Podcast
Questions and Answers
How does the body primarily respond during the fasting phase to maintain energy levels?
How does the body primarily respond during the fasting phase to maintain energy levels?
- By increasing insulin levels to promote glucose uptake by cells.
- By immediately signaling hunger to trigger food consumption.
- By halting glucose usage to conserve energy, regardless of the brain's needs.
- By converting stored glycogen and fat into glucose, facilitated by elevated glucagon levels. (correct)
Which component of the set-point system detects deviations from the ideal energy level?
Which component of the set-point system detects deviations from the ideal energy level?
- Detector Mechanism (correct)
- Set-Point Mechanism
- Effector Mechanism
- Negative Feedback Loop
What is the primary role of insulin in maintaining energy balance?
What is the primary role of insulin in maintaining energy balance?
- To facilitate the storage of glucose after eating and lower blood glucose levels. (correct)
- To convert fatty acids into ketones for energy.
- To suppress hunger signals when energy levels are high.
- To increase blood glucose levels during fasting.
According to the Glucostatic Theory, what primarily drives hunger?
According to the Glucostatic Theory, what primarily drives hunger?
In the context of long-term energy regulation, which theory is most applicable?
In the context of long-term energy regulation, which theory is most applicable?
What is the role of glucagon during periods of fasting?
What is the role of glucagon during periods of fasting?
How do the glucostatic and lipostatic theories interact to regulate hunger and eating behavior?
How do the glucostatic and lipostatic theories interact to regulate hunger and eating behavior?
If someone's body is producing ketones, what does that indicate about their recent eating habits?
If someone's body is producing ketones, what does that indicate about their recent eating habits?
Which of the following scenarios best illustrates the impact of learned taste preferences on hunger?
Which of the following scenarios best illustrates the impact of learned taste preferences on hunger?
How do positive-incentive theories differ from set-point theories in explaining hunger?
How do positive-incentive theories differ from set-point theories in explaining hunger?
According to the information, which factor can most directly influence hunger levels?
According to the information, which factor can most directly influence hunger levels?
Which of the following is an example of how learning influences food preferences?
Which of the following is an example of how learning influences food preferences?
How do animals learn to select a diet that provides the necessary vitamins and minerals?
How do animals learn to select a diet that provides the necessary vitamins and minerals?
If an individual avoids eating a specific dish after experiencing nausea following its consumption, what is this aversion an example of?
If an individual avoids eating a specific dish after experiencing nausea following its consumption, what is this aversion an example of?
In the context of hunger and food preferences, what does the concept of 'cultural specificity' refer to?
In the context of hunger and food preferences, what does the concept of 'cultural specificity' refer to?
Which of the following best represent how group dynamics can impact dietary habits?
Which of the following best represent how group dynamics can impact dietary habits?
How do serotonin agonists like fenfluramine impact hunger and body weight?
How do serotonin agonists like fenfluramine impact hunger and body weight?
What characterizes the hunger and metabolism of individuals with Prader-Willi syndrome?
What characterizes the hunger and metabolism of individuals with Prader-Willi syndrome?
How does the body adjust energy utilization as body fat levels decrease?
How does the body adjust energy utilization as body fat levels decrease?
What happens to energy utilization efficiency as weight is gained?
What happens to energy utilization efficiency as weight is gained?
What effect does being only slightly overweight have on an individual's health risks?
What effect does being only slightly overweight have on an individual's health risks?
What is the correlation between obesity in women and infant health?
What is the correlation between obesity in women and infant health?
What is the general trend of obesity rates worldwide?
What is the general trend of obesity rates worldwide?
How does the body determine the level of food intake needed?
How does the body determine the level of food intake needed?
Which of the following best describes the initial conclusion drawn by Anand and Brobeck regarding the lateral hypothalamus (LH)?
Which of the following best describes the initial conclusion drawn by Anand and Brobeck regarding the lateral hypothalamus (LH)?
