Podcast
Questions and Answers
Why is it not necessary to remove undermined enamel when preparing a tooth for a composite resin restoration?
Why is it not necessary to remove undermined enamel when preparing a tooth for a composite resin restoration?
- Because it does not weaken the tooth structure
- Because it does not affect the bond of the composite resin
- Because it can be blocked out with glass ionomer prior to final preparation and impression (correct)
- Because esthetics is not a consideration
What is the purpose of providing convenience access for the restoration?
What is the purpose of providing convenience access for the restoration?
- To remove compromised tooth structure
- To facilitate easy restoration and maintenance (correct)
- To improve esthetics
- To evaluate affected dentin
What is the recommended reduction for a functional cusp?
What is the recommended reduction for a functional cusp?
- 2.0 - 2.5 mm (correct)
- 1.5 - 2.0 mm
- 1.0 - 1.5 mm
- 2.5 - 3.0 mm
Why is it important to evaluate affected dentin?
Why is it important to evaluate affected dentin?
How should the margins be finished in both capping and shoeing?
How should the margins be finished in both capping and shoeing?
What is the ideal width of the isthmus?
What is the ideal width of the isthmus?
What determines the depth of the pulpal floor?
What determines the depth of the pulpal floor?
What is the purpose of divergent axial walls in preparations?
What is the purpose of divergent axial walls in preparations?
Why may the fossa areas need to be deeper?
Why may the fossa areas need to be deeper?
Why do walls not need to be parallel in these preparations?
Why do walls not need to be parallel in these preparations?
What determines the proximal extensions of the preparation?
What determines the proximal extensions of the preparation?
What is the benefit of increased taper in preparations?
What is the benefit of increased taper in preparations?
What is the purpose of temporization after final impression?
What is the purpose of temporization after final impression?
What is the ideal gingival floor depth?
What is the ideal gingival floor depth?
What is used to create a temporary fabrication?
What is used to create a temporary fabrication?
What is used for directly temporizing a preparation?
What is used for directly temporizing a preparation?
What should be done if the restoration does not seat easily?
What should be done if the restoration does not seat easily?
How should marginal integrity be checked?
How should marginal integrity be checked?
What affects the color of the ceramic restoration?
What affects the color of the ceramic restoration?
Why should occlusal contacts be checked after the restoration has been seated?
Why should occlusal contacts be checked after the restoration has been seated?
What is the purpose of the silane coupling agent?
What is the purpose of the silane coupling agent?
What type of resin is used to link the tooth and restoration interfaces?
What type of resin is used to link the tooth and restoration interfaces?
What should be done to the restoration after it is received from the lab?
What should be done to the restoration after it is received from the lab?
What is the purpose of the try-in process?
What is the purpose of the try-in process?
What is the purpose of using a wet slurry of flour pumice, soft bristle brush, or micro air abrasion in cavity preparation?
What is the purpose of using a wet slurry of flour pumice, soft bristle brush, or micro air abrasion in cavity preparation?
How long should 37% phosphoric acid be applied to the enamel?
How long should 37% phosphoric acid be applied to the enamel?
What is the purpose of applying a thin layer of unfilled resin or enamel bonding agent?
What is the purpose of applying a thin layer of unfilled resin or enamel bonding agent?
Why is a dual cure capacity composite resin luting agent used for onlay/inlay restorations?
Why is a dual cure capacity composite resin luting agent used for onlay/inlay restorations?
What is the minimum thickness of ceramic required in the central fossa?
What is the minimum thickness of ceramic required in the central fossa?
What is the purpose of 'tacking' the restoration onto the tooth?
What is the purpose of 'tacking' the restoration onto the tooth?
Why is it necessary to avoid pooling during the application of the luting agent?
Why is it necessary to avoid pooling during the application of the luting agent?
What is the purpose of applying a thin layer of resin bonding agent to the etched surface of the restoration?
What is the purpose of applying a thin layer of resin bonding agent to the etched surface of the restoration?
