Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary concern when dealing with mandibular first molar sites?
What is the primary concern when dealing with mandibular first molar sites?
- Mesio-distal distance being over 10 mm (correct)
- Abutment selection
- Occlusal plane being too narrow
- Mesio-distal distance being less than 10 mm
What is the recommended diameter of the implant in this case?
What is the recommended diameter of the implant in this case?
- 5 mm (correct)
- 4 mm
- 6 mm
- 3 mm
Why were two 4 mm diameter implants placed in the first molar site?
Why were two 4 mm diameter implants placed in the first molar site?
- Due to insufficient mesio-distal distance
- To distribute the load more efficiently (correct)
- Since the patient had bruxism
- To reduce the risk of overloading
What type of restoration was fabricated in this case?
What type of restoration was fabricated in this case?
What is the primary concern for occlusal guidelines?
What is the primary concern for occlusal guidelines?
What is recommended for bruxors?
What is recommended for bruxors?
What should be considered while selecting an abutment?
What should be considered while selecting an abutment?
What is the minimum interarch distance recommended in the posterior sites?
What is the minimum interarch distance recommended in the posterior sites?
When the ridge position dictates a lingual implant position, what might occur?
When the ridge position dictates a lingual implant position, what might occur?
What is the ideal crown/implant ratio for sound biomechanics?
What is the ideal crown/implant ratio for sound biomechanics?
Why is the prognosis of adjacent teeth important in implant placement?
Why is the prognosis of adjacent teeth important in implant placement?
What should be reviewed to identify deficits that might impact the esthetic outcome?
What should be reviewed to identify deficits that might impact the esthetic outcome?
What should be carefully analyzed to understand the occlusal pattern?
What should be carefully analyzed to understand the occlusal pattern?
What might occur if the position of adjacent teeth is not addressed properly?
What might occur if the position of adjacent teeth is not addressed properly?
What is the minimum distance required between the natural tooth and the implant for viable bone and papilla?
What is the minimum distance required between the natural tooth and the implant for viable bone and papilla?
What is the consequence of a distally placed implant when chewing force is applied at the mesial?
What is the consequence of a distally placed implant when chewing force is applied at the mesial?
For screw-retained restorations, where should the faciolingual position of the anterior implant be aligned?
For screw-retained restorations, where should the faciolingual position of the anterior implant be aligned?
What is the primary goal of centering the implant mesiodistally?
What is the primary goal of centering the implant mesiodistally?
Why is it essential to ensure accurate implant positioning?
Why is it essential to ensure accurate implant positioning?
In posterior implant placement, where should the faciolingual position of the implant be aligned?
In posterior implant placement, where should the faciolingual position of the implant be aligned?
What is the consequence of a faulty mesiodistal implant placement?
What is the consequence of a faulty mesiodistal implant placement?
What is the primary purpose of evaluating the adjacent teeth in implant restoration?
What is the primary purpose of evaluating the adjacent teeth in implant restoration?
How does the rotation of #10 affect the papilla height and contact position?
How does the rotation of #10 affect the papilla height and contact position?
What type of restoration transmits more forces on the implant?
What type of restoration transmits more forces on the implant?
Why is it essential to evaluate the occlusal scheme in implant restoration?
Why is it essential to evaluate the occlusal scheme in implant restoration?
What is the purpose of a diagnostic prototype in the missing tooth site?
What is the purpose of a diagnostic prototype in the missing tooth site?
What is the significance of a surgical template in implant restoration?
What is the significance of a surgical template in implant restoration?
What is the purpose of barium sulfate mixed with clear acrylic in the surgical template?
What is the purpose of barium sulfate mixed with clear acrylic in the surgical template?
Why is it essential to maintain harmonious gingival levels in implant restoration?
Why is it essential to maintain harmonious gingival levels in implant restoration?
What is the potential impact of a compromised tooth opposed by a rigid implant restoration on the canine guidance?
What is the potential impact of a compromised tooth opposed by a rigid implant restoration on the canine guidance?
What is the minimum interarch distance recommended in the anterior sites?
What is the minimum interarch distance recommended in the anterior sites?
What may cause overloading of the implant when the ridge position dictates a lingual implant position?
What may cause overloading of the implant when the ridge position dictates a lingual implant position?
Why is the prognosis of adjacent teeth important in implant placement?
Why is the prognosis of adjacent teeth important in implant placement?
What should be carefully matched for good esthetic results in the anterior region?
What should be carefully matched for good esthetic results in the anterior region?
What is the ideal crown/implant ratio for sound biomechanics?
What is the ideal crown/implant ratio for sound biomechanics?
What is the primary factor in evaluating the prognosis of adjacent teeth in implant restoration?
What is the primary factor in evaluating the prognosis of adjacent teeth in implant restoration?
What is the primary purpose of analyzing the study casts in implant restoration?
What is the primary purpose of analyzing the study casts in implant restoration?
Why is it essential to maintain harmonious gingival levels in implant restoration?
Why is it essential to maintain harmonious gingival levels in implant restoration?
What is the primary purpose of the surgical template in implant restoration?
