Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of accessory organs in the digestive system?
What is the primary function of accessory organs in the digestive system?
- They secrete enzymes to aid in digestion. (correct)
- They absorb nutrients into the bloodstream.
- They move food through the body.
- They handle food directly.
Which structure of the digestive system is responsible for physically breaking down food?
Which structure of the digestive system is responsible for physically breaking down food?
- Small intestine
- Gallbladder
- Pancreas
- Mouth (correct)
What is the primary role of the tongue in the digestion process?
What is the primary role of the tongue in the digestion process?
- To secrete gastric juices
- To absorb nutrients
- To break down proteins
- To form the bolus of food (correct)
Which process is used to push food down the esophagus?
Which process is used to push food down the esophagus?
What mechanism helps move food down the esophagus?
What mechanism helps move food down the esophagus?
What role do villi and microvilli play in the small intestine?
What role do villi and microvilli play in the small intestine?
What happens to water and salts in the large intestine?
What happens to water and salts in the large intestine?
What structure must food pass through before entering the stomach?
What structure must food pass through before entering the stomach?
What is the primary function of gastric juice in the stomach?
What is the primary function of gastric juice in the stomach?
What enzyme in saliva begins the digestion of starch?
What enzyme in saliva begins the digestion of starch?
Which enzyme initiates protein digestion in the stomach?
Which enzyme initiates protein digestion in the stomach?
Which of these structures does NOT belong to the digestive tract?
Which of these structures does NOT belong to the digestive tract?
What is the pH range of gastric juice?
What is the pH range of gastric juice?
Where does the process of digestion first begin?
Where does the process of digestion first begin?
How does the stomach protect itself from its own gastric acid?
How does the stomach protect itself from its own gastric acid?
What enzyme is produced in the stomach that digests proteins?
What enzyme is produced in the stomach that digests proteins?
What thick substance protects the stomach lining from gastric acid?
What thick substance protects the stomach lining from gastric acid?
Which of the following nutrients is primarily absorbed in the ileum?
Which of the following nutrients is primarily absorbed in the ileum?
What is the main function of the large intestine?
What is the main function of the large intestine?
In which part of the small intestine does most chemical digestion occur?
In which part of the small intestine does most chemical digestion occur?
What role do villi play in the small intestine?
What role do villi play in the small intestine?
Which component is NOT found in the digestive fluids of the stomach?
Which component is NOT found in the digestive fluids of the stomach?
How do sphincter muscles contribute to digestion?
How do sphincter muscles contribute to digestion?
What is the primary role of amylase in saliva?
What is the primary role of amylase in saliva?
What is the primary purpose of the appendix according to recent hypotheses?
What is the primary purpose of the appendix according to recent hypotheses?
What condition can result from the appendix absorbing bad bacteria?
What condition can result from the appendix absorbing bad bacteria?
Which enzyme is responsible for digesting starch in the small intestine?
Which enzyme is responsible for digesting starch in the small intestine?
What effect does bile salt have on fats?
What effect does bile salt have on fats?
What pH level does the bicarbonate in pancreatic fluid aim to achieve in the duodenum?
What pH level does the bicarbonate in pancreatic fluid aim to achieve in the duodenum?
What occurs if the appendix is not surgically removed in severe cases of appendicitis?
What occurs if the appendix is not surgically removed in severe cases of appendicitis?
How much pancreatic fluid is delivered to the duodenum each day?
How much pancreatic fluid is delivered to the duodenum each day?
What is a symptom of appendicitis?
What is a symptom of appendicitis?
Flashcards
Digestive System Divisions
Digestive System Divisions
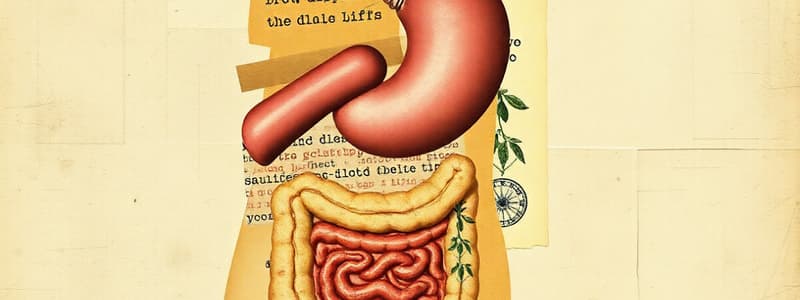
The digestive system is divided into accessory organs and the digestive tract.
Accessory Organs
Accessory Organs
Organs that aid digestion, but don't directly move food.
