Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the enteric nervous system?
What is the primary function of the enteric nervous system?
- To extrinsically innervate the alimentary canal
- To regulate digestive secretions
- To restrict the activity of the autonomic nervous system
- To control the motility of the alimentary canal (correct)
What is the primary function of the parasympathetic nerves in the alimentary canal?
What is the primary function of the parasympathetic nerves in the alimentary canal?
- To increase GI secretion and motility (correct)
- To restrict the activity of the enteric neurons
- To decrease GI secretion and motility
- To extrinsically innervate the alimentary canal
What is the primary function of the hepatic portal system?
What is the primary function of the hepatic portal system?
- To line the abdominal wall with the parietal peritoneum
- To hold the digestive organs in place
- To deliver nutrients and oxygen to the organs of the alimentary canal
- To transport protein and carbohydrate to the liver (correct)
What is the primary function of the parietal peritoneum?
What is the primary function of the parietal peritoneum?
What is the primary function of the mouth in the digestive process?
What is the primary function of the mouth in the digestive process?
What is the primary function of the pharynx in the digestive process?
What is the primary function of the pharynx in the digestive process?
What is the approximate length of the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract?
What is the approximate length of the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract?
What type of epithelium is found in the stomach and intestines?
What type of epithelium is found in the stomach and intestines?
What is the function of the muscularis mucosa layer?
What is the function of the muscularis mucosa layer?
What is the role of the submucosa layer?
What is the role of the submucosa layer?
Which layer of the gastrointestinal tract is responsible for peristalsis?
Which layer of the gastrointestinal tract is responsible for peristalsis?
What is the primary purpose of the digestive process described in the text?
What is the primary purpose of the digestive process described in the text?
Which of the following is NOT a type of regulatory mechanism described in the text?
Which of the following is NOT a type of regulatory mechanism described in the text?
Where is skeletal muscle found in the gastrointestinal tract?
Where is skeletal muscle found in the gastrointestinal tract?
What is the primary function of the tongue according to the text?
What is the primary function of the tongue according to the text?
What is the purpose of the uvula according to the text?
What is the purpose of the uvula according to the text?
What is the primary function of the small intestine described in the text?
What is the primary function of the small intestine described in the text?
Which of the following hormones is NOT mentioned in the text as playing a role in the digestive process?
Which of the following hormones is NOT mentioned in the text as playing a role in the digestive process?
What is the primary function of the stomach in the digestive system?
What is the primary function of the stomach in the digestive system?
Which organ is responsible for releasing bile salts to emulsify lipids for digestion and absorption?
Which organ is responsible for releasing bile salts to emulsify lipids for digestion and absorption?
What is the function of peristalsis in the digestive system?
What is the function of peristalsis in the digestive system?
Which process exposes a larger surface area of food to digestive juices?
Which process exposes a larger surface area of food to digestive juices?
What is the role of the gallbladder in the digestive system?
What is the role of the gallbladder in the digestive system?
Which part of the digestive system absorbs some fat-soluble substances such as alcohol and aspirin?
Which part of the digestive system absorbs some fat-soluble substances such as alcohol and aspirin?
What is the primary digestive organ responsible for most absorption?
What is the primary digestive organ responsible for most absorption?
Which section of the small intestine is the longest and has more vascular and mucosal folds?
Which section of the small intestine is the longest and has more vascular and mucosal folds?
What initiates peristalsis in the intestine to move chyme through?
What initiates peristalsis in the intestine to move chyme through?
Which contractions mix chyme with digestive juices and force particles toward the mucosa for absorption?
Which contractions mix chyme with digestive juices and force particles toward the mucosa for absorption?
What part of the small intestine contains circular folds, villi, and microvilli to enhance absorption?
What part of the small intestine contains circular folds, villi, and microvilli to enhance absorption?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
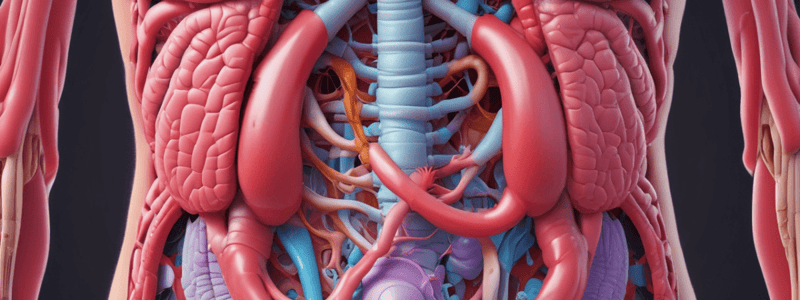
Digestive System Overview
- The digestive system, also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal (GI) tract, is approximately 25 ft long from mouth to anus.
- It has 4 layers: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, and serosa.
GI Tract Layers
- Mucosa: mucous membrane epithelium in contact with food, with epithelium, lamina propria, and muscularis mucosa.
- Submucosa: dense connective tissue with blood and lymphatic vessels, and has a collection of nerves called the submucosal plexus.
- Muscularis: inner circular layer and outer longitudinal layer in the small intestine, responsible for mechanical digestion and peristalsis.
- Serosa: most superficial layer, only in the region inside the abdominal cavity, made of loose connective tissue.
Small Intestine
- Primary digestive organ and most absorption occurs here.
- Longest part of the canal, with a huge surface area.
- Has 3 regions: duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
- Contains circular folds, villi, and microvilli to enlarge surface area and enhance absorption.
Mechanical Digestion
- Peristalsis: moving chyme through the intestine, started by hormone motilin, takes 90-120 minutes for chyme to reach the end of the ileum.
- Segmentation: back and forth contractions to mix chyme with digestive juices and force particles toward the mucosa to be absorbed.
Nerve Supply
- Enteric nervous system runs from esophagus to anus and is separated into 2 plexuses: myenteric and submucosal.
- Autonomic nervous system extrinsically innervates the alimentary canal.
- Sympathetic nerves restrict enteric neurons, while parasympathetic nerves increase GI secretion and motility.
Blood Supply
- Hepatic portal system delivers nutrients and oxygen to organs of the alimentary canal.
- While resting and digesting, 25% of blood pumped enters arteries serving the intestines.
The Peritoneum
- Holds digestive organs in place, with 2 different regions: parietal peritoneum and visceral peritoneum.
- Peritoneal cavity: space between parietal and visceral peritoneum.
Digestive System Processes
- Ingestion: entry of food into the alimentary canal through the mouth.
- Mechanical digestion: physical process that does not change the chemical nature of food (mastication, churning, segmentation).
- Chemical digestion: breaking down complex food molecules into their building blocks (water, acid, enzymes, and salts).
- Absorption: primarily in the small intestine, taking nutrients into the bloodstream or lipids into lymphatic system.
- Defecation: undigested materials are removed from the body.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.