Podcast
Questions and Answers
What movement of the shoulder joint involves the upper limb moving away from the midline?
What movement of the shoulder joint involves the upper limb moving away from the midline?
- Extension
- Adduction
- Abduction (correct)
- Flexion
Which structure is subject to impingement beneath the acromial arch if inflamed and swollen?
Which structure is subject to impingement beneath the acromial arch if inflamed and swollen?
- Coracoacromial arch
- Supraspinatus tendon (correct)
- Subdeltoid bursa
- Deltoid muscle
Which movement of the shoulder joint is mechanically impossible due to the presence of the trunk?
Which movement of the shoulder joint is mechanically impossible due to the presence of the trunk?
- Abduction
- Extension
- Adduction (correct)
- Flexion
At what degree does extension of the shoulder joint typically occur?
At what degree does extension of the shoulder joint typically occur?
Which structure is located between the deltoid muscle and the fibrous capsule of the shoulder?
Which structure is located between the deltoid muscle and the fibrous capsule of the shoulder?
What axis does flexion and extension of the shoulder joint occur around?
What axis does flexion and extension of the shoulder joint occur around?
After reaching 90° abduction, what direction does further abduction move the limb towards?
After reaching 90° abduction, what direction does further abduction move the limb towards?
Which movement allows a bit of adduction starting from the reference position?
Which movement allows a bit of adduction starting from the reference position?
Which movement of the scapula involves the glenoid cavity rotating superiorly and the inferior angle rotating away from the midline?
Which movement of the scapula involves the glenoid cavity rotating superiorly and the inferior angle rotating away from the midline?
What is the typical displacement of the scapular inferior angle during shoulder movement?
What is the typical displacement of the scapular inferior angle during shoulder movement?
What type of joint is the sternoclavicular joint?
What type of joint is the sternoclavicular joint?
What is the range of motion for clavicular elevation?
What is the range of motion for clavicular elevation?
What ligament anchors the lateral end of the clavicle and prevents superior dislocation of the acromioclavicular joint?
What ligament anchors the lateral end of the clavicle and prevents superior dislocation of the acromioclavicular joint?
What type of joint is the glenohumeral (shoulder) joint?
What type of joint is the glenohumeral (shoulder) joint?
Which of the following movements is mechanically impossible for the shoulder joint due to the presence of the trunk?
Which of the following movements is mechanically impossible for the shoulder joint due to the presence of the trunk?
Which movement of the clavicle involves a range of motion of 25-30 degrees?
Which movement of the clavicle involves a range of motion of 25-30 degrees?
What structure is located between the deltoid muscle and the fibrous capsule of the shoulder joint?
What structure is located between the deltoid muscle and the fibrous capsule of the shoulder joint?
Which movement of the shoulder joint allows a bit of adduction starting from the reference position?
Which movement of the shoulder joint allows a bit of adduction starting from the reference position?
What is the primary function of the articular disc in the distal radioulnar joint?
What is the primary function of the articular disc in the distal radioulnar joint?
What type of joint is the distal radioulnar joint?
What type of joint is the distal radioulnar joint?
What is the primary movement that occurs at the middle radioulnar joint?
What is the primary movement that occurs at the middle radioulnar joint?
What is the range of motion for supination of the forearm?
What is the range of motion for supination of the forearm?
Which muscle is responsible for pronation of the forearm?
Which muscle is responsible for pronation of the forearm?
Which of the following ligaments is primarily responsible for preventing sideways movements of the elbow joint?
Which of the following ligaments is primarily responsible for preventing sideways movements of the elbow joint?
Which muscle is considered the strongest of the three heads of the triceps brachii and plays a major role in elbow extension?
Which muscle is considered the strongest of the three heads of the triceps brachii and plays a major role in elbow extension?
Which of the following muscles is responsible for both elbow flexion and forearm supination?
Which of the following muscles is responsible for both elbow flexion and forearm supination?
In the case of cubitus varus deformity, which direction does the extended forearm deviate towards?
In the case of cubitus varus deformity, which direction does the extended forearm deviate towards?
Which of the following statements about cubitus valgus deformity is correct?
Which of the following statements about cubitus valgus deformity is correct?
What is the primary function of the elbow joint ligaments?
What is the primary function of the elbow joint ligaments?
Which of the following joints is NOT part of the elbow complex?
Which of the following joints is NOT part of the elbow complex?
Which of the following statements about the elbow joint is FALSE?
