Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is formed by the merging of the medial nasal processes?
What is formed by the merging of the medial nasal processes?
- Philtrum of the lip (correct)
- Upper jaw
- Mandibular process
- Bridge of the nose
Which process is responsible for forming the lower jaw?
Which process is responsible for forming the lower jaw?
- Lateral nasal process
- Mandibular process (correct)
- Maxillary process
- Frontonasal process
The maxillary processes contribute to the formation of which facial feature?
The maxillary processes contribute to the formation of which facial feature?
- Philtrum
- Cheeks (correct)
- Bridge of nose
- Forehead
What do the lateral nasal processes primarily develop into?
What do the lateral nasal processes primarily develop into?
Which of the following is NOT a derivative of the frontonasal process?
Which of the following is NOT a derivative of the frontonasal process?
The fusion of which structures completes the formation of the upper lip?
The fusion of which structures completes the formation of the upper lip?
What primary structure gives rise to the most significant features of the forehead and nose?
What primary structure gives rise to the most significant features of the forehead and nose?
Which of the following components does NOT arise from the maxillary process?
Which of the following components does NOT arise from the maxillary process?
Which anatomical structure is not derived from the first branchial arch?
Which anatomical structure is not derived from the first branchial arch?
What is the primary nerve associated with the third branchial arch?
What is the primary nerve associated with the third branchial arch?
Which structure is primarily formed from the fourth branchial arch?
Which structure is primarily formed from the fourth branchial arch?
Which cleft is associated with the formation of the cervical sinus?
Which cleft is associated with the formation of the cervical sinus?
Which of the following structures forms from branchial arches five and six?
Which of the following structures forms from branchial arches five and six?
During which weeks does the external human face develop?
During which weeks does the external human face develop?
What does the myotome contribute to during embryonic development?
What does the myotome contribute to during embryonic development?
By which week is the palate fully developed, establishing a distinction between the nasal and oral cavities?
By which week is the palate fully developed, establishing a distinction between the nasal and oral cavities?
Which of the following structures is NOT a derivative of the ectoderm?
Which of the following structures is NOT a derivative of the ectoderm?
Which region of the paraxial mesoderm is responsible for bone and cartilage formation?
Which region of the paraxial mesoderm is responsible for bone and cartilage formation?
What type of tissue does the lateral plate mesoderm primarily give rise to?
What type of tissue does the lateral plate mesoderm primarily give rise to?
Which of the following is formed from the intermediate mesoderm?
Which of the following is formed from the intermediate mesoderm?
What aspect of the ectoderm is the adrenal medulla derived from?
What aspect of the ectoderm is the adrenal medulla derived from?
The development of which of the following organs originates from the lateral plate mesoderm?
The development of which of the following organs originates from the lateral plate mesoderm?
What is the main contribution of the dermatome during development?
What is the main contribution of the dermatome during development?
What does the endoderm develop into?
What does the endoderm develop into?
During which week does the foregut develop into structures including the trachea?
During which week does the foregut develop into structures including the trachea?
Which of the following is NOT a derivative of the endoderm?
Which of the following is NOT a derivative of the endoderm?
What connects the midgut to the yolk sac?
What connects the midgut to the yolk sac?
The formation of which structure indicates the breakdown of the cloacal membrane?
The formation of which structure indicates the breakdown of the cloacal membrane?
Which of the following is included in the derivatives of the endoderm?
Which of the following is included in the derivatives of the endoderm?
Which part of the gastrointestinal tract does not develop from the foregut?
Which part of the gastrointestinal tract does not develop from the foregut?
At what developmental stage do the anal canal structures begin to form?
At what developmental stage do the anal canal structures begin to form?
The epithelial lining of which organ is derived from the endoderm?
The epithelial lining of which organ is derived from the endoderm?
Where does the foregut connect to after the breakdown of the oropharyngeal membrane?
Where does the foregut connect to after the breakdown of the oropharyngeal membrane?
