saliva when food is in the oral cavity?
What triggers the secretion of saliva when food is in the oral cavity?
Which of the following provides the most energy per molecule compared to carbohydrates?
Which of the following provides the most energy per molecule compared to carbohydrates?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Digestive System Overview
- Undigested material can be expelled from the mouth.
- The alimentary canal includes a one-way flow with sequential compartments: pharynx, esophagus, stomach, intestine, and anus.
- Humans possess a stomach, while some animals have additional structures such as a crop and gizzard.
Gastrovascular Cavity vs Alimentary Canal
- Gastrovascular cavities feature a single opening for digestion.
- Alimentary canals consist of multiple compartments and have both a mouth and an anus, facilitating nutrient absorption.
Regulation of Digestion
- Digestion is activated step-wise as food progresses through compartments.
- Nervous reflexes stimulate saliva release and initiate swallowing upon food entry into the oral cavity.
- The arrival of food in the stomach encourages churning and gastric juice release, controlled by the enteric nervous system.
Energy Storage Regulations
- Excess energy-rich molecules are stored when intake surpasses metabolic needs.
- In humans, energy is stored as glycogen within liver and muscle cells; surplus converts to fat in adipose tissues.
- During energy deficits, the body utilizes stored glycogen and fat, with fats providing roughly double the energy of carbohydrates.
Food Processing Stages
- Ingestion: Eating and forming a bolus through mechanical digestion.
- Digestion: Breakdown of food into smaller molecules for absorption.
- Mechanical: Consumption and salivation aid swallowing and increase surface area for digestion.
- Chemical: Large molecules (proteins, polysaccharides, nucleic acids, fats) are broken down into smaller units (amino acids, monosaccharides, nucleotides, glycerol, and fatty acids) for absorption.
Absorption Details
- Contents move through the jejunum and ileum via peristalsis.
- Villi and microvilli in the intestinal lining increase surface area for nutrient absorption.
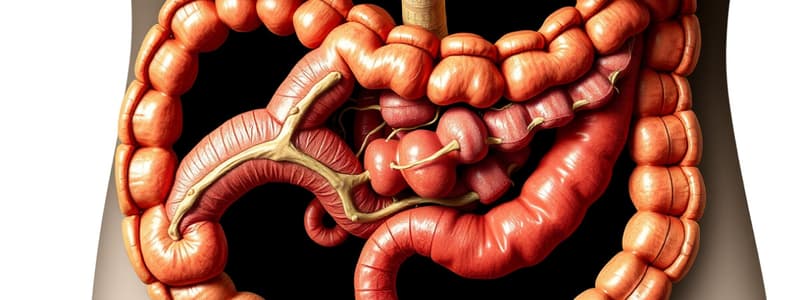
- Nutrient-rich blood travels to the liver via the hepatic portal vein, where nutrient distribution and detoxification occur.
Fat Digestion and Absorption
- Bile and the enzyme lipase are crucial for fat digestion.
- Fatty acids and monoglycerides are absorbed into intestinal cells, forming triglycerides and subsequently chylomicrons, which enter the lymphatic system.
Elimination Process
- Undigested material exits the body as feces through the large intestine, rectum, and anus.
- The large intestine reclaims water from waste.
Evolutionary Adaptations
- Animals possess specialized compartments for digestion to prevent self-digestion.
- Sponges digest food within vacuoles, while cnidarians and flatworms utilize a gastrovascular cavity for enzymatic breakdown and absorption.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.