Which of the following statements about the elbow joint is FALSE?
Which of the following articular surfaces is NOT present at the distal end of the humerus?
Which of the following articular surfaces is NOT present at the distal end of the humerus?
Which of the following statements about the elbow joint is TRUE?
Which of the following statements about the elbow joint is TRUE?
Which of the following structures articulates with the trochlea of the humerus?
Which of the following structures articulates with the trochlea of the humerus?
Which of the following structures articulates with the capitulum of the humerus?
Which of the following structures articulates with the capitulum of the humerus?
Which structure primarily prevents the superior displacement of the humeral head from the glenoid cavity?
Which structure primarily prevents the superior displacement of the humeral head from the glenoid cavity?
Which structure converts the intertubercular groove of the humerus into a canal and retains the long head of the biceps brachii tendon?
Which structure converts the intertubercular groove of the humerus into a canal and retains the long head of the biceps brachii tendon?
Which of the following structures is an intrinsic ligament of the shoulder joint?
Which of the following structures is an intrinsic ligament of the shoulder joint?
Which bursa is located between the acromion and the tendon of the supraspinatus muscle?
Which bursa is located between the acromion and the tendon of the supraspinatus muscle?
Which of the following ligaments reinforces the anterior aspect of the shoulder joint capsule?
Which of the following ligaments reinforces the anterior aspect of the shoulder joint capsule?
Which structure overlies the anterior joint capsule of the shoulder and lies beneath the subscapularis muscle?
Which structure overlies the anterior joint capsule of the shoulder and lies beneath the subscapularis muscle?
What are the two muscles responsible for wrist adduction?
What are the two muscles responsible for wrist adduction?
Which muscle is NOT involved in wrist extension?
Which muscle is NOT involved in wrist extension?
What type of joint is the carpometacarpal (CMC) joint of the thumb?
What type of joint is the carpometacarpal (CMC) joint of the thumb?
Which muscle assists in both wrist flexion and wrist adduction?
Which muscle assists in both wrist flexion and wrist adduction?
What is the primary function of the Flexor Digitorum Profundus muscle in wrist movement?
What is the primary function of the Flexor Digitorum Profundus muscle in wrist movement?
Which two muscles work together to produce wrist abduction?
Which two muscles work together to produce wrist abduction?
During adduction of the wrist, which ligament becomes taut?
During adduction of the wrist, which ligament becomes taut?
Which ligament becomes taut during wrist flexion?
Which ligament becomes taut during wrist flexion?
In which position are the carpal ligaments relaxed?
In which position are the carpal ligaments relaxed?
What muscles are involved in wrist flexion and extension?
What muscles are involved in wrist flexion and extension?
What is the axis of motion for abduction and adduction at the radiocarpal joint?
What is the axis of motion for abduction and adduction at the radiocarpal joint?
Which ligament is involved in wrist extension?
Which ligament is involved in wrist extension?
What type of joint is the middle radioulnar joint?
What type of joint is the middle radioulnar joint?
Which structure primarily prevents the inferior displacement of the humeral head from the glenoid cavity?
Which structure primarily prevents the inferior displacement of the humeral head from the glenoid cavity?
Which movement at the elbow joint is mechanically impossible due to the shape of the articulating bones?
Which movement at the elbow joint is mechanically impossible due to the shape of the articulating bones?
What is the primary function of the radial collateral ligament at the elbow joint?
What is the primary function of the radial collateral ligament at the elbow joint?
Which muscle is NOT involved in elbow flexion?
Which muscle is NOT involved in elbow flexion?
What type of joint is the proximal radioulnar joint?
What type of joint is the proximal radioulnar joint?
What is the typical displacement of the scapular inferior angle during shoulder movement?
What is the typical displacement of the scapular inferior angle during shoulder movement?
Which movement of the scapula involves the glenoid cavity rotating superiorly and the inferior angle rotating away from the midline?
Which movement of the scapula involves the glenoid cavity rotating superiorly and the inferior angle rotating away from the midline?
What type of joint is the sternoclavicular joint?
What type of joint is the sternoclavicular joint?
Which ligament anchors the lateral end of the clavicle and prevents superior dislocation of the acromioclavicular joint?
Which ligament anchors the lateral end of the clavicle and prevents superior dislocation of the acromioclavicular joint?
What type of joint is the glenohumeral (shoulder) joint?
What type of joint is the glenohumeral (shoulder) joint?
Which movement of the shoulder joint allows a bit of adduction starting from the reference position?