Teitelbaum and Epstein's research on LH-lesioned rats revealed which significant finding regarding recovery from aphagia?
Teitelbaum and Epstein's research on LH-lesioned rats revealed which significant finding regarding recovery from aphagia?
Later research reinterpreted the function of the lateral hypothalamus (LH), moving away from Anand and Brobeck's original conclusion. Which of the following is the most accurate description of this updated understanding?
Later research reinterpreted the function of the lateral hypothalamus (LH), moving away from Anand and Brobeck's original conclusion. Which of the following is the most accurate description of this updated understanding?
Research in the 1980s suggested the gastrointestinal tract plays a critical role in satiety. What evidence supported this view?
Research in the 1980s suggested the gastrointestinal tract plays a critical role in satiety. What evidence supported this view?
What was the critical characteristic of the transplanted stomach used in experiments investigating satiety signals?
What was the critical characteristic of the transplanted stomach used in experiments investigating satiety signals?
Based on the findings with transplanted stomachs, what conclusion was drawn about the nature of the satiety signal?
Based on the findings with transplanted stomachs, what conclusion was drawn about the nature of the satiety signal?
If a rat with a VMH lesion, already exhibiting hyperphagia, then receives an LH lesion, what is the likely outcome, according to the information provided?
If a rat with a VMH lesion, already exhibiting hyperphagia, then receives an LH lesion, what is the likely outcome, according to the information provided?
How did the discovery of adipsia in LH-lesioned rats influence the understanding of the LH's function?
How did the discovery of adipsia in LH-lesioned rats influence the understanding of the LH's function?
Why are weight-loss programs often ineffective in achieving permanent weight loss?
Why are weight-loss programs often ineffective in achieving permanent weight loss?
What is the primary role of leptin in regulating body fat, as demonstrated in ob/ob mice studies?
What is the primary role of leptin in regulating body fat, as demonstrated in ob/ob mice studies?
In what area of the nervous system are receptors for peptide hormones that regulate body weight primarily located?
In what area of the nervous system are receptors for peptide hormones that regulate body weight primarily located?
What are the two classes of neurons within the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus that are involved in regulating hunger and satiety?
What are the two classes of neurons within the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus that are involved in regulating hunger and satiety?
Why has α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH) been a significant focus in research related to weight loss?
Why has α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH) been a significant focus in research related to weight loss?
What were the two major snags encountered when research on leptin transitioned from ob/ob mice to obese humans?
What were the two major snags encountered when research on leptin transitioned from ob/ob mice to obese humans?
How did the discovery of ob/ob mice contribute to the understanding of obesity?
How did the discovery of ob/ob mice contribute to the understanding of obesity?
Which statement best describes the relationship between exercise and weight loss, according to the information?
Which statement best describes the relationship between exercise and weight loss, according to the information?
Which of the following statements best describes the key difference between the settling-point model and the set-point model of weight regulation?
Which of the following statements best describes the key difference between the settling-point model and the set-point model of weight regulation?
According to the presented information, what evolutionary advantage led to the current obesity epidemic?
According to the presented information, what evolutionary advantage led to the current obesity epidemic?
What is the primary factor that determines whether an individual becomes obese, according to the text?
What is the primary factor that determines whether an individual becomes obese, according to the text?
How does the concept of 'positive-incentive value' contribute to overconsumption in today's environment?
How does the concept of 'positive-incentive value' contribute to overconsumption in today's environment?
Considering the information, which of the following scenarios would be MOST consistent with the settling-point model of weight regulation?
Considering the information, which of the following scenarios would be MOST consistent with the settling-point model of weight regulation?
Based on the information provided about the obesity epidemic and its cause, which of the following interventions would be MOST effective at population level?
Based on the information provided about the obesity epidemic and its cause, which of the following interventions would be MOST effective at population level?
In the context of weight regulation, what critical role does negative feedback play, according to the settling-point model?
In the context of weight regulation, what critical role does negative feedback play, according to the settling-point model?