What type of restoration is indicated for an extensive preparation that requires strength greater than a composite or amalgam restoration but does not require cuspal coverage?
What type of restoration is indicated for an extensive preparation that requires strength greater than a composite or amalgam restoration but does not require cuspal coverage?
What is the primary difference between an inlay and an onlay?
What is the primary difference between an inlay and an onlay?
What is the purpose of beveling the gingival cavosurface?
What is the purpose of beveling the gingival cavosurface?
What is the ideal degree of beveling for the gingival cavosurface?
What is the ideal degree of beveling for the gingival cavosurface?
What is the purpose of the occlusal dovetail?
What is the purpose of the occlusal dovetail?
What is the reduction of nonfunctional cusps for an onlay?
What is the reduction of nonfunctional cusps for an onlay?
What is the recommended height of the shoulder following the lingual or facial axial walls of the cusp?
What is the recommended height of the shoulder following the lingual or facial axial walls of the cusp?
What is the purpose of 'tacking' the restoration onto the tooth?
What is the purpose of 'tacking' the restoration onto the tooth?
What type of resin is used for linking the tooth and restoration interfaces?
What type of resin is used for linking the tooth and restoration interfaces?
Why is a dual cure capacity composite resin luting agent used for onlay/inlay restorations?
Why is a dual cure capacity composite resin luting agent used for onlay/inlay restorations?
How long should 37% phosphoric acid be applied to the enamel?
How long should 37% phosphoric acid be applied to the enamel?
What is the purpose of applying a thin layer of unfilled resin or enamel bonding agent?
What is the purpose of applying a thin layer of unfilled resin or enamel bonding agent?
What is the minimum thickness of ceramic required in the central fossa?
What is the minimum thickness of ceramic required in the central fossa?
Why is it necessary to avoid pooling during the application of the luting agent?
Why is it necessary to avoid pooling during the application of the luting agent?
What is the purpose of applying a thin layer of resin bonding agent to the etched surface of the restoration?
What is the purpose of applying a thin layer of resin bonding agent to the etched surface of the restoration?
What is the minimum recommended width of the isthmus to avoid fracture?
What is the minimum recommended width of the isthmus to avoid fracture?
What type of walls are recommended for onlay and inlay preparations?
What type of walls are recommended for onlay and inlay preparations?
Why are thin areas of ceramic prone to fracture?
Why are thin areas of ceramic prone to fracture?
What is the purpose of rounding all line angles in onlay and inlay preparations?
What is the purpose of rounding all line angles in onlay and inlay preparations?
Why is it important to avoid concavities and divots in the floors and walls of onlay and inlay preparations?
Why is it important to avoid concavities and divots in the floors and walls of onlay and inlay preparations?
What is the retention mechanism for onlay and inlay restorations?
What is the retention mechanism for onlay and inlay restorations?
Why are cavosurface margins placed to avoid contact with opposing teeth?
Why are cavosurface margins placed to avoid contact with opposing teeth?
What is the characteristic of the prep for onlay and inlay restorations?
What is the characteristic of the prep for onlay and inlay restorations?
Why should occlusal contacts be analyzed after the restoration has been seated?
Why should occlusal contacts be analyzed after the restoration has been seated?
What is the purpose of trying in a restoration with a light transmitting medium?
What is the purpose of trying in a restoration with a light transmitting medium?
What should be done if the restoration does not seat easily?
What should be done if the restoration does not seat easily?
What affects the color of the ceramic restoration?
What affects the color of the ceramic restoration?
What is the purpose of applying a silane coupling agent to the restoration?
What is the purpose of applying a silane coupling agent to the restoration?
What links the tooth and restoration interfaces?
What links the tooth and restoration interfaces?
What should be done to the restoration after it is received from the lab?
What should be done to the restoration after it is received from the lab?
Why is it important to check for residual provisional material?
Why is it important to check for residual provisional material?
What is the recommended reduction for a functional cusp in onlay restorations?