Which movement of the shoulder joint allows a bit of adduction starting from the reference position?
What is the range of extension in the elbow joint for most subjects?
What is the range of extension in the elbow joint for most subjects?
Which structure articulates with the capitulum of the humerus in the proximal radio-ulnar joint?
Which structure articulates with the capitulum of the humerus in the proximal radio-ulnar joint?
What type of joint is the proximal radio-ulnar joint?
What type of joint is the proximal radio-ulnar joint?
What is the position of reference defined as in the elbow joint?
What is the position of reference defined as in the elbow joint?
What movement does the elbow joint allow from any position of flexion?
What movement does the elbow joint allow from any position of flexion?
How does the annular ligament attach in the proximal radio-ulnar joint?
How does the annular ligament attach in the proximal radio-ulnar joint?
What is the primary reason for bending the elbow at 90° when measuring the range of rotation at the shoulder joint?
What is the primary reason for bending the elbow at 90° when measuring the range of rotation at the shoulder joint?
Which of the following muscles is NOT involved in horizontal adduction of the shoulder joint?
Which of the following muscles is NOT involved in horizontal adduction of the shoulder joint?
What is the maximum range of medial rotation at the shoulder joint, as described in the text?
What is the maximum range of medial rotation at the shoulder joint, as described in the text?
Which of the following statements regarding transverse movements of the shoulder joint is TRUE?
Which of the following statements regarding transverse movements of the shoulder joint is TRUE?
Which of the following muscles is involved in both horizontal adduction and horizontal abduction of the shoulder joint?
Which of the following muscles is involved in both horizontal adduction and horizontal abduction of the shoulder joint?
What is the correct sequence of muscles involved in horizontal abduction of the shoulder joint, from the text?
What is the correct sequence of muscles involved in horizontal abduction of the shoulder joint, from the text?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Here are the study notes in a concise and organized format:
Cubitus Varus and Cubitus Valgus
- Cubitus varus: a deformity where the extended forearm deviates towards the midline of the body
- Cubitus valgus: a deformity where the elbow is turned in
Elbow Joint Ligaments
- Main function: keep articular surfaces in apposition
- Located on either side of the joint: medial (ulnar) collateral ligament and lateral (radial) collateral ligament
- Prevent sideways movements and keep half-ring fitted to the pulley
- Capsule strengthened anteriorly by anterior ligament and oblique anterior ligament
Elbow Joint Flexor and Extensor Muscles
- Extension of elbow: depends on triceps brachii, with anconeus exerting minor action
- Flexor muscles:
- Brachialis
- Brachioradialis
- Biceps brachii (main action is to flex the elbow, also main supinator of the forearm)
Glenohumeral Joint
- Articular surfaces: glenoid fossa of the scapula and the head of the humerus
- Type of joint: synovial ball and socket joint (multi-axial - 3 degrees of freedom)
- Ligaments:
- Glenohumeral ligaments (multiple)
- Coracohumeral ligament
- Transverse humeral ligament
- Bursae: several around the shoulder joint, including subscapular bursa and subacromial bursa
Radiocarpal Joint
- Articular surfaces: distal end of the radius and the scaphoid, lunate, and triquetrum bones
- Type of joint: synovial condyloid joint
- Ligaments:
- Volar radiocarpal ligament
- Dorsal radiocarpal ligament
- Interosseous ligament
- Movement: flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, rotation, and circumduction
Scapulothoracic Joint
- Articular surfaces: scapula and thoracic cage
- Type of joint: physiological joint (no true articulation)
- Movements: protraction, retraction, elevation, depression, and rotation of scapula
Sternoclavicular Joint
- Articular surfaces: medial end of the clavicle and the manubrium of the sternum
- Type of joint: synovial saddle joint
- Ligaments:
- Anterior sternoclavicular ligament
- Posterior sternoclavicular ligament
- Interclavicular ligament
- Movement: elevation, depression, protraction, and retraction of clavicle
Acromioclavicular Joint
-