Considering both evolutionary factors and current environmental conditions, which statement best explains why some individuals are more prone to obesity?
Considering both evolutionary factors and current environmental conditions, which statement best explains why some individuals are more prone to obesity?
Flashcards
Glycogen
Glycogen
A stored form of glucose found in muscles and liver.
Set-Point Mechanism
Set-Point Mechanism
Defines the ideal energy level in the body.
Detector Mechanism
Detector Mechanism
It detects changes in energy levels.
Effector Mechanism
Effector Mechanism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glucostatic Theory
Glucostatic Theory
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lipostatic Theory
Lipostatic Theory
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glucagon
Glucagon
Signup and view all the flashcards
Combination Theory
Combination Theory
Signup and view all the flashcards
Learned Taste Preferences
Learned Taste Preferences
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cultural Food Preferences
Cultural Food Preferences
Signup and view all the flashcards
Time Since Last Meal
Time Since Last Meal
Signup and view all the flashcards
Social Influences on Hunger
Social Influences on Hunger
Signup and view all the flashcards
Flexible Eating vs. Set-Point Theory
Flexible Eating vs. Set-Point Theory
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nutrition Learning in Animals
Nutrition Learning in Animals
Signup and view all the flashcards
Influence of Group Rearing
Influence of Group Rearing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dietary Deficiencies and Selection
Dietary Deficiencies and Selection
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lateral Hypothalamus (LH)
Lateral Hypothalamus (LH)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Aphagia
Aphagia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adipsia
Adipsia
Signup and view all the flashcards
VMH Lesions
VMH Lesions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Satiety Signals
Satiety Signals
Signup and view all the flashcards
Role of Gastrointestinal Tract
Role of Gastrointestinal Tract
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tube Feeding Recovery
Tube Feeding Recovery
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chemical Satiety Mechanisms
Chemical Satiety Mechanisms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Serotonin Agonists
Serotonin Agonists
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prader-Willi Syndrome
Prader-Willi Syndrome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Energy Utilization Efficiency
Energy Utilization Efficiency
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diet-induced Thermogenesis
Diet-induced Thermogenesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Health Risks of Obesity
Health Risks of Obesity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Weight Loss Limitation
Weight Loss Limitation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rising Obesity Rates
Rising Obesity Rates
Signup and view all the flashcards
Settling-Point Model
Settling-Point Model
Signup and view all the flashcards
Set-Point Model
Set-Point Model
Signup and view all the flashcards
Negative Feedback
Negative Feedback
Signup and view all the flashcards
Leaky Barrel Model
Leaky Barrel Model
Signup and view all the flashcards
Positive Incentive
Positive Incentive
Signup and view all the flashcards
Energy Surplus
Energy Surplus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Energy Deficit
Energy Deficit
Signup and view all the flashcards
Obesity Factors
Obesity Factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Leptin
Leptin
Signup and view all the flashcards
ob/ob Mice
ob/ob Mice
Signup and view all the flashcards
Arcuate Nucleus
Arcuate Nucleus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Melanocortins
Melanocortins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neuropeptide Y (NPY)
Neuropeptide Y (NPY)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Exercise and Weight Loss
Exercise and Weight Loss
Signup and view all the flashcards
Effectiveness of Weight-Loss Programs
Effectiveness of Weight-Loss Programs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Leptin Treatment Challenges
Leptin Treatment Challenges
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
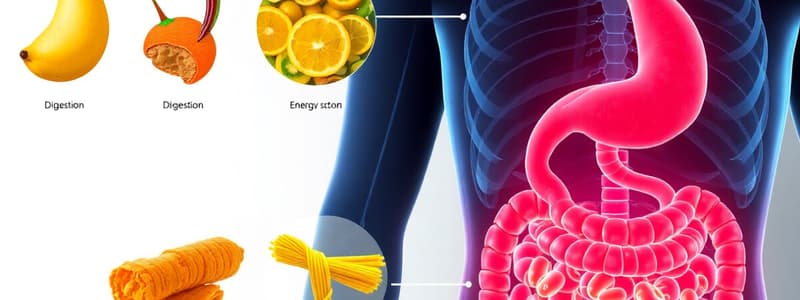
Digestion, Energy Storage, and Energy Utilization
- The primary purpose of hunger is to increase the likelihood of eating to provide the body with essential building blocks and energy for survival.