Flashcards
Frontonasal process
Frontonasal process
A structure that forms parts of the forehead, nose bridge, and nasal prominences during facial development.
Medial nasal process
Medial nasal process
Develops into the philtrum(central groove) of the upper lip and parts of the nose.
Lateral nasal process
Lateral nasal process
Produces the side parts of the nose.
Maxillary process
Maxillary process
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mandibular process
Mandibular process
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intermaxillary Segment
Intermaxillary Segment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Primary Palate
Primary Palate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Facial Development (Week 4)
Facial Development (Week 4)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endoderm's role
Endoderm's role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Foregut origin
Foregut origin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Midgut connection
Midgut connection
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hindgut development
Hindgut development
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endoderm Derivatives
Endoderm Derivatives
Signup and view all the flashcards
Embryo folding
Embryo folding
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oropharyngeal membrane
Oropharyngeal membrane
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cloacal membrane
Cloacal membrane
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pharyngeal clefts/pouches
Pharyngeal clefts/pouches
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitelline duct
Vitelline duct
Signup and view all the flashcards
First Branchial Arch Components
First Branchial Arch Components
Signup and view all the flashcards
Second Branchial Arch Structures
Second Branchial Arch Structures
Signup and view all the flashcards
Third Arch Components
Third Arch Components
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fourth Branchial Arch Structures
Fourth Branchial Arch Structures
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fifth & Sixth Arches Influence
Fifth & Sixth Arches Influence
Signup and view all the flashcards
Embryonic Face Development
Embryonic Face Development
Signup and view all the flashcards
Palate Development
Palate Development
Signup and view all the flashcards
Skin Ectoderm Derivatives
Skin Ectoderm Derivatives
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neural Crest Derivatives
Neural Crest Derivatives
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neural Ectoderm Derivatives
Neural Ectoderm Derivatives
Signup and view all the flashcards
Somites
Somites
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intermediate Mesoderm
Intermediate Mesoderm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lateral Plate Mesoderm
Lateral Plate Mesoderm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sclerotome
Sclerotome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myotome
Myotome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Development of the Face + Palate: Summary
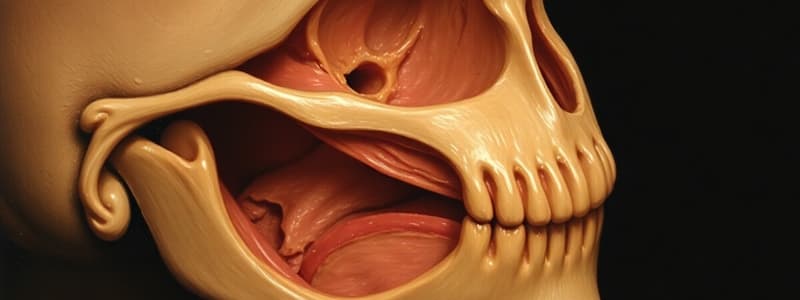
- Development of the face begins by week 4 of development from three main structures:
- The frontonasal process
- Gives rise to medial nasal processes and lateral nasal processes
- The two medial nasal processes merge in the midline forming the intermaxillary segment, which gives rise to the philtrum of the lip
- The maxillary process
- The fusion of the maxillary processes with the intermaxillary segment completes the formation of the upper lip
- The mandibular process
- Gives rise to the lower jaw/mandible
- The frontonasal process
Prominences & Derivatives
| Prominence | Derivatives |
|---|---|
| Frontonasal | Forehead, bridge of nose, medial and lateral nasal prominences |
| Medial nasal | Philtrum, primary palate, four upper incisors & associated jaw |
| Lateral nasal | Sides of the nose |
| Maxillary (1st pharyngeal arch) | Cheeks, lateral upper lip, secondary palate, lateral upper jaw |
| Mandibular (1st pharyngeal arch) | Lower lip, mandible |
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.