What is the recommended reduction for a functional cusp in onlay restorations?
What is the purpose of temporization after final impression?
What is the purpose of temporization after final impression?
What is used to create a temporary fabrication in indirect temporary cementation?
What is used to create a temporary fabrication in indirect temporary cementation?
How should the margins be finished in both capping and shoeing?
How should the margins be finished in both capping and shoeing?
What is the benefit of using a hollow-ground chamfer in onlay restorations?
What is the benefit of using a hollow-ground chamfer in onlay restorations?
What is the purpose of using a non-eugenol temporary cement in indirect temporary cementation?
What is the purpose of using a non-eugenol temporary cement in indirect temporary cementation?
What is the recommended method for directly temporizing a preparation?
What is the recommended method for directly temporizing a preparation?
Why is it important to have divergent axial walls in onlay preparations?
Why is it important to have divergent axial walls in onlay preparations?
What is the primary indication for an onlay restoration?
What is the primary indication for an onlay restoration?
What is the purpose of beveling the gingival cavosurface?
What is the purpose of beveling the gingival cavosurface?
What is the ideal degree of beveling for the gingival cavosurface?
What is the ideal degree of beveling for the gingival cavosurface?
What is the purpose of the occlusal dovetail?
What is the purpose of the occlusal dovetail?
What is the reduction of nonfunctional cusps for an onlay?
What is the reduction of nonfunctional cusps for an onlay?
What is the recommended height of the shoulder following the lingual or facial axial walls of the cusp?
What is the recommended height of the shoulder following the lingual or facial axial walls of the cusp?
What type of restoration is indicated for compromised teeth in high-stress areas?
What type of restoration is indicated for compromised teeth in high-stress areas?
What is the primary difference between an inlay and an onlay?
What is the primary difference between an inlay and an onlay?
What is the primary indication for using ceramic onlays?
What is the primary indication for using ceramic onlays?
What is the purpose of beveling the gingival cavosurface in onlay preparations?
What is the purpose of beveling the gingival cavosurface in onlay preparations?
What is the recommended occlusal reduction for non-functional cusps in onlay preparations?
What is the recommended occlusal reduction for non-functional cusps in onlay preparations?
What is the purpose of the occlusal dovetail in onlay preparations?
What is the purpose of the occlusal dovetail in onlay preparations?
What is the recommended height of the shoulder following the lingual or facial axial walls of the cusp?
What is the recommended height of the shoulder following the lingual or facial axial walls of the cusp?
What type of walls are recommended for onlay and inlay preparations?
What type of walls are recommended for onlay and inlay preparations?
What is the purpose of secondary flaring of the proximal facial and lingual cavosurfaces?
What is the purpose of secondary flaring of the proximal facial and lingual cavosurfaces?
What is the primary difference between an inlay and an onlay?
What is the primary difference between an inlay and an onlay?
What is the primary consideration for determining the extent of proximal extensions in a tooth preparation?
What is the primary consideration for determining the extent of proximal extensions in a tooth preparation?
What is the recommended height of the shoulder following the lingual or facial axial walls of the cusp in a tooth preparation?
What is the recommended height of the shoulder following the lingual or facial axial walls of the cusp in a tooth preparation?
Why may the fossa areas need to be deeper in a tooth preparation?
Why may the fossa areas need to be deeper in a tooth preparation?
What is the purpose of blocking out undermined enamel with glass ionomer prior to final preparation and impression?
What is the purpose of blocking out undermined enamel with glass ionomer prior to final preparation and impression?
What is the recommended width of the isthmus in a tooth preparation?
What is the recommended width of the isthmus in a tooth preparation?
Why is it important to evaluate affected dentin during tooth preparation?
Why is it important to evaluate affected dentin during tooth preparation?
What is the primary purpose of having a divergent axial wall in an onlay preparation?
What is the primary purpose of having a divergent axial wall in an onlay preparation?
What type of finish line is recommended for proximal boxes?