Digestive Tract
Digestive Tract
Path the food takes through the body for digestion and absorption.
Mouth Digestion
Mouth Digestion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peristalsis
Peristalsis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Small Intestine Absorption
Small Intestine Absorption
Signup and view all the flashcards
Salivary Amylase
Salivary Amylase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Large Intestine Function
Large Intestine Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bolus
Bolus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Esophageal Sphincter
Esophageal Sphincter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Churning
Churning
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gastric Juice
Gastric Juice
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chyme
Chyme
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pepsin
Pepsin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mucus Protection
Mucus Protection
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pepsin Activation
Pepsin Activation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stomach Absorption
Stomach Absorption
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pyloric Sphincter Role
Pyloric Sphincter Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Small Intestine Function
Small Intestine Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Villi and Microvilli
Villi and Microvilli
Signup and view all the flashcards
Duodenum Chemical Digestion
Duodenum Chemical Digestion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Jejunum Function
Jejunum Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ileum Role
Ileum Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bowel Movement Trigger
Bowel Movement Trigger
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fiber's Role in Digestion
Fiber's Role in Digestion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Appendix's Purpose
Appendix's Purpose
Signup and view all the flashcards
Appendicitis
Appendicitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pancreas's Digestive Role
Pancreas's Digestive Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Liver's Role in Digestion
Liver's Role in Digestion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gallbladder's Function
Gallbladder's Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Emulsification
Emulsification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Digestive System Overview
- The digestive system has two main divisions: accessory organs and digestive tract.
- Accessory organs aid in digestion by secreting enzymes; they don't handle food directly (salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas).
- Digestive tract structures move food through the body (mouth, esophagus, stomach, small & large intestine, rectum, anus).
Digestive System Structures
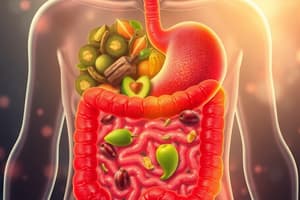
- Mouth: Digestion starts here, with teeth breaking down food physically and salivary enzymes (amylase) chemically breaking down starch.
- Esophagus: Transports food (bolus) to the stomach via peristalsis (wave-like muscle contractions).
- Stomach: Undergoes both physical (churning) and chemical (acid, enzymes) digestion. Produces chyme (processed food).
- Small Intestine: Completes digestion and absorbs nutrients. Has villi and microvilli to maximize absorption surface area.
- Large Intestine: Absorbs water and electrolytes; concentrates and eliminates waste.
Accessory Organs Detail
- Pancreas: Delivers enzymes (trypsin, chymotrypsin, amylase, lipase) to the duodenum that complete digestion of carbs, protein, and fats. Produces bicarbonate which neutralizes stomach acid.
- Liver: Produces bile which emulsifies fats, increasing the surface area for lipase enzymes to break them down more efficiently.
- Gallbladder: Stores and releases bile into the small intestine when needed.
Small Intestine Regions
- Duodenum: First part of the small intestine; site of most chemical digestion.
- Jejunum: Middle section; continues breaking down food.
- Ileum: Final section; absorbs nutrients and moves remaining undigested material to the large intestine.
Large Intestine
- The large intestine is shorter but wider than the small intestine, and it absorbs water from the digested food and eliminates wastes. Cellulose, a carbohydrate in plants, is undigested by the human body but adds bulk to the waste materials. Colon cancer correlates to poor diets.
Stomach Digestion
- Stomach has three methods of protection: 1. producing gastric juice only when food is present, 2. secreting mucus to prevent the stomach lining from damage and 3. producing a protein-digesting enzyme called pepsin. Pepsin is active in a highly acidic environment (pH 1-3).
- Gastric juice is made of water, mucus, salts, hydrochloric acid, and enzymes; it helps to soften and break down proteins, and kills bacteria.
Appendix
- The appendix, once believed to be vestigial (having no function), is now hypothesized to aid in digestion by storing "good" bacteria. In cases of bacterial infection, it is surgically removed. Inflammation of the appendix is called appendicitis.
Ingestion Summary
- Saliva contains amylase to start starch digestion.
- Teeth break down food into smaller particles and crush them.
- Peristalsis moves food through the esophagus.
- Sphincters control food movement in and out of the stomach.
- The stomach contains HCI, pepsinogens and mucous.
- Peristalsis mixes food in the stomach.
Protein Digestion
- Pepsin, a protein-digesting enzyme, starts to breakdown protein present in the food in the stomach. A thick mucus prevents the acid from damaging the stomach lining.
- The stomach doesn't usually digest its own proteins.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.