Articular surfaces: lateral end of the clavicle and the acromion of the scapula
-
Type of joint: synovial plane joint
-
Ligaments:
- Acromioclavicular ligament
- Coracoclavicular ligament
-
Movement: slight movement in the joint, but serves as a pivot point for movements of the scapula### Wrist Movements
-
Wrist Flexion: a combined effort of 6 muscles: Flexor Carpi Radialis, Flexor Carpi Ulnaris, Palmaris Longus, Flexor Digitorum Superficialis, Flexor Digitorum Profundus, and Flexor Pollicis Longus
-
Wrist Extension: a combined effort of 8 muscles: Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus, Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis, Extensor Carpi Ulnaris, Extensor Digitorum, Extensor Digiti Minimi, Extensor Pollicis Longus, Extensor Pollicis Brevis, and Extensor Indicis
Wrist Adduction and Abduction
- Wrist Adduction: a combined effort of Flexor Carpi Ulnaris and Extensor Carpi Ulnaris
- Wrist Abduction: a combined effort of Flexor Carpi Radialis, Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus, Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis, and Abductor Pollicis Longus
Carpometacarpal (CMC) Joint
- The CMC joint of the thumb is a synovial saddle joint with 3 degrees of freedom
- Motions include abduction/adduction, flexion/extension, and opposition
- The joint capsule is thick but loose
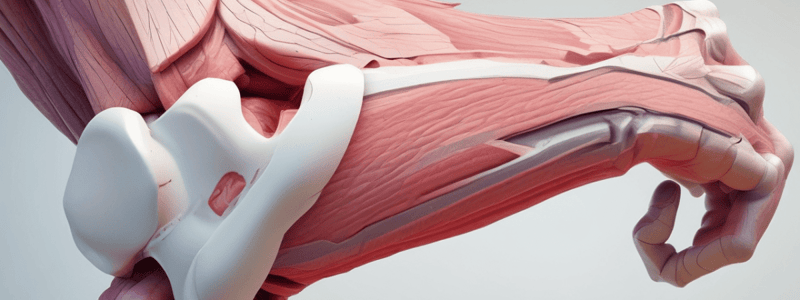
Elbow Joint
- The position of reference is defined as the position achieved when the axes of the arm and forearm are in a straight line
- The range of extension is 0°, except in subjects with great laxity of the ligaments, allowing hyperextension of 5° to 10°
- Active flexion has a range of 145°, and passive flexion has a range of 160°
Proximal (Superior) Radio-Ulnar Joint
- This joint is a synovial pivot joint with one type of movement: rotation about the axis of the two cylinders in contact
- The joint consists of the head of the radius and the cupped surface of the head, which also articulates with the capitulum of the humerus
Scapular Movements
- Scapular movements include protraction, retraction, elevation, depression, and rotation
- Protraction is abduction away from the midline, while retraction is adduction towards the midline
- Rotation of the scapula occurs around the glenoid cavity and inferior angle
- Displacement of the inferior angle is 10-12 cm, and that of the lateral angle is 5-6 cm
Sternoclavicular Joint
- The joint has articular surfaces on the lateral end of the clavicle and the medial end of the acromion
- The joint is a plane synovial joint, allowing for slide and glide movements
- The joint has 3 supportive ligaments
Acromioclavicular Joint
- The joint has articular surfaces on the lateral end of the clavicle and the medial end of the acromion
- The joint is a plane synovial joint, allowing for slide and glide movements
- The joint moves as a result of scapular movement
- The joint has 3 ligaments: Acromioclavicular Ligament, Trapezoid Ligament, and Conoid Ligament
Glenohumeral (Shoulder) Joint
- The joint has articular surfaces on the glenoid fossa of the scapula and the head of the humerus
- The joint is a ball and socket synovial joint, allowing for multi-axial movements
Radiocarpal Joint
- The joint has articular surfaces on the radius and carpal bones
- The joint has anterior and posterior ligaments, which vary in action depending on the type of movement
- The joint has a range of abduction and adduction, which is minimal when the wrist is fully flexed or extended, and maximal when the hand is in the plane of reference or slightly flexed
Elbow Complex
- The elbow complex contains three bony articulations: humero-ulnar, humero-radial, and proximal radio-ulnar
- The humero-ulnar and humero-radial joints are typically referred to as the "elbow" joint
- The elbow joint is a synovial hinge joint, allowing for flexion and extension movements
Scapulohumeral Rhythm
- The scapulohumeral rhythm refers to the coordination of scapular and humeral movements
Rotation of the Shoulder Joint
- Rotation occurs about the longitudinal axis of the humerus
- The range of lateral rotation is 80°, and the range of medial rotation is 95°
Transverse Movements of the Shoulder Joint
- Horizontal movements take place about a vertical axis and involve both the shoulder joint and the scapula
- The range of horizontal adduction is 140°, and the range of horizontal abduction is 30°
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.