What is the primary purpose of the surgical template in implant restoration?
What is the consequence of a faulty mesiodistal implant placement?
What is the consequence of a faulty mesiodistal implant placement?
What occurs when an implant is placed too far beneath the gingiva?
What occurs when an implant is placed too far beneath the gingiva?
What is the ideal location for the head of the implant in relation to the adjacent gingival margin?
What is the ideal location for the head of the implant in relation to the adjacent gingival margin?
What is the purpose of creating an emergence profile from the implant's round form to a natural tooth's elliptical form?
What is the purpose of creating an emergence profile from the implant's round form to a natural tooth's elliptical form?
What technique is employed to raise a flap for tissue esthetics in implant placement?
What technique is employed to raise a flap for tissue esthetics in implant placement?
What is the direction of the osteotomy in screw-retained restorations?
What is the direction of the osteotomy in screw-retained restorations?
What is the primary consequence of a distally placed implant when chewing force is applied at the mesial?
What is the primary consequence of a distally placed implant when chewing force is applied at the mesial?
What is the recommended faciolingual position of the anterior implant for cement retained restorations?
What is the recommended faciolingual position of the anterior implant for cement retained restorations?
What is the minimum distance required between the natural tooth and the implant to ensure viable bone and papilla?
What is the minimum distance required between the natural tooth and the implant to ensure viable bone and papilla?
Why is it essential to center the implant mesiodistally?
Why is it essential to center the implant mesiodistally?
What is the consequence of a faulty mesiodistal implant placement?
What is the consequence of a faulty mesiodistal implant placement?
What is an advantage of a cement retained restoration over a screw retained restoration?
What is an advantage of a cement retained restoration over a screw retained restoration?
What is a disadvantage of a screw retained restoration?
What is a disadvantage of a screw retained restoration?
What is a consideration in selecting an abutment for a screw retained restoration?
What is a consideration in selecting an abutment for a screw retained restoration?
What is a consequence of a faulty abutment selection for a screw retained restoration?
What is a consequence of a faulty abutment selection for a screw retained restoration?
Why is it essential to consider the patient's smile line when selecting an abutment for a screw retained restoration?
Why is it essential to consider the patient's smile line when selecting an abutment for a screw retained restoration?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Treatment Planning
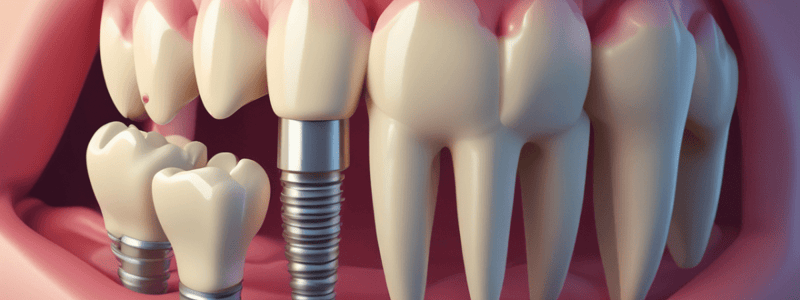
- Biomechanical considerations for mandibular first molar sites: mesio-distal distance should be carefully studied, especially when it's over 10 mm (e.g., 12 mm in this case).
- Placement of a wide body implant (5 mm diameter) along with narrowing the occlusal plane can compensate for overloading.
- Two 4 mm diameter implants can be placed in the first molar site with over 12 mm mesiodistal distance, and a splinted restoration can be fabricated using custom abutments and screw-retained PFM crowns.
Occlusal Guidelines
- Light centric contact should be established.
- Shim stock should only be grasped when the musculature is fully engaged.
- Eccentric contacts should be avoided.
- Over-engineering and night guards are suggested for bruxors.
- Mild cusp heights are preferable to avoid bending moments and load magnification.
Abutment Selection Guidelines
- Screw or cement retained implant restorations can be fabricated.
- Various reasons (retrievability, amount of space, esthetics, occlusion, ease of operation, etc.) can be considered in choosing one over the other option.
- The decision should be made prior to the placement of the implant, as the position of the implant might be slightly different in each option.
Diagnosis - Clinical Evaluation
- Residual edentulous space: interarch distance should be minimum 2 mm in anterior sites and 4 mm in posterior sites.
- Mesio-distal distance should be about 7 mm.
- When there is over 10 mm of distance, implant size and number should be carefully considered to avoid implant overloading.
- Crown/implant ratio should be kept to 1:1 for sound biomechanics.
Adjacent-Teeth Clinical Evaluation
- Prognosis of the adjacent teeth is very important for avoiding potential implant failure inflicted from adjacent pathology.
- Soft tissue contours and levels should be reviewed to identify any deficits that might have direct impact on the esthetic outcome.
- Position of the adjacent teeth (rotated, tilted, out of curve, extruded, intruded) along with position of proximal contacts can cause functional and esthetic problems if not addressed properly.
- Wear facets should be carefully analyzed to understand the occlusal pattern.