What type of finish line is recommended for proximal boxes?
What is the purpose of providing a rounded internal line and point angles in a tooth preparation?
What is the purpose of providing a rounded internal line and point angles in a tooth preparation?
What is the purpose of temporization after final impression?
What is the purpose of temporization after final impression?
What is the purpose of using a flat-ended diamond in a tooth preparation?
What is the purpose of using a flat-ended diamond in a tooth preparation?
What is the recommended method for direct temporization?
What is the recommended method for direct temporization?
What is the recommended reduction for a non-functional cusp?
What is the recommended reduction for a non-functional cusp?
What is the purpose of having a butt joint in functional cusps?
What is the purpose of having a butt joint in functional cusps?
What is the benefit of having a hollow-ground chamfer?
What is the benefit of having a hollow-ground chamfer?
What is the purpose of finishing the margins in capping and shoeing?
What is the purpose of finishing the margins in capping and shoeing?
What should you do if the restoration does not seat easily?
What should you do if the restoration does not seat easily?
Why should occlusal contacts be checked after the restoration has been seated?
Why should occlusal contacts be checked after the restoration has been seated?
What determines the color of the ceramic restoration?
What determines the color of the ceramic restoration?
What is the purpose of the silane coupling agent?
What is the purpose of the silane coupling agent?
What is used to link the tooth and restoration interfaces?
What is used to link the tooth and restoration interfaces?
What should be done to the restoration after it is received from the lab?
What should be done to the restoration after it is received from the lab?
Why is it important to check for marginal integrity?
Why is it important to check for marginal integrity?
What is the purpose of the try-in process?
What is the purpose of the try-in process?
What is the primary purpose of placing cavosurface margins in a specific location?
What is the primary purpose of placing cavosurface margins in a specific location?
Why are thin areas of ceramic prone to fracture?
Why are thin areas of ceramic prone to fracture?
What is the minimum recommended width of the isthmus to avoid fracture?
What is the minimum recommended width of the isthmus to avoid fracture?
Why are divergent axial walls recommended for onlay and inlay preparations?
Why are divergent axial walls recommended for onlay and inlay preparations?
What is the purpose of applying a thin layer of unfilled resin or enamel bonding agent?
What is the purpose of applying a thin layer of unfilled resin or enamel bonding agent?
Why is a dual cure capacity composite resin luting agent used for onlay/inlay restorations?
Why is a dual cure capacity composite resin luting agent used for onlay/inlay restorations?
What is the purpose of 'tacking' the restoration onto the tooth?
What is the purpose of 'tacking' the restoration onto the tooth?
Why is it necessary to avoid pooling during the application of the luting agent?
Why is it necessary to avoid pooling during the application of the luting agent?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
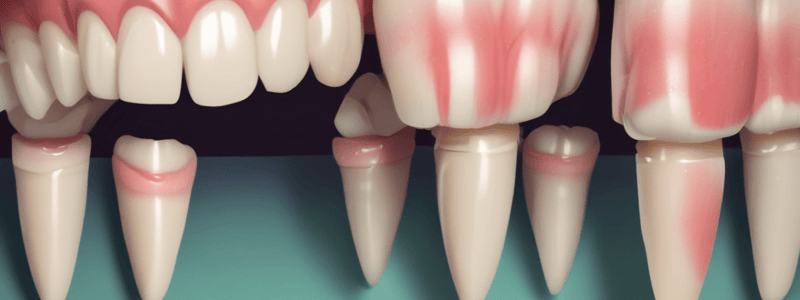
Inlay vs. Onlay
- Inlay: an intracoronal indirect restoration that does not involve cuspal coverage
- Onlay: a partial extracoronal indirect restoration that involves one or more cuspal coverage
Indications for Inlay and Onlay
- Inlay: indicated for extensive preparations that require strength greater than a composite or amalgam restoration but do not require cuspal coverage
- Onlay: indicated for compromised teeth in high stress areas, and for large restorative defects in low stress areas where esthetics are involved
Advantages of Inlay and Onlay
- Improved esthetics
- Cover and reinforce cusps without removal of healthy tooth structure
- Supragingival margins for easier maintenance
Preparation for Inlay and Onlay
- Removal of caries or defect
