Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the average half-life of a microtubule?
What is the average half-life of a microtubule?
- 10 minutes (correct)
- 60 minutes
- 30 minutes
- 2 minutes
Which of the following accurately describes the composition of a microtubule?
Which of the following accurately describes the composition of a microtubule?
- Made solely of actin filaments
- Made of heterodimers of α- and β-tubulin subunits (correct)
- Formed by lipid bilayers
- Composed of 13 filamentous proteins
What role do microtubules play during cell division?
What role do microtubules play during cell division?
- They form the mitotic spindle (correct)
- They store genetic information
- They stabilize the cell membrane
- They create energy for cellular functions
Which component of the cytoskeleton is responsible for providing rigidity and maintaining cell shape?
Which component of the cytoskeleton is responsible for providing rigidity and maintaining cell shape?
Which motor proteins are relevant to cell trafficking associated with microtubules?
Which motor proteins are relevant to cell trafficking associated with microtubules?
What is the primary function of the centrosome in relation to microtubules?
What is the primary function of the centrosome in relation to microtubules?
How do microtubules contribute to ciliary and flagellar motion?
How do microtubules contribute to ciliary and flagellar motion?
What is a key feature of the dynamic nature of microtubules?
What is a key feature of the dynamic nature of microtubules?
What is the primary effect of colchicine on microtubule formation?
What is the primary effect of colchicine on microtubule formation?
Which family of microtubule motor proteins is responsible for moving vesicles toward the minus end of the microtubule?
Which family of microtubule motor proteins is responsible for moving vesicles toward the minus end of the microtubule?
During cell division, what is the role of centrioles?
During cell division, what is the role of centrioles?
Microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) primarily function to:
Microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) primarily function to:
What component is primarily found in the structure of centrioles?
What component is primarily found in the structure of centrioles?
The movement of organelles along microtubules occurs in what direction?
The movement of organelles along microtubules occurs in what direction?
Which of the following is NOT a function of centrioles?
Which of the following is NOT a function of centrioles?
What type of protein makes up the thin filaments known as actin filaments?
What type of protein makes up the thin filaments known as actin filaments?
Flashcards
Colchicine's effect on microtubules
Colchicine's effect on microtubules
Colchicine prevents microtubule polymerization by binding to tubulin molecules.
Microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs)
Microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs)
Motor proteins that move organelles and vesicles along microtubules.
Dynein's movement
Dynein's movement
Moves vesicles towards the minus end of a microtubule.
Kinesin's movement
Kinesin's movement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Centrioles composition
Centrioles composition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Centrosome's function
Centrosome's function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Centrioles in cell division
Centrioles in cell division
Signup and view all the flashcards
Actin filaments (microfilaments)
Actin filaments (microfilaments)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Microtubules (MTs)
Microtubules (MTs)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Centrosome
Centrosome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Microtubule Dynamics
Microtubule Dynamics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Protofilaments
Protofilaments
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cytoskeleton Function
Cytoskeleton Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cell Shape Maintenance
Cell Shape Maintenance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Motor Proteins
Motor Proteins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Microtubules and Cell Division
Microtubules and Cell Division
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Cytoskeletal Microtubules & Microfilaments & Motility
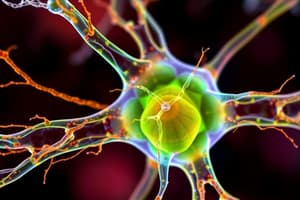
- Microtubules (MTs) are hollow, straight structures acting as intracellular pathways
- Centrosome, located near the nucleus, houses centrioles and y-tubulin ring complexes, which nucleate microtubules
- Microtubules are dynamic, changing length by growth spurts and shortening at the plus end (away from the nucleus). Average half-life is about 10 minutes.
- Microtubules are composed of 13 parallel protofilaments made of α and β-tubulin heterodimers
- Microtubules provide rigidity, maintain cell shape, regulate organelle and vesicle movement, and establish intracellular compartments. They are involved in cilia/flagella movement and mitotic spindle formation.
- Colchicine disrupts microtubule formation, impacting leukocyte migration, phagocytosis and inflammatory mediator release
- Microtubule-associated proteins are motor proteins facilitating organelle and vesicle transport. Dynein moves toward the minus end (and kinesin toward the plus end) of the microtubule in the presence of ATP.
Microfilaments (Actin Filaments)
- Actin filaments (microfilaments) are thin, composed of G-actin subunits forming F-actin
- Actin filaments have a faster-growing plus end and a slower-growing minus end
- Contractile bundles of actin filaments are arranged loosely, parallel to each other, plus/minus ends alternating, forming cleavage furrows during mitosis
- Gel-like networks of actin filaments provide structural support in the cell cortex
- Actin bundles form the core of microvilli (apical cell projections)
- Focal points are actin-based structures at contact points between the cell and extracellular matrix
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.