Surgical Placement
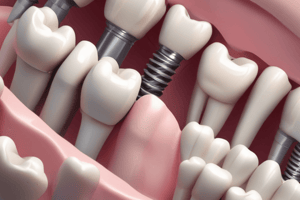
- Biomechanical success and restoration/tissue esthetics depend on the correct positioning of the implant in the bone.
- Implant should be centered mesiodistally for minimizing cantilevering effect and creating normal emergence profile.
- Accurate implant position provides natural tissue contours.
- Faciolingual position of the anterior implant should be aligned under the cingulum of the proposed crown for screw-retained restorations and under the incisal edge for cement-retained restorations.
- Posterior implant should be centered faciolingually for reducing the potential for overloading.
Restorations and Materials
- Restorations and materials on the adjacent teeth would assist in designing the optimal implant restoration.
- Prognosis of endodontically treated teeth should be assessed and pathology should be ruled out.
- Integrity of the restorations should be examined.
- Existence and maintenance of harmonious gingival levels provide esthetic outcome.
Diagnosis - Opposing Teeth
- Plane of occlusion and occlusion play an important role on the loads exerted on the implant restoration.
- Occlusal scheme should be carefully evaluated for planning the centric and laterotrusive contacts.
- Type of restoration; Fixed would transmit more forces than the removable restoration.
Study Casts
- Edentulous site along with the adjacent structures can be analyzed in detail on the casts.
- Diagnostic prototype in the missing tooth site would help visualize the proposed restoration.
- Location and alignment of the proposed implant can be studied through the diagnostic work up.
Surgical Template
- It is used for imaging and surgical purposes.
- Fabricating a good template would enhance the diagnostic value of imaging and then guide successful placement of the implant.
- The template contains barium sulfate mixed with clear acrylic at the missing tooth site for radio-opaque marking during tomographic imaging.
Diagnosis - Clinical Evaluation
- Residual edentulous space:
- Minimum 2 mm interarch distance in anterior sites and 4 mm in posterior sites
- Mesio-distal distance should be approximately 7 mm
- Implant size and number should be carefully considered to avoid overloading
- Buccal cantilevering might cause overloading due to off-axial loads
- Crown/implant ratio should be kept to 1:1 for sound biomechanics
Adjacent Teeth Clinical Evaluation
- Prognosis of adjacent teeth is very important for avoiding potential implant failure
- Soft tissue contours and levels should be reviewed to identify any deficits that might impact esthetic outcome
- Position of adjacent teeth (rotated, tilted, out of curve, extruded, intruded) can cause functional and esthetic problems if not addressed properly
- Wear facets should be carefully analyzed to understand the occlusal pattern
- Restorations and materials on adjacent teeth would assist in designing the optimal implant restoration
Opposing Teeth Clinical Evaluation
- Plane of occlusion and occlusion play an important role in the loads exerted on the implant restoration
- Occlusal scheme should be carefully evaluated for planning centric and laterotrusive contacts
- Type of restoration (fixed or removable) affects the transmission of forces to the implant
- Prognosis of compromised teeth might be negatively impacted when opposed by rigid implant restoration
Study Casts
- Edentulous site and adjacent structures can be analyzed in detail on the casts
- Diagnostic prototype in the missing tooth site helps visualize the proposed restoration
- Location and alignment of the proposed implant can be studied through the diagnostic work-up
Surgical Template
- Used for imaging and surgical purposes
- Fabricating a good template enhances diagnostic value of imaging and guides successful implant placement
- Template contains barium sulfate mixed with clear acrylic at the missing tooth site for radio-opaque marking during tomographic imaging
Surgical Placement
- Biomechanical success and restoration/tissue esthetics depend on correct positioning of the implant in the bone
- Optimal 3-D position of implant can be achieved by:
- Centering mesiodistally for minimizing cantilevering effect and creating normal emergence profile
- Avoiding faulty mesiodistal implant placement (lack of sufficient space between tooth and implant)
- Achieving faciolingual position under the cingulum of the proposed crown for screw-retained restorations and under the incisal edge for cement-retained restorations
- Centering posterior implant for reducing potential for overloading
- Creating emergence profile from implant's round form to natural tooth's elliptical form for achieving natural esthetics
- Positioning the head of the implant 2-4 mm below the adjacent gingival margin
- Faulty implant placement can lead to esthetic harmony issues, bone loss, and peri-implantitis
Surgery - Implant Placement
- Flap is raised by employing papilla preservation technique for tissue esthetics
- Osteotomy is oriented through the cingulum for screw-retained restoration
Screw-Retained UCLA Abutment Restoration (Two-Piece)
- Resin pattern of custom abutment which changes the direction of the implant long axis
- Full-contour wax pattern of custom labially inclined implant abutment
- Metal coping for the second piece fits over the first piece, and a PFM crown is placed
Abutment Selection
- Cement-retained restoration can also be fabricated as an alternative
- Advantages: more esthetic, especially at posterior sites, and similar to conventional crown
- Disadvantages: risk of leaving cement in the sulcus, not being able to seat the crown due to hydraulic pressure, and increased need for space to accommodate two-piece restoration
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.