- Initial preparation similar to direct restoration
- Cavosurface margins are beveled, including the proximal box
- All walls are divergent
- Occlusal dovetail is placed if mesial or distal proximal box is not prepared
- Secondary flaring of the proximal facial and lingual cavosurfaces joins the gingival bevel uninterrupted
Occlusal Reduction for Onlay
- Functional cusps: reduced 1.5 mm
- Nonfunctional cusps: reduced 0.75-1.0 mm with minimal extension onto the axial wall
- Shoulder following the lingual or facial axial walls of the cusp has a depth of 0.8 mm and occlusogingival height of 2.0-3.0 mm
Conservative Preparation
- Remove only compromised tooth structure
- Convenience access is provided for the restoration
- Affected dentin should be evaluated
- Dentin discolored by caries or amalgam may need to be removed or covered by an opaquer
Internal Line Angles and Isthmus Width
- Rounded internal line and point angles
- Flat ended diamonds work well to define internal line angles
- Isthmus width: 1.5-2.0 mm
Pulpal Floor and Proximal Extensions
- Pulpal floor can vary according to the planned restored anatomy
- Should be 1.5-2.0 mm for adequate bulk for fabrication
- Proximal extensions are determined by the extent of caries or previous restoration
Gingival Floor Depth and Cuspal Protection
- Gingival floor depth: 1.0-1.5 mm
- Should be maintained in enamel whenever possible
- Cuspal protection or replacement: extensions of the coverage are a clinical judgment, considering factors such as amount of enamel, occlusal forces, size of functional contact, esthetics, and mesial-distal width of affected area
Cuspal Reduction for Bulk of Restorations
- Functional cusp: 2.0-2.5 mm
- Nonfunctional cusp: 1.5-2.0 mm
Finish Line and Axial Wall
- Finish line should NOT be beveled
- Two schools of thought for the finish line:
- A well-defined, smooth butt joint (shoulder)
- A hollow-ground chamfer (deep chamfer, or modified butt joint)
- Axial wall should be divergent, more than what is required of a gold restoration
Temporization and Cementation
- After final impression, the preparation(s) need to be temporized to avoid shifting of the teeth and sensitivity
- Indirectly using a preoperative matrix, poured model, temporary fabrication with cementation using a non-eugenol temporary cement
- Directly with composite with NO etching or bonding
Try-In and Cementation
- Try-in of the restoration with a light transmitting medium like glycerine, water, or try-in paste
- Check for proximal contact, marginal integrity, and color
- Bonding of the ceramic restoration involves a series of individual links, including tooth interface, restoration interface, and hybrid resin luting cement
Bonding and Cementation
- Clean the restoration of any debris
- Coat the restoration with a silane coupling agent
- Apply a thin layer of unfilled resin or enamel bonding agent
- Light cure
- Apply composite resin luting agent to the preparation and restoration
- Seat the restoration into the preparation, cement should extrude from the margins
- Clean off excess cement and floss
Onlay/Inlay Preparation and Cementation
- The coupling agent is volatile and allowed to vaporize, leaving a reactive silane on the surface (Crispin, 1994)
- A thin layer of unfilled resin or enamel bonding agent is applied to the etched surface of the restoration
- The cavity preparation is cleaned using a wet slurry of flour of pumice, soft bristle brush, or micro air abrasion
Luting Agent Application
- A thin layer of luting agent is applied to the etched surface of the restoration
- The luting agent should be of dual cure capacity due to the thickness and opacity of the onlay/inlay
- The restoration is seated into the preparation, and the cement should extrude from the margins
Cementation and Occlusal Reduction
- Clean off excess cement and floss to check for any interproximal overhangs
- Occlusal reduction should be uniform and of sufficient thickness for ceramic to provide optimal strength
- Thickness of ceramic should be at least 1.5 mm in the central fossa and over nonfunctional cusps