- Digestion breaks down food and absorbs nutrients into the body.
- Steps in digestion include chewing, swallowing, stomach action, small intestine absorption, and the role of enzymes from pancreas and gallbladder.
- Proteins are broken down into amino acids, carbohydrates into simple sugars (for energy), and fats into tiny droplets that go to the lymphatic system.
- The liver makes bile, which is stored in the gallbladder to aid fat digestion.
- The large intestine absorbs water and minerals from leftover food.
- The body stores energy in three main forms: fat (primary), glycogen (in liver and muscles), and proteins (for structure and function, not energy).
- Fat is the best energy storage form because it holds more energy than glycogen and is not bulky, requiring less water to store energy.
Three Phases of Energy Metabolism
- Cephalic phase: preparatory phase, starts with thoughts of food to absorption.
- Absorptive phase: the body absorbs nutrients and uses energy from food.
- Fasting phase: body uses stored energy reserves when no food is being absorbed.
Theories of Hunger and Eating: Set Points vs. Positive Incentives
- Set-point assumption: the body regulates hunger to maintain a stable energy (body fat or glucose) level.
- Glucostatic theory: low blood glucose levels trigger hunger; eating restores glucose levels.
- Lipostatic theory: low body fat triggers hunger; eating restores fat levels.
- Combination theory: interactions between glucostatic and lipostatic factors to regulate eating.
Factors that Determine What, When, and How Much We Eat
- Tastes (sweet, fatty, salty) are crucial factors in food preferences; bitter tastes are often aversive as they can signal potential toxins
- Learned taste preferences based on past experiences or culture.
- Timing and social cues influence when and how much is eaten and consumed.
Problems with Set-Point Theories
- Theories struggle to explain the obesity epidemic, as they assume stable body weight regulation, which is not accurate in modern society.
Premeal Hunger and Satiety Signals
- Eating causes homeostasis disruption; the body tries to maintain balance.
- Satiety signals from the gut and blood inhibit further consumption.
- Sham eating experiment indicated that the gut and blood are not necessary to signal the end of a meal.
- Other factors to influence how much is eaten include taste, amount/size of serving, appetizers, social factors.
Hypothalamic Hunger and Satiety Centers
- Early research hypothesized different regions of the hypothalamus as feeding (LH) and satiety (VMH) centers, which turned out not to be accurate
- VMH lesions led to hyperphagia and obesity, potentially due to altered insulin levels, which have been associated with impaired fat metabolism.
- LH lesions caused aphagia (cessation of eating) and adipsia (loss of the desire to drink).
Hunger and Satiety Peptides
- Peptides like ghrelin and leptin play crucial roles in hunger regulation.
- Several hunger and satiety peptides involved in signaling the hypothalamus about nutrient status.
- These findings have significantly advanced our understanding of the complex neural pathways involved in eating behavior.
- Serotonin is another key factor that plays a role in satiety.
Gastric Surgery
- Gastric bypass and adjustable gastric band procedures are surgical treatments for severe obesity; these procedures reduce the size of the stomach to limit intake.
Anorexia and Bulimia Nervosa
- Anorexia Nervosa: characterized by extreme underconsumption, distorted body image (seeing themselves fatter), with health risks and high rates of complications.
- Bulimia Nervosa: characterized by periods of rapid consumption of large amounts of food followed by behaviors meant to eliminate the calories, such as vomiting or using laxatives; also have body image concerns. Both conditions share similar characteristics but are not identical.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.