- Marginal integrity: A sharp explorer should travel from the restoration to tooth structure, and vice versa, smoothly and without catching
Bonding of Ceramic Restoration
- Tooth interface: etched enamel micro mechanically bonds with the bonding agent
- Restoration interface: The etched porcelain is made reactive by a silane, causing it to mechanically and chemically bond to an unfilled resin layer
- Both interfaces are linked together by a dual cured hybrid resin luting cement
Ceramic Restoration Preparation
- Cavosurface margins should be placed to avoid contact with opposing teeth
- Margins should be smooth and well-defined with no beveling
- Thin areas of the ceramic are prone to fracture
- Onlay/Inlays rely on adhesion of the resin cement to the dentin and enamel for retention
Preparation Requirements
- Prep is nonmechanically retentive
- Floors and walls should avoid concavities and divots
- All line angles are rounded
- Isthmus is at least 2.0 mm to avoid onlay/inlay fracture
Final Thoughts
- Occlusal contacts should be checked AFTER the restoration has been seated
- Centric and excursive contacts should be checked and adjusted as needed
- Bonding of the ceramic restoration involves a series of individual links
Inlays and Onlays
- Inlays: intracoronal indirect restorations, not involving cuspal coverage
- Onlays: partial extracoronal indirect restorations, involving one or more cuspal coverage
Indications and Contraindications
- Inlays: indicated for extensive preparations requiring strength greater than a composite or amalgam restoration, but not requiring cuspal coverage
- Onlays: indicated for compromised teeth in high-stress areas, large restorative defects in low-stress areas, and when esthetics are involved
Advantages
- Conservative, as only compromised tooth structure is removed
- Improved esthetics
- Cover and reinforce cusps without removing healthy tooth structure
- Supragingival margins, easier for patients to maintain
Preparation
- Initial preparation similar to direct restoration
- Cavosurface margins are beveled, including the proximal box
- All walls are divergent
- Occlusal dovetail is placed if mesial or distal proximal box is not prepared
- Secondary flaring of the proximal facial and lingual cavosurfaces joins the gingival bevel uninterrupted
Onlay Preparation
- Similar to inlay preparation, but with one or more cuspal coverage
- Occlusal reduction of nonfunctional cusps is 0.75-1.0 mm with minimal extension onto the axial wall
- Functional cusps are reduced 1.5 mm
- Shoulder following the lingual or facial axial walls of the cusp has a depth of 0.8 mm and occlusogingival height of 2.0-3.0 mm
Cuspal Reduction
- Functional cusps: 2.0-2.5 mm, capped with a butt joint shoulder
- Nonfunctional cusps: 1.5-2.0 mm, shoed just beyond the tip and ridge of the cusp
- In both capping and shoeing, the margins should follow the contour of the cusp tip and ridges
Finish Line
- Two schools of thought: well-defined, smooth butt joint (shoulder) or hollow-ground chamfer (deep chamfer, or modified butt joint)
- Axial wall should be divergent, more than what is required of a gold restoration
- Increased taper, without unnecessary removal of tooth structure, allows for easier placement and removal when trying the restoration in
Temporization and Cementation
- After final impression, the preparation(s) need to be temporized to avoid shifting of the teeth and sensitivity
- Indirectly using a preoperative matrix, poured model, temporary fabrication with cementation using a non-eugenol temporary cement
- Directly with composite with NO etching or bonding
- Light-cured temporary resin material
Try-in and Cementation
- Check for residual provisional material, interproximal overhangs, and marginal integrity
- Color is dependent on shade selection, opacity versus translucency of the ceramic restoration, and the resin luting cement
- Occlusal contacts should be checked AFTER the restoration has been seated
- Bonding of the ceramic restoration involves a series of individual links: tooth interface, restoration interface, and a dual-cured hybrid resin luting cement
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.